IPEX (immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)) syndrome is a rare congenital T-cell deficiency associated with transcription factor Transcription factor Generic term for proteins necessary for transcription Regulation of Transcription FOXP3 dysfunction. This factor regulates the development of a regulatory T cell line and dysfunctions usually result in autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity is a pathologic immune response toward self-antigens, resulting from a combination of factors: immunologic, genetic, and environmental. The immune system is equipped with self-tolerance, allowing immune cells such as T cells and B cells to recognize self-antigens and to not mount a reaction against them. Defects in this mechanism, along with environmental triggers (such as infections) and genetic susceptibility factors (most notable of which are the HLA genes) can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity. The condition manifests as autoimmune enteropathy, eczematous dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), nail dystrophy, autoimmune endocrinopathies, and autoimmune skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions conditions. The only form of management for IPEX is bone marrow transplantation Bone marrow transplantation Transfer of hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow or blood between individuals within the same species (homologous transplantation) or transfer within the same individual (autologous transplantation). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has been used as an alternative to bone marrow transplantation in the treatment of a variety of neoplasms. Organ Transplantation.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Epidemiology
Etiology
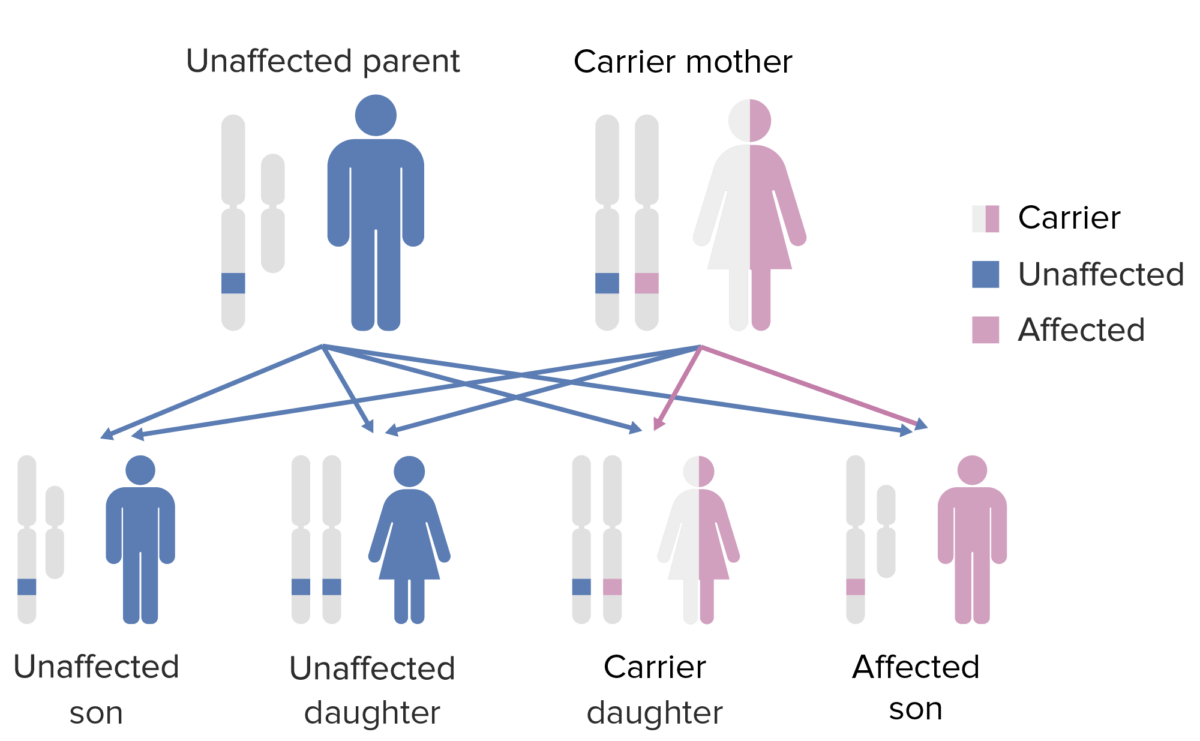
The pattern of inheritance of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Note that the mother must contribute the defective X-gene to the male child in order for him to express this phenotype.
Image by Lecturio.Signs of systemic autoimmunity Autoimmunity Autoimmunity is a pathologic immune response toward self-antigens, resulting from a combination of factors: immunologic, genetic, and environmental. The immune system is equipped with self-tolerance, allowing immune cells such as T cells and B cells to recognize self-antigens and to not mount a reaction against them. Defects in this mechanism, along with environmental triggers (such as infections) and genetic susceptibility factors (most notable of which are the HLA genes) can lead to autoimmune diseases. Autoimmunity begin presenting in the 1st year of life.

Patient presenting with cervical lymphadenopathy
Image: “Ixodholfem8” by Hudson, Bernard. License: CC BY 3.0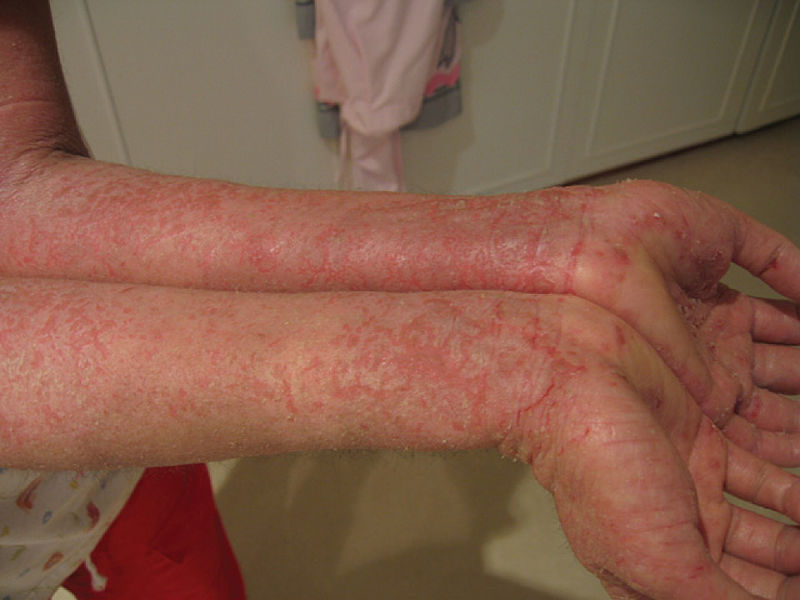
Severe eczema presented by a patient with IPEX syndrome
Image: “Eczema” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0Diagnostic testing for IPEX syndrome follows systematic criteria consistent with:
Numerous medications are used and administration depends on each patient’s manifestations:
The following conditions are differential diagnoses for IPEX syndrome: