The inguinal region Inguinal region Anterior Abdominal Wall: Anatomy, or the groin Groin The external junctural region between the lower part of the abdomen and the thigh. Male Genitourinary Examination, is located in the RLQ and LLQ of the anterior abdominal wall Abdominal wall The outer margins of the abdomen, extending from the osteocartilaginous thoracic cage to the pelvis. Though its major part is muscular, the abdominal wall consists of at least seven layers: the skin, subcutaneous fat, deep fascia; abdominal muscles, transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and the parietal peritoneum. Surgical Anatomy of the Abdomen, bordered by the thigh Thigh The thigh is the region of the lower limb found between the hip and the knee joint. There is a single bone in the thigh called the femur, which is surrounded by large muscles grouped into 3 fascial compartments. Thigh: Anatomy inferiorly, the pubis medially, and the iliac crest superolaterally. The inguinal canal is a tubular structure that runs in a straight line from the anterior superior iliac spine Anterior Superior Iliac Spine Chronic Apophyseal Injury to the pubic tubercle. The canal contains the spermatic cord Spermatic Cord Either of a pair of tubular structures formed by ductus deferens; arteries; veins; lymphatic vessels; and nerves. The spermatic cord extends from the deep inguinal ring through the inguinal canal to the testis in the scrotum. Testicles: Anatomy in men and the round ligament Round ligament A fibromuscular band that attaches to the uterus and then passes along the broad ligament, out through the inguinal ring, and into the labium majus. Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy in women. An inguinal hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias occurs when tissue or an organ (such as a portion of the intestine) protrudes through in the abdominal wall Abdominal wall The outer margins of the abdomen, extending from the osteocartilaginous thoracic cage to the pelvis. Though its major part is muscular, the abdominal wall consists of at least seven layers: the skin, subcutaneous fat, deep fascia; abdominal muscles, transversalis fascia, extraperitoneal fat, and the parietal peritoneum. Surgical Anatomy of the Abdomen and into the inguinal canal. Inguinal hernias are the most common type of hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias, and may be classified as indirect (tissue protrudes through the deep inguinal ring) or direct (tissue protrudes through the posterior wall of the inguinal canal). A hernia Hernia Protrusion of tissue, structure, or part of an organ through the bone, muscular tissue, or the membrane by which it is normally contained. Hernia may involve tissues such as the abdominal wall or the respiratory diaphragm. Hernias may be internal, external, congenital, or acquired. Abdominal Hernias may cause pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways or discomfort, and there is a risk of bowel obstruction Bowel obstruction Any impairment, arrest, or reversal of the normal flow of intestinal contents toward the anal canal. Ascaris/Ascariasis due to bowel incarceration with possible strangulation and infarction. Surgery is indicated for inguinal hernias which are high-risk or cause significant pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
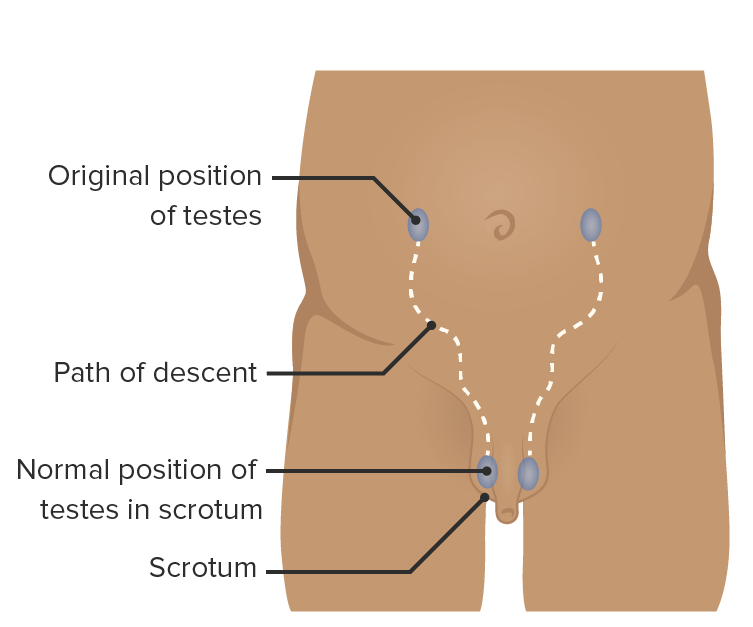
Pathway of testicular descent from the posterior abdominal wall into the scrotum: The testicles pass through the inguinal canal.
