Ichthyosis vulgaris is the most common type of keratinization disorders. The condition occurs due to an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the filaggrin gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics, which results in skin-barrier dysfunction. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present in early childhood with rough, dry, and scaly skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions that worsens during cold, dry months. The diagnosis is usually clinical, but often aided with a skin biopsy Skin Biopsy Secondary Skin Lesions showing hyperkeratosis and a diminished stratum granulosum Stratum granulosum Skin: Structure and Functions. Emollients Emollients Oleaginous substances used topically to soothe, soften or protect skin or mucous membranes. They are used also as vehicles for other dermatologic agents. Pityriasis Rosea, moisturizers, keratolytics, and retinoids Retinoids Retinol and derivatives of retinol that play an essential role in metabolic functioning of the retina, the growth of and differentiation of epithelial tissue, the growth of bone, reproduction, and the immune response. Dietary vitamin A is derived from a variety of carotenoids found in plants. It is enriched in the liver, egg yolks, and the fat component of dairy products. Fat-soluble Vitamins and their Deficiencies are the mainstays of management.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Ichthyosis vulgaris is the most common keratinization disorder.
Hereditary ichthyosis vulgaris:
Acquired ichthyosis vulgaris:
Clinical course:
Skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions findings:
Location:
Associated with:
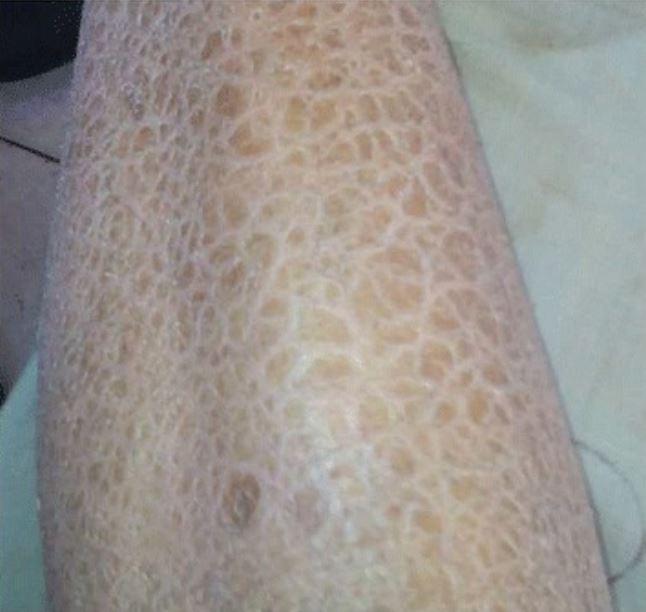
Thickened, “lizard skin” appearance of ichthyosis
Image: “In vivo confocal microscopy of pre-Descemet corneal dystrophy associated with X-linked ichthyosis: a case report” by BMC Ophthalmology. License: CC BY 4.0The diagnosis is based on the clinical exam and family history Family History Adult Health Maintenance. In patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with a milder phenotype Phenotype The complete genetic complement contained in the DNA of a set of chromosomes in a human. The length of the human genome is about 3 billion base pairs. Basic Terms of Genetics, the following may be used:
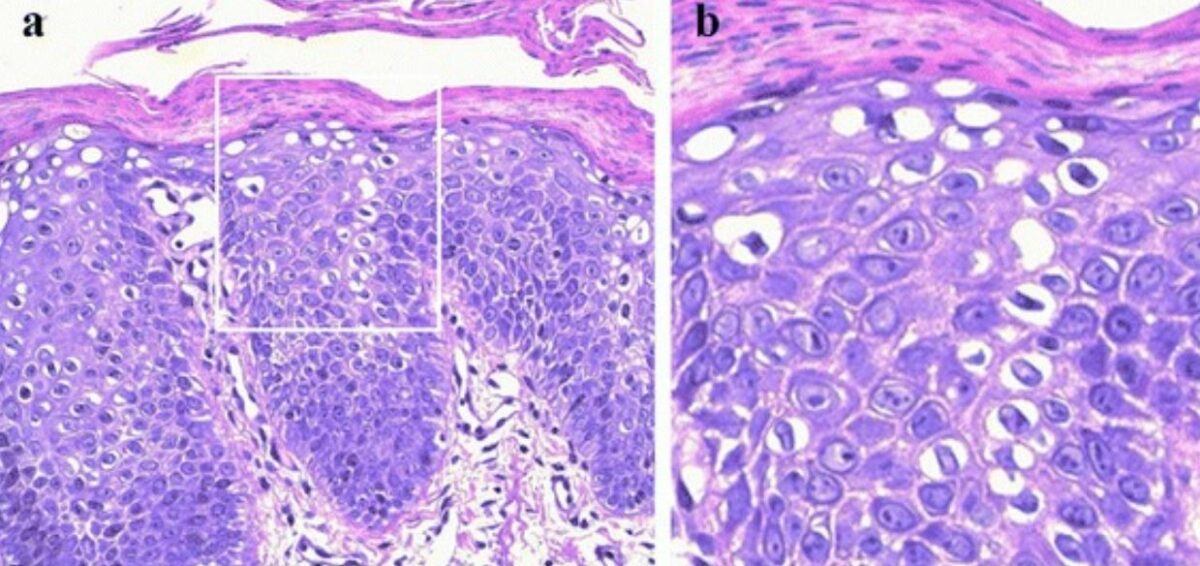
Histological findings in ichthyosis:
The epidermis appears acanthotic and hyperkeratotic, with parakeratosis, a reduced granular layer, and cytoplasmic vacuolization in suprabasal keratinocytes.
There is no definitive treatment for ichthyosis vulgaris. The goal is to avoid excessive drying, remove scales Scales Dry or greasy masses of keratin that represent thickened stratum corneum. Secondary Skin Lesions, and improve skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions appearance.