Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension has many adverse effects on the eye, of which retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome is the most common presentation. Hypertensive retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome consists of retinal vascular changes that develop as a direct effect of elevated blood pressure. In acute increases of blood pressure, autoregulation Autoregulation Systemic and Special Circulations results in retinal arteriolar narrowing. In chronic hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, structural changes consistent with arteriosclerosis affect the retinal vasculature. Endothelial wall damage ensues and various signs appear including hemorrhages, cotton-wool spots, and exudates. In severe cases of uncontrolled hypertension Uncontrolled hypertension Although hypertension is defined as a blood pressure of > 130/80 mm Hg, individuals can present with comorbidities of severe asymptomatic or "uncontrolled" hypertension (≥ 180 mm Hg systolic and/or ≥ 120 mm Hg diastolic) that carries with it a significant risk of morbidity and mortality. Uncontrolled Hypertension, papilledema Papilledema Swelling of the optic disk, usually in association with increased intracranial pressure, characterized by hyperemia, blurring of the disk margins, microhemorrhages, blind spot enlargement, and engorgement of retinal veins. Chronic papilledema may cause optic atrophy and visual loss. Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension is seen. Management is focused on controlling hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with severe hypertensive retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome have an increased risk for coronary artery Coronary Artery Truncus Arteriosus disease and stroke; therefore, detection and treatment of underlying hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension are important.
Last updated: Aug 4, 2025
Hypertensive retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome:
Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension:
| Blood pressure category | Systolic blood pressure | Diastolic blood pressure | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elevated blood pressure | 120–129 mm Hg | AND | < 80 mm Hg |
| Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension stage 1 Stage 1 Trypanosoma brucei/African trypanosomiasis | 130–139 mm Hg | OR | 80–89 mm Hg |
| Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension stage 2 | ≥ 140 mm Hg | OR | ≥ 90 mm Hg |
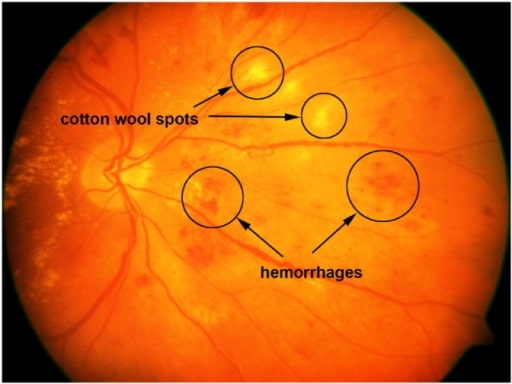
Retinal image with cotton-wool spots and hemorrhages.
Image: “A sample retinal image with cotton-wool spots and hemorrhages” by the United States National Library of Medicine. License: CC BY 4.0.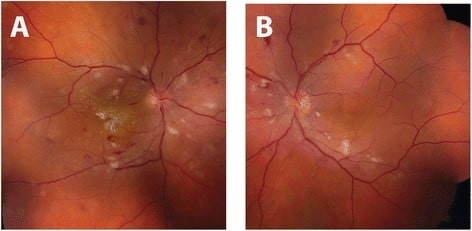
Fundus photograph of hypertensive retinopathy: Right eye (A) and left eye (B) demonstrate bilateral arteriolar narrowing, and cotton-wool spots with dot-blot and flame-shaped intraretinal hemorrhages. Intraretinal exudates in the form of a macular star are also visible on the right eye.
