Insecticides Insecticides Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. Trypanosoma cruzi/Chagas disease are chemical substances used to kill or control insects, to improve crop yields, and to prevent diseases. Human exposures to insecticides Insecticides Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. Trypanosoma cruzi/Chagas disease can be by direct contact, inhalation, or ingestion. Important insecticides Insecticides Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. Trypanosoma cruzi/Chagas disease that can affect humans include organochlorines (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)), organophosphates ( malathion Malathion A wide spectrum aliphatic organophosphate insecticide widely used for both domestic and commercial agricultural purposes. Cholinomimetic Drugs and parathion), and carbamates (carbaryl, propoxur, aldicarb, and methomyl). Because of DDT's long-term adverse effects on wildlife and the environment, it is now not used in many areas. However, it is still in use in areas with high rates of malaria Malaria Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease affecting humans and other animals. Most commonly transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito infected with microorganisms of the Plasmodium genus. Patients present with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and diaphoresis. Plasmodium/Malaria infection. The chemical produces neurotoxicity and endocrine disruption. Organophosphates and carbamates produce cholinergic effects, given their similar mechanism of action of inhibiting acetylcholinesterase. Organophosphates, though, bind BIND Hyperbilirubinemia of the Newborn the enzyme irreversibly, while carbamates inhibit the enzyme for < 48 hours. Diagnosis is based on history and clinical findings, with tests available for confirmation. Management involves decontamination, supportive care, and symptom control. For the cholinergic toxidrome Toxidrome A toxidrome describes a group of signs, symptoms, and/or characteristic effects associated with exposure to a particular substance or class of substances. General Principles of Toxidromes, atropine Atropine An alkaloid, originally from atropa belladonna, but found in other plants, mainly solanaceae. Hyoscyamine is the 3(s)-endo isomer of atropine. Anticholinergic Drugs and pralidoxime Pralidoxime Various salts of a quaternary ammonium oxime that reconstitute inactivated acetylcholinesterase, especially at the neuromuscular junction, and may cause neuromuscular blockade. They are used as antidotes to organophosphorus poisoning as chlorides, iodides, methanesulfonates (mesylates), or other salts. General Principles of Toxidromes are given to reverse the effects of cholinergic excess.
Last updated: Mar 11, 2025
Insecticides Insecticides Pesticides designed to control insects that are harmful to man. The insects may be directly harmful, as those acting as disease vectors, or indirectly harmful, as destroyers of crops, food products, or textile fabrics. Trypanosoma cruzi/Chagas disease are substances used to kill insects or prevent them from destructive behaviors.
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane:
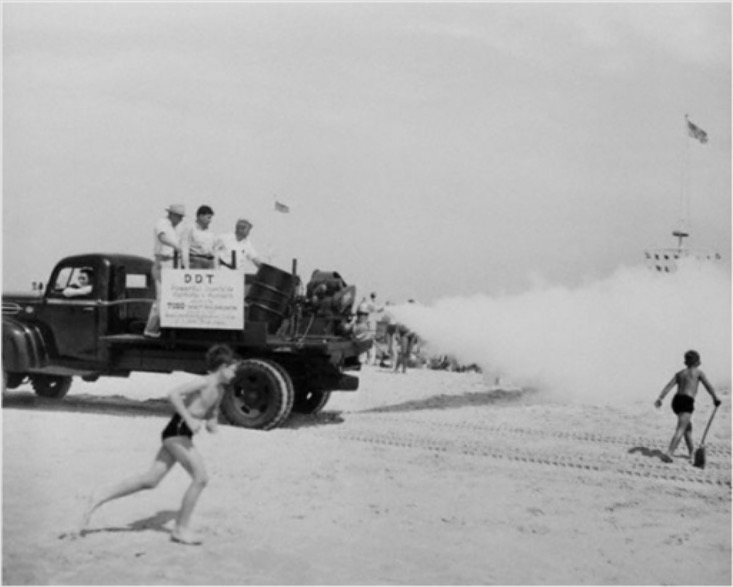

Spraying of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT):
This chemical was widely used as an insecticide, with the chemical sprayed as shown in the image (Jones Beach, New York). The use of DDT was stopped in 1972 by the EPA because of its adverse effects on wildlife and the environment.
Organophosphates:
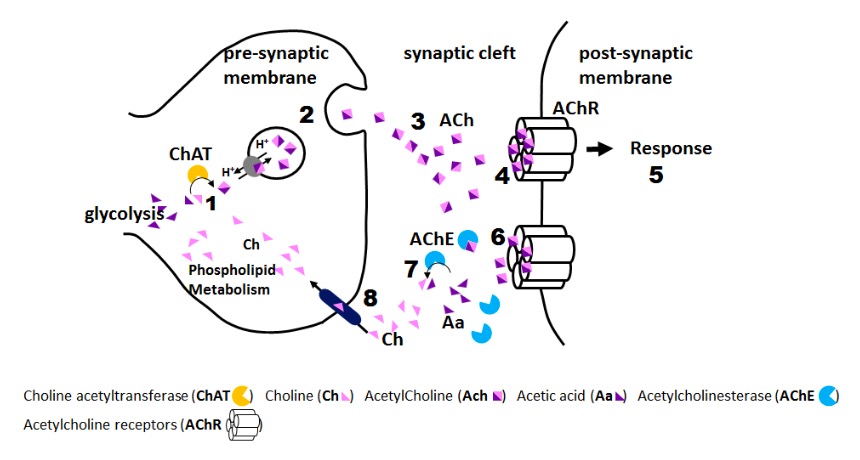
Pesticide/herbicide effect (organophosphate):
1: Pesticide accumulation in synaptic cleft
2: Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by pesticide
3: Constant activation of acetylcholine receptors
SLUDGE BBB BBB Specialized non-fenestrated tightly-joined endothelial cells with tight junctions that form a transport barrier for certain substances between the cerebral capillaries and the brain tissue. Nervous System: Histology (muscarinic effects):
DUMBELS (muscarinic effects):
Carbamates: