Leptospira is a spiral Spiral Computed tomography where there is continuous x-ray exposure to the patient while being transported in a spiral or helical pattern through the beam of irradiation. This provides improved three-dimensional contrast and spatial resolution compared to conventional computed tomography, where data is obtained and computed from individual sequential exposures. Computed Tomography (CT) or question mark–shaped, gram-negative spirochete Spirochete Treponema is a gram-negative, microaerophilic spirochete. Owing to its very thin structure, it is not easily seen on Gram stain, but can be visualized using dark-field microscopy. This spirochete contains endoflagella, which allow for a characteristic corkscrew movement. Treponema with hook-shaped ends. The disease, leptospirosis, is a zoonosis, infecting animals Animals Unicellular or multicellular, heterotrophic organisms, that have sensation and the power of voluntary movement. Under the older five kingdom paradigm, animalia was one of the kingdoms. Under the modern three domain model, animalia represents one of the many groups in the domain eukaryota. Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic. Rodents are the most important reservoir Reservoir Animate or inanimate sources which normally harbor disease-causing organisms and thus serve as potential sources of disease outbreaks. Reservoirs are distinguished from vectors (disease vectors) and carriers, which are agents of disease transmission rather than continuing sources of potential disease outbreaks. Humans may serve both as disease reservoirs and carriers. Escherichia coli. Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology shed in the urine of rodents and other animals Animals Unicellular or multicellular, heterotrophic organisms, that have sensation and the power of voluntary movement. Under the older five kingdom paradigm, animalia was one of the kingdoms. Under the modern three domain model, animalia represents one of the many groups in the domain eukaryota. Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic can be transmitted to humans via contaminated water. The major clinical species is Leptospira interrogans, which causes a mild flu-like illness in a majority of cases. The manifestations are biphasic, with Leptospira found in the blood initially. In the immune phase, the bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology disappear from the bloodstream and can be detected in the urine. In about 10% of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis develops, manifesting as hemorrhage, renal failure Renal failure Conditions in which the kidneys perform below the normal level in the ability to remove wastes, concentrate urine, and maintain electrolyte balance; blood pressure; and calcium metabolism. Renal insufficiency can be classified by the degree of kidney damage (as measured by the level of proteinuria) and reduction in glomerular filtration rate. Crush Syndrome, and jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice. Bacterial culture takes weeks, so other diagnostic tests Diagnostic tests Diagnostic tests are important aspects in making a diagnosis. Some of the most important epidemiological values of diagnostic tests include sensitivity and specificity, false positives and false negatives, positive and negative predictive values, likelihood ratios, and pre-test and post-test probabilities. Epidemiological Values of Diagnostic Tests such as serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus and dark field microscopy are used. Treatment is primarily with penicillin Penicillin Rheumatic Fever.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
There are pathogenic (disease-causing) and saprophytic types (free living and generally do not cause disease). The following types are all pathogenic:
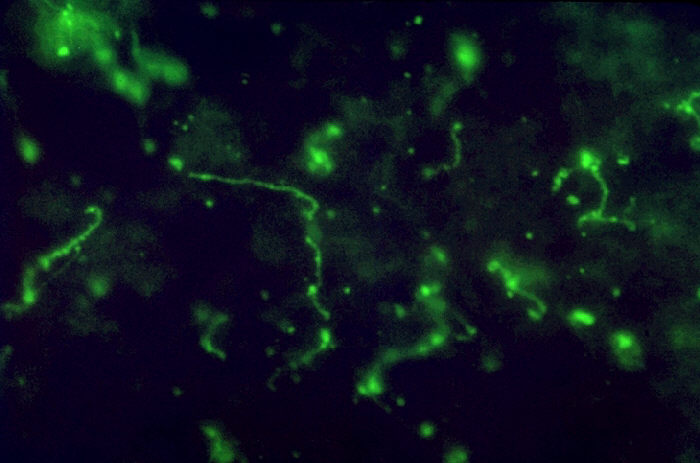
Visualizing Leptospira, the spirochete seen in a liver impression smear (fluorescent antibody stain)
Image: “Leptospira bacteria in liver impression smear. FA stain.” by the CDC/Mildred Galton. License: Public domain.| Characteristics | Leptospirosis | Weil’s syndrome (icterohemorrhagic leptospirosis) |
|---|---|---|
| Presentation | Mild flu-like infection | Severe form |
| Population at risk | Prevalent among surfers and in the tropics | Develops in 10% of infected patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship |
| Signs and symptoms |
|
|
| Diagnosis | Urine is an excellent body fluid to identify the organisms. | |
| Management |
|
|
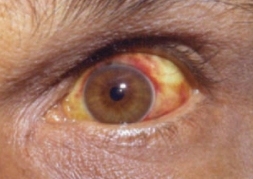
Image of eye changes noted in leptospirosis: Conjunctival suffusion and jaundice are seen.