Image by Lecturio.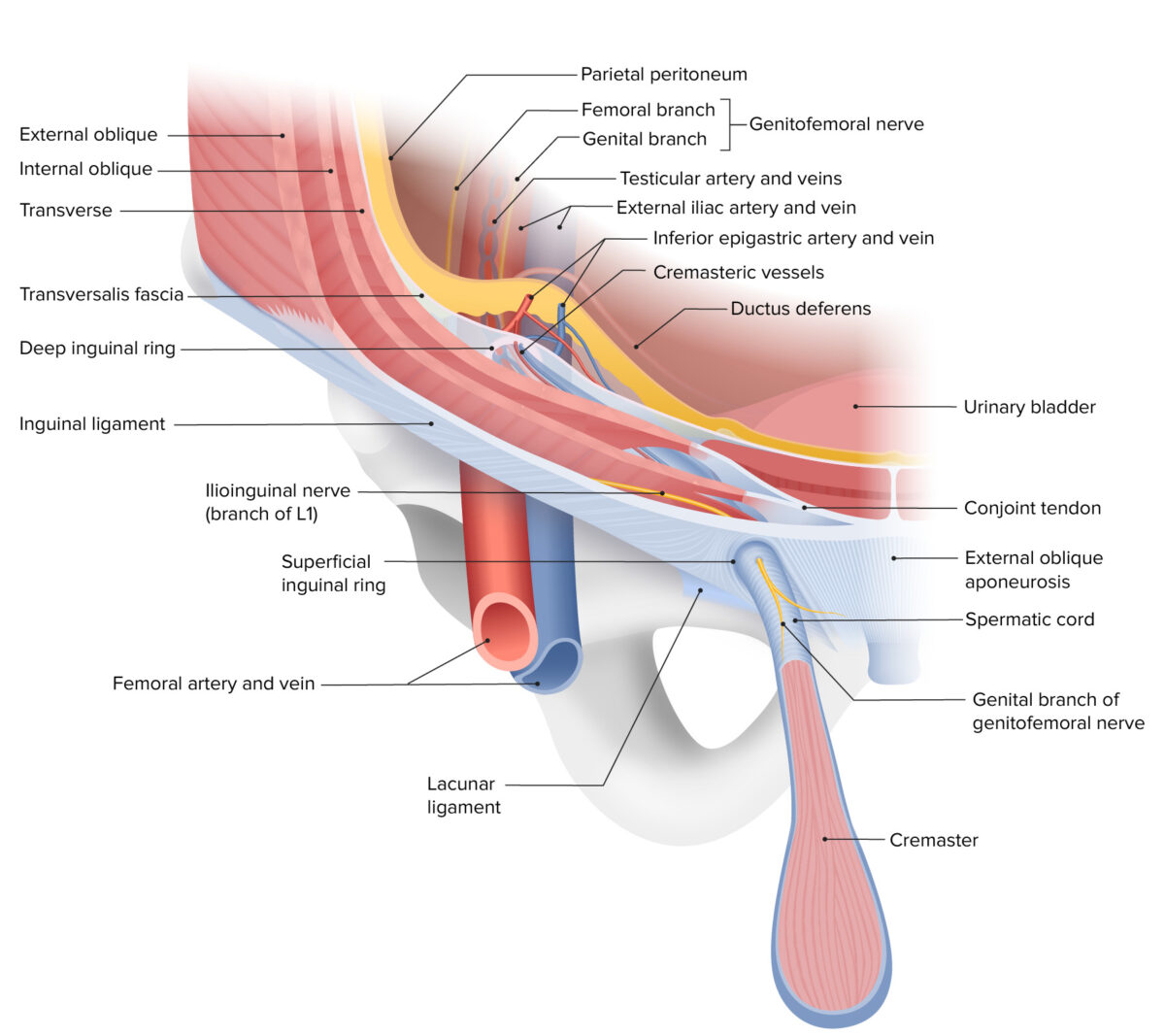
The layers of the anterior abdominal wall, depicting the course of the inguinal canal and the composition of the deep and superficial inguinal rings
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The boundaries of the inguinal canal vary throughout its course.
