Kallmann syndrome (KS), also called olfacto-genital syndrome, is a genetic condition that causes hypogonadotropic hypogonadism Hypogonadotropic Hypogonadism Hypogonadism due to decreased secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies of gonadotropin-releasing hormone Gonadotropin-releasing hormone A decapeptide that stimulates the synthesis and secretion of both pituitary gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone. Gnrh is produced by neurons in the septum preoptic area of the hypothalamus and released into the pituitary portal blood, leading to stimulation of gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. Puberty (GnRH) by the hypothalamus Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is a collection of various nuclei within the diencephalon in the center of the brain. The hypothalamus plays a vital role in endocrine regulation as the primary regulator of the pituitary gland, and it is the major point of integration between the central nervous and endocrine systems. Hypothalamus. Both sexes can be affected, although the incidence Incidence The number of new cases of a given disease during a given period in a specified population. It also is used for the rate at which new events occur in a defined population. It is differentiated from prevalence, which refers to all cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency is much higher in males. The lack of sex Sex The totality of characteristics of reproductive structure, functions, phenotype, and genotype, differentiating the male from the female organism. Gender Dysphoria hormones Hormones Hormones are messenger molecules that are synthesized in one part of the body and move through the bloodstream to exert specific regulatory effects on another part of the body. Hormones play critical roles in coordinating cellular activities throughout the body in response to the constant changes in both the internal and external environments. Hormones: Overview and Types results in impaired pubertal development. Characteristically, there is an associated absence or decreased sense of smell Smell The sense of smell, or olfaction, begins in a small area on the roof of the nasal cavity, which is covered in specialized mucosa. From there, the olfactory nerve transmits the sensory perception of smell via the olfactory pathway. This pathway is composed of the olfactory cells and bulb, the tractus and striae olfactoriae, and the primary olfactory cortex and amygdala. Olfaction: Anatomy ( hyposmia Hyposmia reduced ability to smell Cranial Nerve Palsies or anosmia Anosmia Complete or severe loss of the subjective sense of smell. Loss of smell may be caused by many factors such as a cold, allergy, olfactory nerve diseases, viral respiratory tract infections (e.g., COVID-19), aging and various neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer disease). Cranial Nerve Palsies), which helps differentiate KS from other conditions. The diagnosis is made by hormone levels in blood and brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification imaging showing the absence of olfactory structures. Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies may assist in establishing a definite diagnosis. Treatment consists of hormone replacement therapy Hormone Replacement Therapy Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is used to treat symptoms associated with female menopause and in combination to suppress ovulation. Risks and side effects include uterine bleeding, predisposition to cancer, breast tenderness, hyperpigmentation, migraine headaches, hypertension, bloating, and mood changes. Noncontraceptive Estrogen and Progestins.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure listed above are involved in the migration of olfactory neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology and neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology involved in gonadotropin-releasing hormone Gonadotropin-releasing hormone A decapeptide that stimulates the synthesis and secretion of both pituitary gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone and follicle stimulating hormone. Gnrh is produced by neurons in the septum preoptic area of the hypothalamus and released into the pituitary portal blood, leading to stimulation of gonadotrophs in the anterior pituitary gland. Puberty (GnRH) production to their proper functional place in the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification during development.