Image: “Conjunctival suffusion of the eyes due to leptospirosis” by Daniel Ostermayer. License: CC BY 4.0.Serology Serology The study of serum, especially of antigen-antibody reactions in vitro. Yellow Fever Virus:
Isolation of leptospires (blood, urine, tissue, or cerebrospinal fluid Cerebrospinal Fluid A watery fluid that is continuously produced in the choroid plexus and circulates around the surface of the brain; spinal cord; and in the cerebral ventricles. Ventricular System: Anatomy (CSF)):
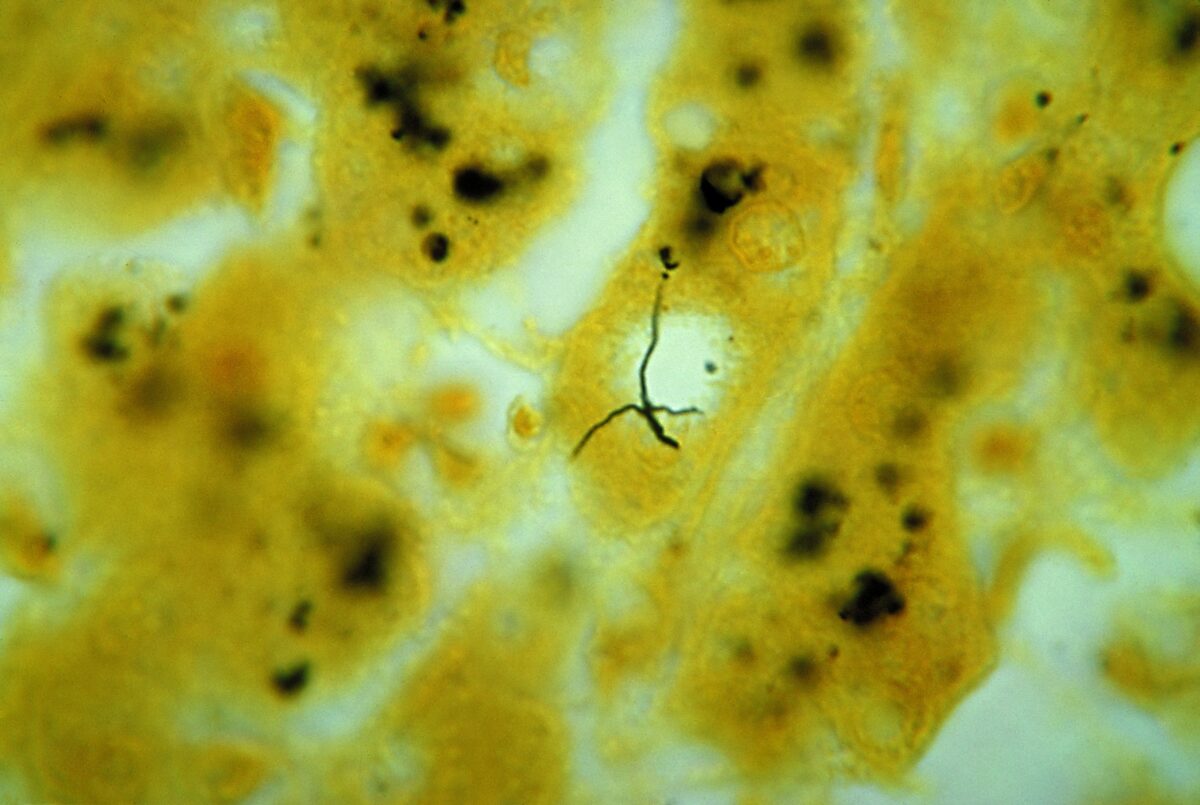
Leptospira sp. bacteria:
photomicrograph of liver tissue specimen, with 2 darkly stained Leptospira sp. bacteria
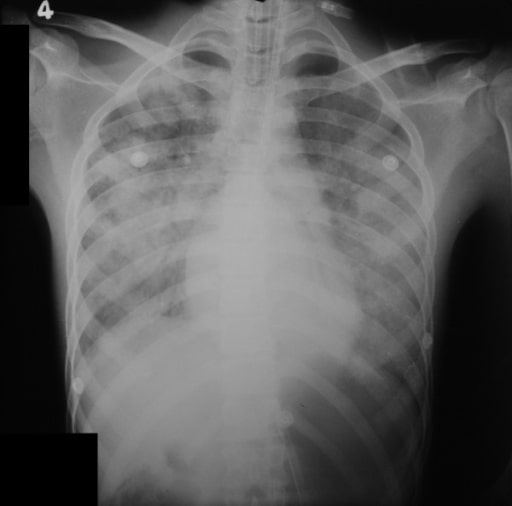
Chest X-ray of a patient with severe leptospirosis:
The image shows a chest X-ray with diffuse pulmonary hemorrhages.