Hypokalemia is defined as plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia (K+) concentration < 3.5 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products concentration between 3.5–5.2 mEq/L despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hypokalemia can be due to renal losses, GI losses, transcellular Transcellular The movement of one cell into, through, and out of another cell. Tubular System shifts, or poor dietary intake. If minor in severity, hypokalemia is usually asymptomatic. However, acute reductions in K+ level or severe hypokalemia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, muscle weakness, rhabdomyolysis Rhabdomyolysis Rhabdomyolysis is characterized by muscle necrosis and the release of toxic intracellular contents, especially myoglobin, into the circulation. Rhabdomyolysis, paralysis, and respiratory failure Respiratory failure Respiratory failure is a syndrome that develops when the respiratory system is unable to maintain oxygenation and/or ventilation. Respiratory failure may be acute or chronic and is classified as hypoxemic, hypercapnic, or a combination of the two. Respiratory Failure. Diagnosis is by clinical history and lab testing. Management is guided by severity and includes treating urgent symptoms, replacing the K+ deficit, and treating the underlying cause.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia (K+) is the main intracellular cation in all cells and is distributed unevenly between the intracellular fluid Intracellular fluid The fluid inside cells. Body Fluid Compartments (98%) and extracellular fluid Extracellular fluid The fluid of the body that is outside of cells. It is the external environment for the cells. Body Fluid Compartments (2%). The large disparity is necessary for maintaining the resting membrane potential Resting membrane potential Membrane Potential of cells.
Hypokalemia is defined as plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products K+ concentration < 3.5 mEq/L.
The etiologies of hypokalemia can be grouped by 4 distinct mechanisms: poor dietary K+ intake, transcellular Transcellular The movement of one cell into, through, and out of another cell. Tubular System shift, GI losses, and renal losses.

Transcellular shift of K+:
Extracellular shift of K+:
1. Acidosis (increased H+) causes blockage of the Na+/H+ exchanger, which causes a decrease in intracellular Na+, in turn blocking Na+/K+ ATPase. On the other hand, acidosis activates the H+/K+ exchanger. Both cause an increase in extracellular K+.
2. Increased osmolarity in extracellular space (hyperglycemia, IV contrast, mannitol) shifts water outside the cell, decreasing K+ concentration. Increased gradient causes K+ diffusion outside.
Intracellular shift of K+:
1. Alkalosis (decreased H+) causes activation of the Na+/H+ exchanger, which causes an increase in intracellular Na+, in turn activating Na+/K+ ATPase. On the other hand, alkalosis blocks the H+/K+ exchanger. Both cause a decrease in extracellular K+.
2. Insulin and β2 adrenergic agonists activate Na+/K+ ATPase, lowering plasma K+ concentration.
Presentation of hypokalemia may include nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, vomiting, constipation Constipation Constipation is common and may be due to a variety of causes. Constipation is generally defined as bowel movement frequency < 3 times per week. Patients who are constipated often strain to pass hard stools. The condition is classified as primary (also known as idiopathic or functional constipation) or secondary, and as acute or chronic. Constipation, skeletal muscle manifestations, and cardiac manifestations, which are potentially very serious. Symptoms are more likely to appear as the severity of hypokalemia increases, but patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may be asymptomatic even with relatively severe hypokalemia.
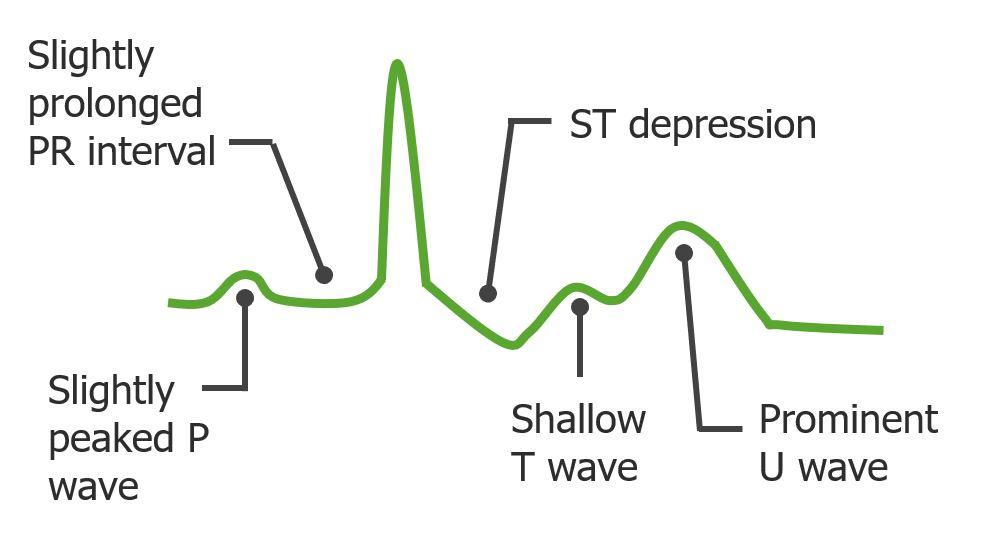
ECG changes seen in hypokalemia
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0