Impetigo is a highly contagious superficial bacterial infection typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess (most common) and Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes. Impetigo most commonly presents in children aged 2 to 5 years with lesions that evolve from papules to vesicles Vesicles Female Genitourinary Examination to pustules, which eventually break down to form characteristic “honey-colored” crusts. Infection can either be primary (bacterial infection of healthy, intact skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions) or secondary (infection of pre-existing abrasions Abrasions Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers). The diagnosis is clinical, and management includes topical or systemic antibiotic therapy. Complications of impetigo include post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, cellulitis Cellulitis Cellulitis is a common infection caused by bacteria that affects the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. It is frequently caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. The skin infection presents as an erythematous and edematous area with warmth and tenderness. Cellulitis, and scarlet fever Scarlet fever Infection with group a Streptococci that is characterized by tonsillitis and pharyngitis. An erythematous rash is commonly present. Scarlet Fever.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
There are 3 variants of impetigo:
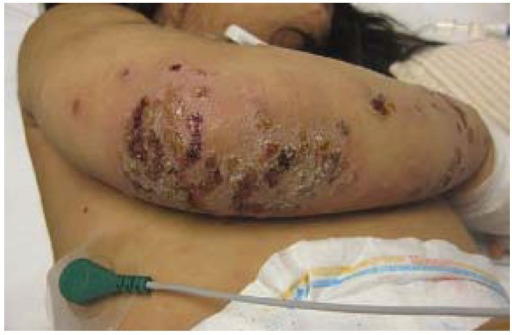
Crusted non-bullous impetigo on the upper extremity of a pediatric patient
Image: “ Impetigo” by Saint Louis University, Cardinal Glennon Children’s Hospital, 1465 South Grand Avenue, St. Louis, MO 63104, USA. License: CC BY 4.0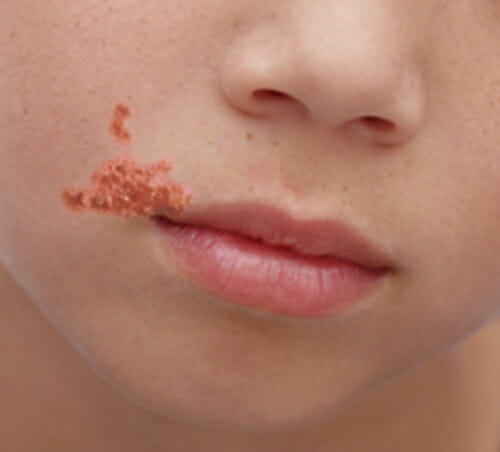
A child with honey-colored crust due to impetigo
Image: “OSC Microbio 21 02 impetigo” by CNX OpenStax. License: CC BY 4.0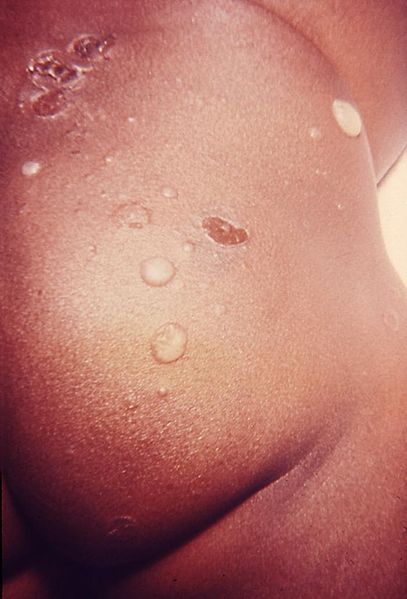
Bullous impetigo on the gluteal region of an infected infant
Image: “Skin lesions that proved to be impetigo” by US Department of Health and Human Services. License: Public Domain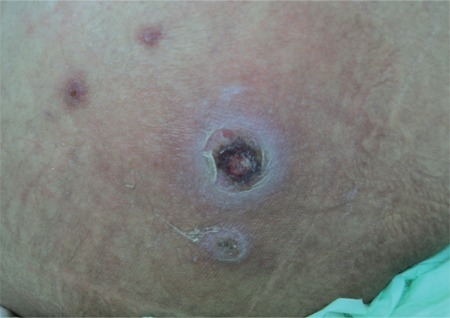
Coin-sized crusted ulcer typical of ecthyma (fusariosis is a fungal mold infection caused by Fusarium spp.)
Image: “Ectyhma gangrenosum” by İstanbul University Cerrahpasa Medical Faculty, Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology İstanbul, Turkey. License: CC BY 2.5Diagnosis is usually clinical, based on the natural sequence of the lesions and the presence of honey-colored crusts on pediatric patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship aged 2–5 years.
Management depends on the type and severity of the infection.
The following conditions also present with bullae Bullae Erythema Multiforme and serve as differential diagnoses for bullous impetigo:
The following conditions are other types of superficial skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease that are included in the differential diagnoses of impetigo: