Infectious folliculitis is a common skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions condition characterized by the inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of hair follicles caused by an infectious agent (bacterial, fungal, viral, or parasitic). Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess is the most common causative agent. Diagnosis is clinical and presentations include pruritus Pruritus An intense itching sensation that produces the urge to rub or scratch the skin to obtain relief. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), follicular pustules, and erythematous papules. Management is usually supportive care but topical or oral antibiotic therapy may be required in severe cases.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Infectious folliculitis occurs due to inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the superficial or deep portion of the hair follicle Hair follicle A tube-like invagination of the epidermis from which the hair shaft develops and into which sebaceous glands open. The hair follicle is lined by a cellular inner and outer root sheath of epidermal origin and is invested with a fibrous sheath derived from the dermis. Follicles of very long hairs extend into the subcutaneous layer of tissue under the skin. Cowden Syndrome caused by an infectious agent (see table below).
| Etiology | Risk factors | Pathogens |
|---|---|---|
| Bacterial |
|
Gram-positive
Gram-Positive
Penicillins
bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases.
Bacteriology: Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess (most common), both methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant ( MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus) (folliculitis contributes to the increasing prevalence Prevalence The total number of cases of a given disease in a specified population at a designated time. It is differentiated from incidence, which refers to the number of new cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency of community-acquired MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease). |