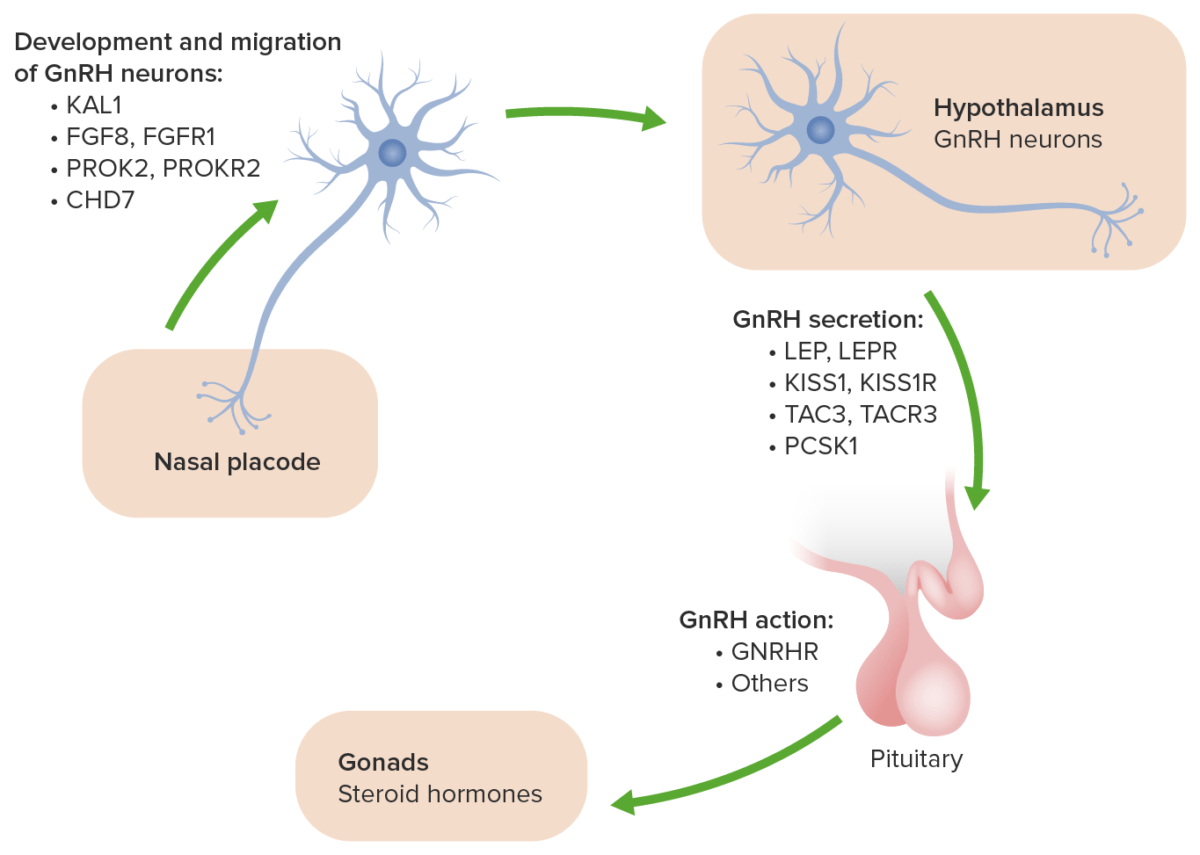
The genetic and molecular basis of idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism:
The ANOS1 gene was previously called KAL1. It causes the x-linked form of Kallmann syndrome and is associated with the additional symptoms of anosmia, bimanual synkinesis and renal agenesis.
The clinical presentation is highly variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables due to the different gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics mutations and penetrance Penetrance The percent frequency with which a dominant or homozygous recessive gene or gene combination manifests itself in the phenotype of the carriers. Familial Juvenile Polyposis levels. However, all individuals with KS show abnormal sexual development and hyposmia Hyposmia reduced ability to smell Cranial Nerve Palsies or anosmia Anosmia Complete or severe loss of the subjective sense of smell. Loss of smell may be caused by many factors such as a cold, allergy, olfactory nerve diseases, viral respiratory tract infections (e.g., COVID-19), aging and various neurological disorders (e.g., Alzheimer disease). Cranial Nerve Palsies.
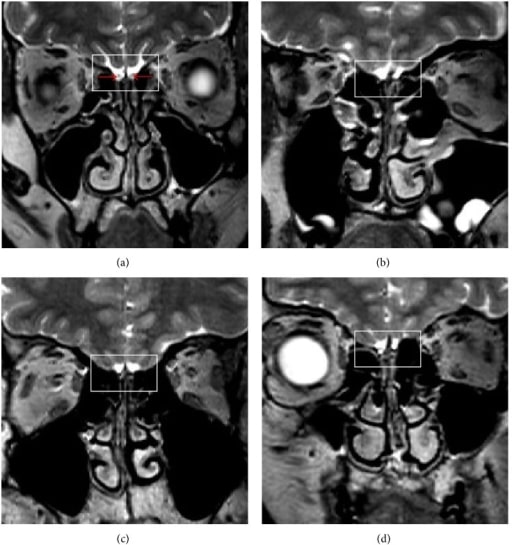
Brain MRI findings in KS
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of 3 male patients with KS (b)-(d). Image (a) shows normal structures in a healthy control. The red arrows indicate olfactory bulbs. Images (b), (c), and (d) show the lack of the bilateral olfactory bulb, the olfactory tract, and the sulcus (squares), respectively.