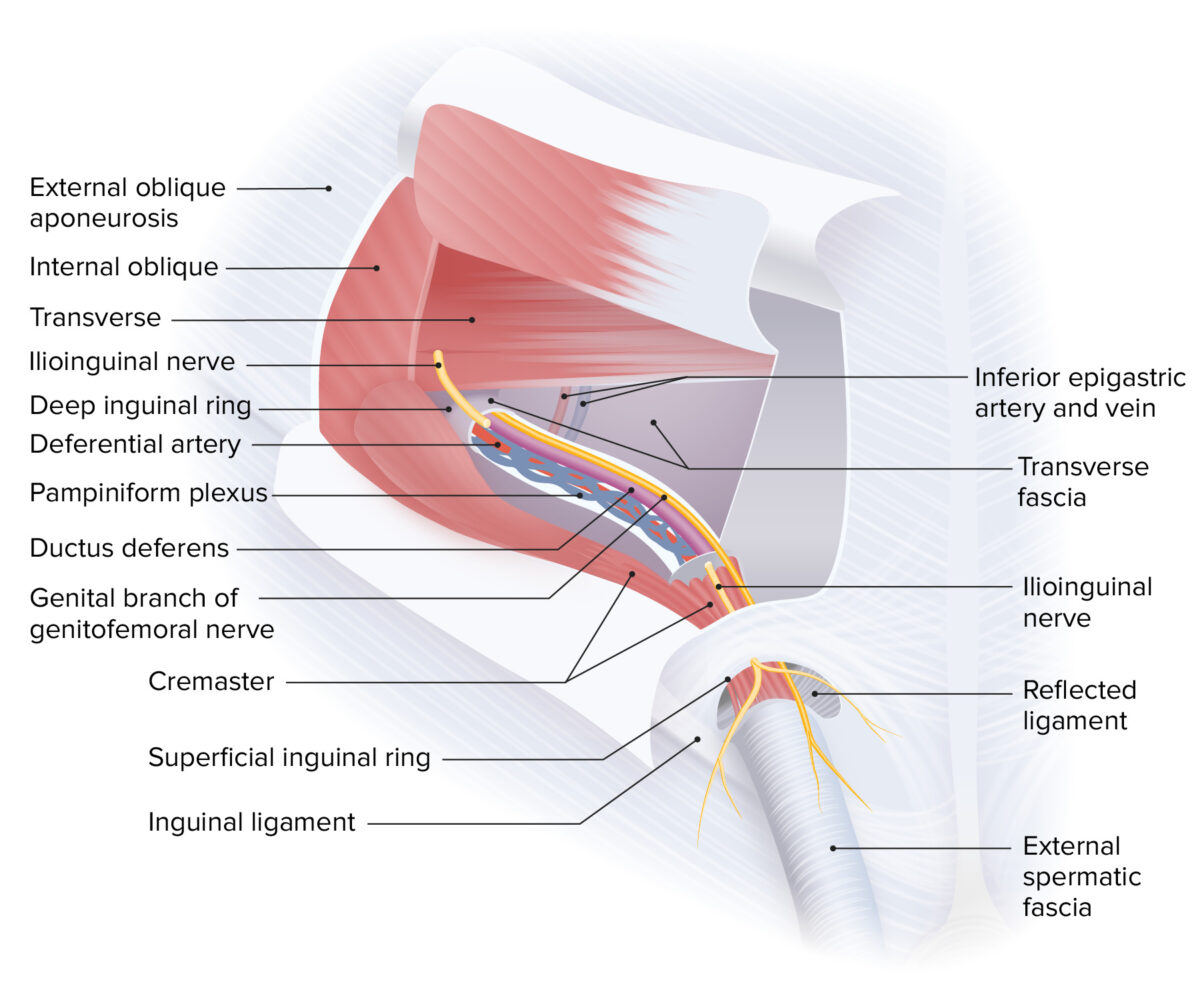
Boundaries and contents of the male inguinal canal:
Note that the ilioinguinal nerve runs along the inguinal canal externally from the spermatic cord.