Gram-negative bacteria
gram-negative bacteria
Bacteria which lose crystal violet stain but are stained pink when treated by gram’s method.
Bacteriology (more common in
groin
Groin
The external junctural region between the lower part of the abdomen and the thigh.
Male Genitourinary Examination areas):
|
||
| Fungal |
|
|
| Viral |
|
|
| Parasitic | Demodex folliculitis | Demodex folliculorum, a parasitic mite |
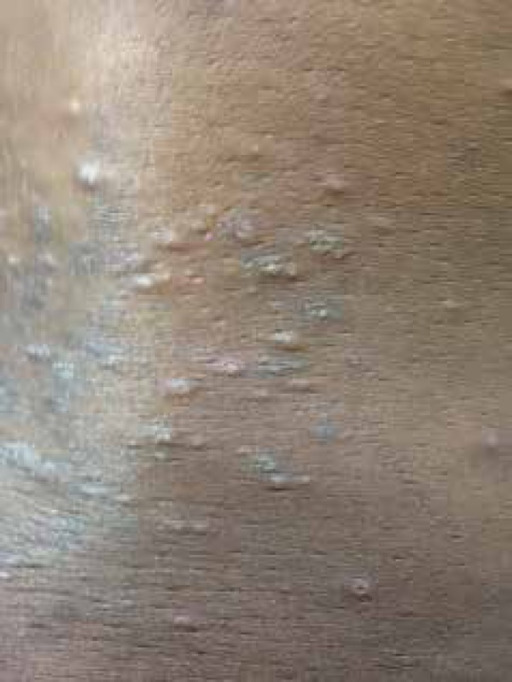
Pruritic folliculitis of pregnancy, with lesions on the lower back
Image: “Lesions on the lower back” by U.S. National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0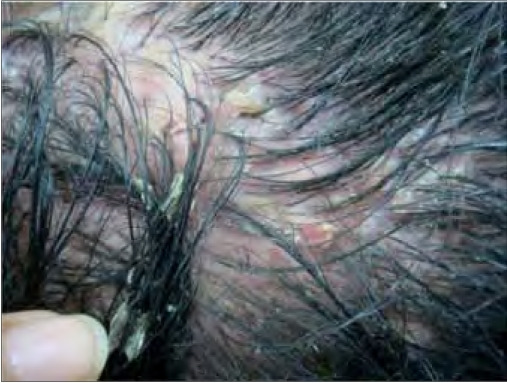
Folliculitis decalvans, induration of the scalp that can present as pustules, erosions, crusts, ulcers, and scale
Image: “Patient 11 on presentation” by Department of Dermatology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, People’s Republic of China. License: CC BY 2.0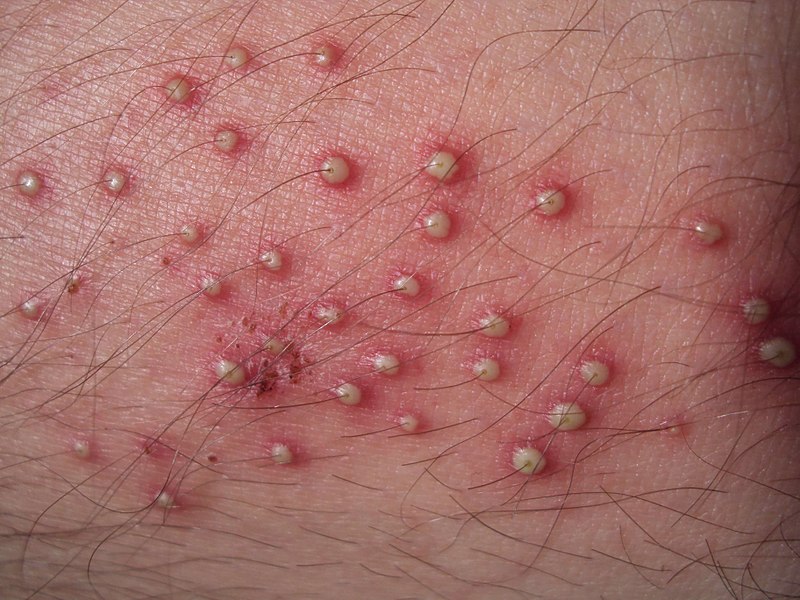
Bacterial folliculitis on lower leg presenting as follicular pustules
Image: “Folliculitis on lower leg” by Da pacem Domine. License: Public Domain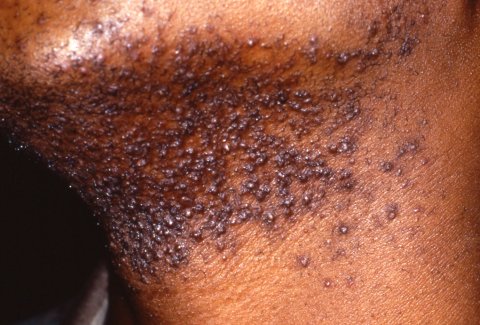
Pseudofolliculitis barbae presenting as firm hyperpigmented papules on the neck and jawline. This is caused by inflammation provoked by hair penetrating interfollicular skin after shaving (“ingrown hairs”) and can occur anywhere hair is shaved or plucked.
Image: “Picture of Pseudofolliculitis Barbae” by Army Medical Department. License: Public Domain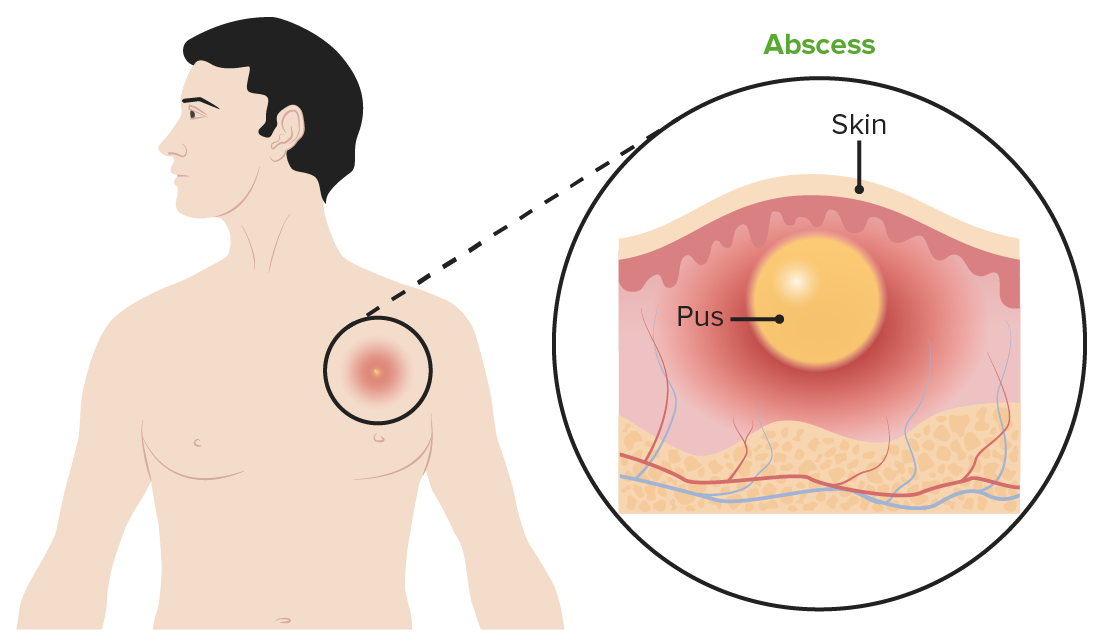
Subcutaneous abscess
Image by Lecturio.Management consists mostly of supportive measures:
Antibiotic therapy is guided by the suspected or known causative organism:
The following conditions can be confused with infectious folliculitis.