BK virus (BKV) and JC virus (JCV) are small, nonenveloped, double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Polyomaviridae family, which are ubiquitous in the human population. While the primary infection is usually asymptomatic, the virus remains latent in the kidneys and lymphoid organs. Latent infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease can become active in immunosuppressed patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship. Reactivation Reactivation Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 of BKV is most often seen in transplant patients Transplant patients Individuals receiving tissues or organs transferred from another individual of the same or different species, or from within the same individual. Human Herpesvirus 8 and can lead to nephropathy, allograft loss, hemorrhagic cystitis Hemorrhagic Cystitis Alkylating Agents and Platinum, and urethral stenosis Stenosis Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS). Reactivation Reactivation Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 of JCV causes progressive multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma leukoencephalopathy (PML), which is considered an AIDS-defining condition. Diagnosis can be confirmed with PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) or tissue biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma. Specific therapy is not available. Management aims to reduce immunosuppression.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
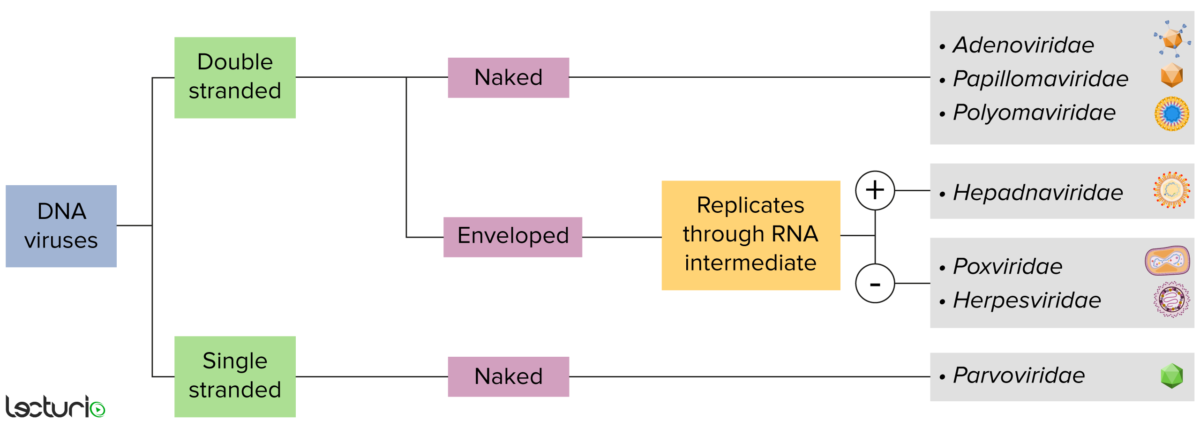
Identification of DNA viruses:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. Viruses with a DNA genome can be further characterized as single or double stranded. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane, which is usually taken from the host cell. If the coat is absent, however, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Some enveloped viruses translate DNA into RNA before incorporating into the genome of the host cell.
BKV and JCV share similar characteristics:
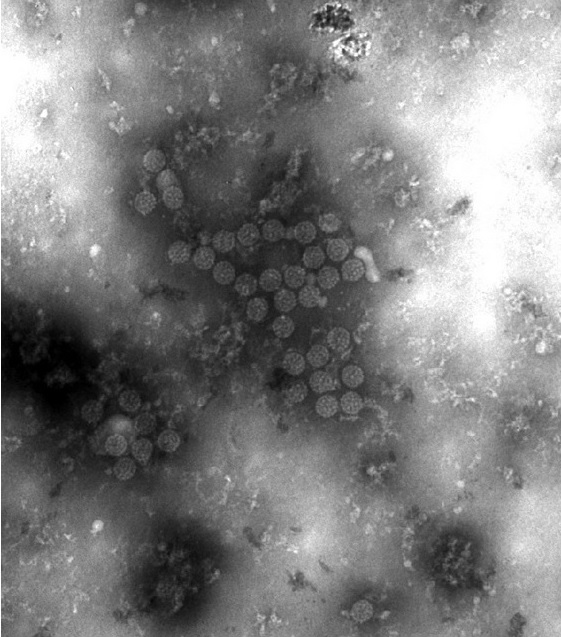
Electron micrograph showing BK virus (BKV) virions:
Notice the small size and icosahedral symmetry.
Humans are the natural host for JCV and BKV (no animal reservoir Reservoir Animate or inanimate sources which normally harbor disease-causing organisms and thus serve as potential sources of disease outbreaks. Reservoirs are distinguished from vectors (disease vectors) and carriers, which are agents of disease transmission rather than continuing sources of potential disease outbreaks. Humans may serve both as disease reservoirs and carriers. Escherichia coli).
The clinical disease most often arises from reactivation Reactivation Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 of the virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship:
Primary infection Primary infection Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2:
Secondary infection:
PML is a progressive (and often fatal) condition most commonly seen in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with AIDS (considered an AIDS-defining condition) with a CD4 count < 200 cells/µL.
BKV:
JCV:
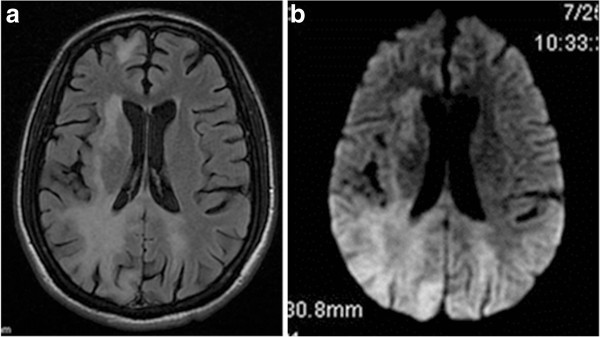
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of a patient with progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML):
a: axial T2-flair MRI of the brain showing bilateral signal hyperintensity in the parietooccipital white matter
b: axial T2-flair diffuse-weighted image of the same lesions
No specific therapies are available for BKV or JCV. Management is generally aimed at reducing immunosuppression.