Klinefelter syndrome is a chromosomal aneuploidy characterized by the presence of 1 or more extra X chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure in a male karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System, most commonly leading to karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System 47,XXY. Klinefelter syndrome is associated with decreased levels of testosterone Testosterone A potent androgenic steroid and major product secreted by the leydig cells of the testis. Its production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. In turn, testosterone exerts feedback control of the pituitary LH and FSH secretion. Depending on the tissues, testosterone can be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol. Androgens and Antiandrogens and is the most common cause of congenital hypogonadism Hypogonadism Hypogonadism is a condition characterized by reduced or no sex hormone production by the testes or ovaries. Hypogonadism can result from primary (hypergonadotropic) or secondary (hypogonadotropic) failure. Symptoms include infertility, increased risk of osteoporosis, erectile dysfunction, decreased libido, and regression (or absence) of secondary sexual characteristics. Hypogonadism. Symptoms are often not noticed until adolescence or adulthood. Individuals with this condition tend to present as tall, phenotypic men with small testes Testes Gonadal Hormones, decreased body hair, gynecomastia Gynecomastia Gynecomastia is a benign proliferation of male breast glandular ductal tissue, usually bilateral, caused by increased estrogen activity, decreased testosterone activity, or medications. The condition is common and physiological in neonates, adolescent boys, and elderly men. Gynecomastia, and infertility Infertility Infertility is the inability to conceive in the context of regular intercourse. The most common causes of infertility in women are related to ovulatory dysfunction or tubal obstruction, whereas, in men, abnormal sperm is a common cause. Infertility. Treatment consists of life-long testosterone Testosterone A potent androgenic steroid and major product secreted by the leydig cells of the testis. Its production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. In turn, testosterone exerts feedback control of the pituitary LH and FSH secretion. Depending on the tissues, testosterone can be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol. Androgens and Antiandrogens replacement therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
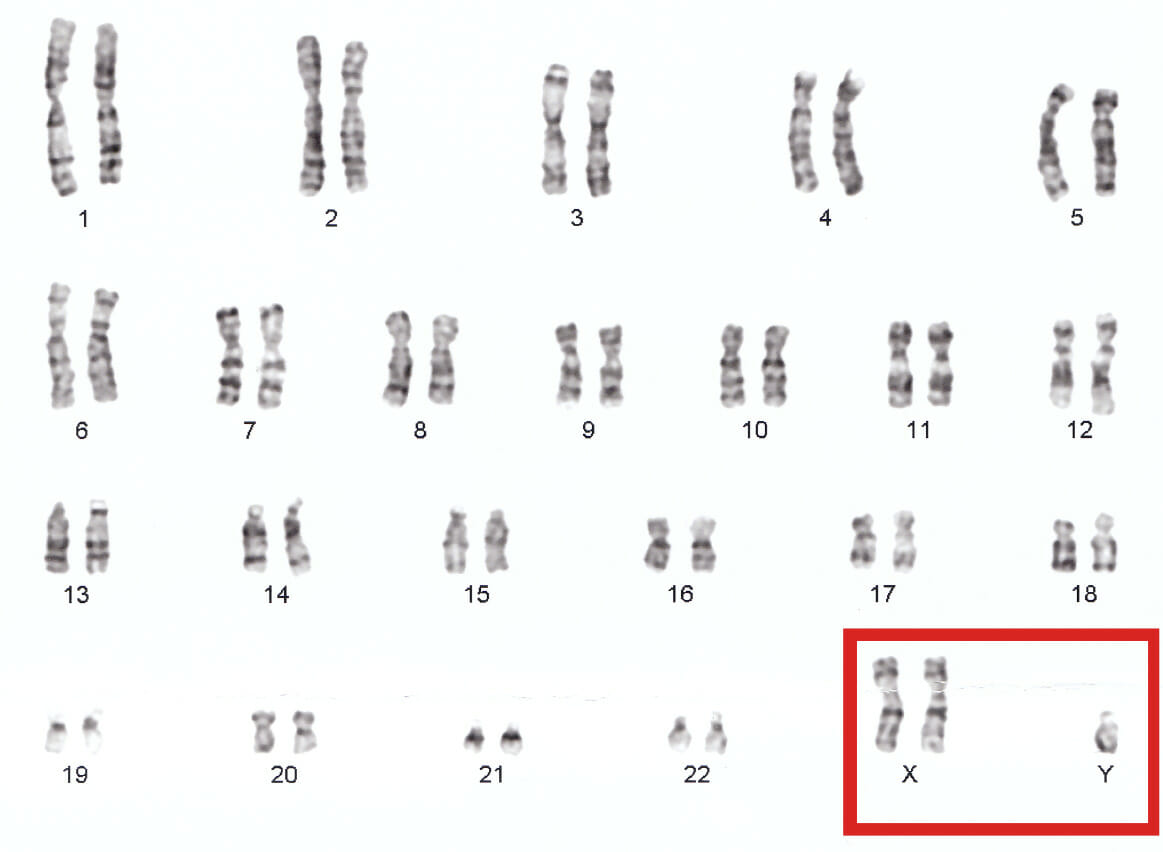
The most common karyotype in Klinefelter syndrome is 47, XXY
Image: “Human chromosomes XXY” by Nami-ja. License: Public Domain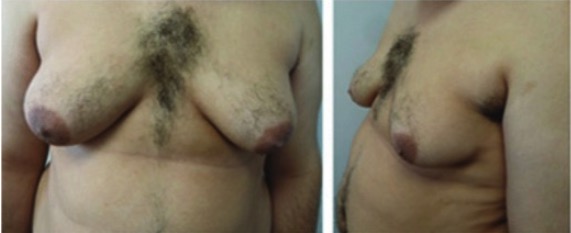
Preoperative photograph of a 22-year-old patient with Klinefelter syndrome demonstrating a grade III gynecomastia
Image: “Grade 3 gynecomastia” by Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, Department of Pediatrics, New Jersey Medical School, Rutgers University, Newark. License: CC BY 2.0, edited by Lecturio.The following conditions are differential diagnoses of Klinefelter syndrome:
The following condition is related to Klinefelter syndrome as it also causes gonadal insufficiency due to a chromosomal abnormality:
Turner syndrome Turner syndrome Turner syndrome is a genetic condition affecting women, in which 1 X chromosome is partly or completely missing. The classic result is the karyotype 45,XO with a female phenotype. Turner syndrome is associated with decreased sex hormone levels and is the most common cause of primary amenorrhea. Turner Syndrome: a chromosomal abnormality disorder affecting only women. Karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System is 45,X0 instead of XX. Causes delayed puberty Delayed Puberty Delayed puberty (DP) is defined as the lack of testicular growth in boys past the age of 14 and the lack of thelarche in girls past the age of 13. Delayed puberty affects up to 5% of healthy boys and girls, and half of all cases are due to constitutional growth delay. Delayed Puberty and primary hypergonadotropic hypogonadism Hypergonadotropic Hypogonadism Hypogonadism (ovarian failure) in women. Affected women are characterized by short stature, widely spaced nipples, and webbed neck Webbed neck Turner Syndrome. Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies confirms the diagnosis. Management includes hormone replacement therapy Hormone Replacement Therapy Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins and fertility treatments if desired.