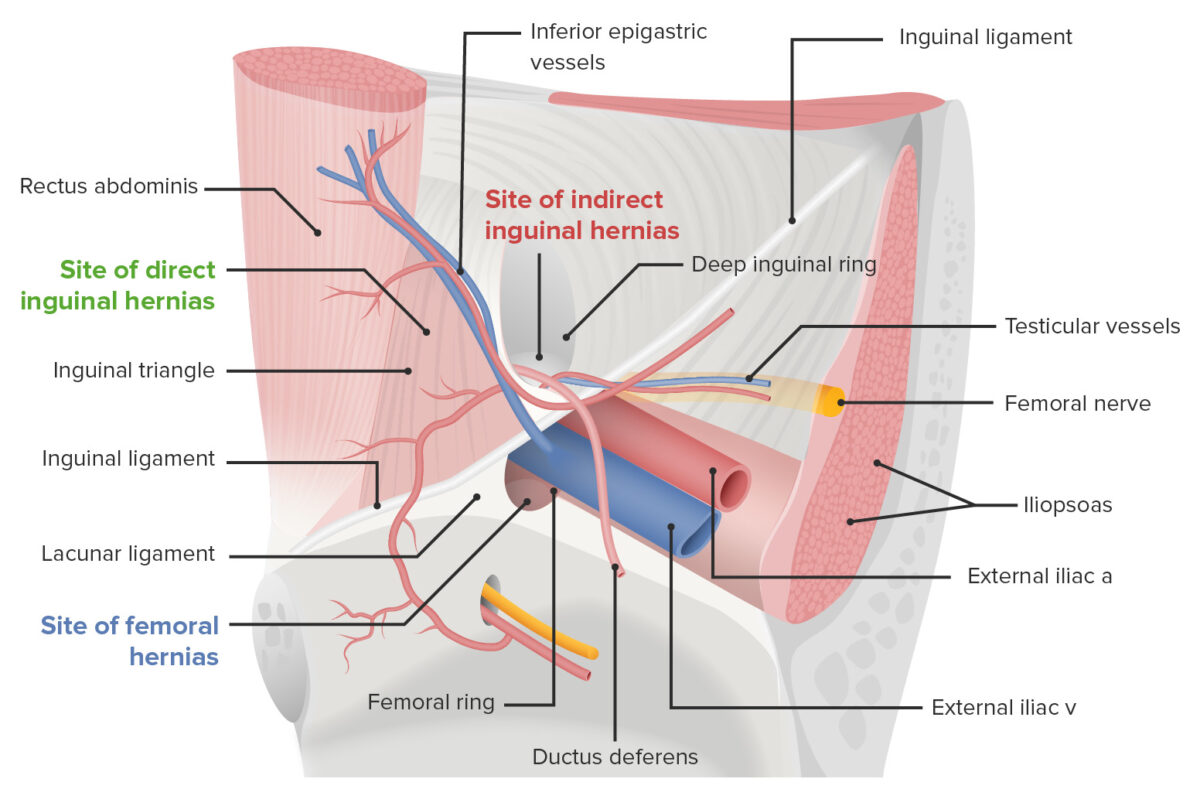
View of the left inguinal canal: Indirect inguinal hernias arise lateral to the epigastric vessels, while direct inguinal hernias arise medial to the epigastric vessels.
Image by Lecturio.