Image: “Initial fundus exam” by the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, University of Michigan, 500 S State St, Ann Arbor, MI 48109 USA. License: CC BY 4.0.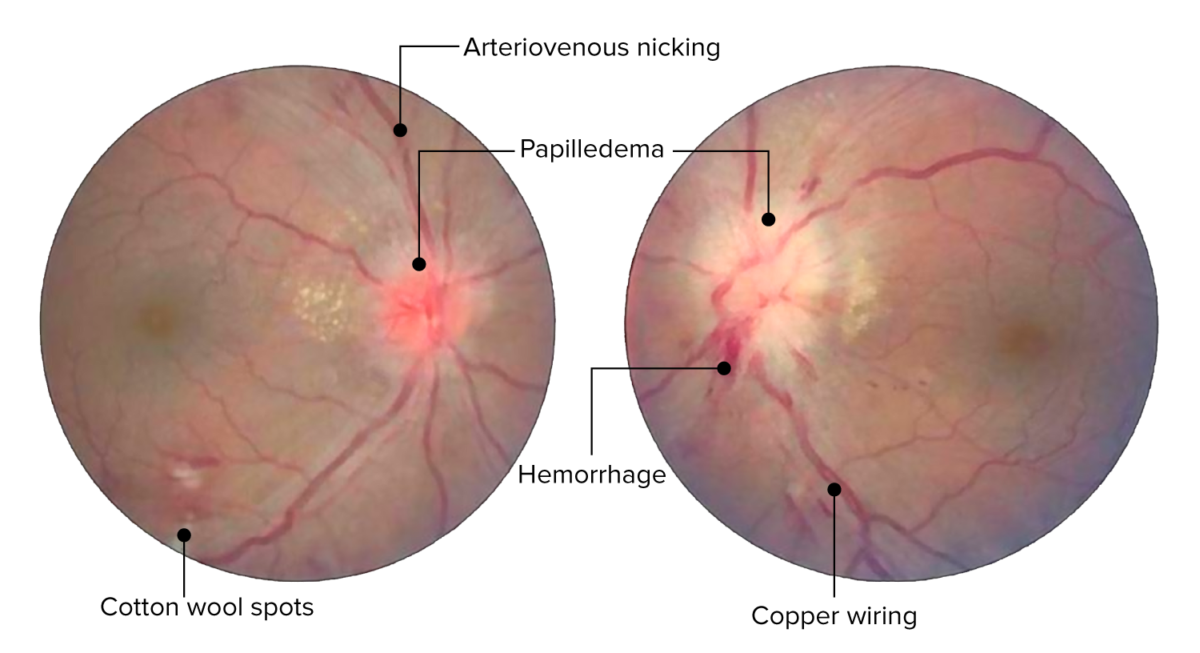
Retinal changes in acute hypertensive retinopathy. Image shows arteriovenous nicking, copper wire arterial changes, hemorrhages, and cotton-wool spots. Bilateral optic disc edema present bilaterally (left more than the right).
Image: “Central retinal vein occlusion” by Doheny Eye Institute, University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90033 USA. License: CC BY 3.0. Edited by Lecturio.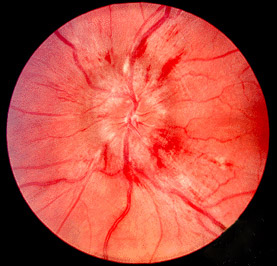
Photo demonstrating papilledema (swollen optic disc with blurred disc margins).
Image: “Papilledema” by Jonathan Trobe, MD. License: CC BY 3.0.| Grade I | Slight or modest narrowing of the retinal arterioles Arterioles The smallest divisions of the arteries located between the muscular arteries and the capillaries. Arteries: Histology, with an arteriovenous ratio of ≥ 1:2 |
|---|---|
| Grade II | Modest-to-severe narrowing of retinal arterioles Arterioles The smallest divisions of the arteries located between the muscular arteries and the capillaries. Arteries: Histology with an arteriovenous ratio < 1:2 or arteriovenous nicking |
| Grade III | Soft exudates or flame-shaped hemorrhages |
| Grade IV | Bilateral optic edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema |
| Grade of retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome | Retinal findings | Systemic risks |
|---|---|---|
| None | No detectable signs | None |
| Mild |
|
Modest association with risk of clinical stroke, subclinical stroke, coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease, describes a situation in which an inadequate supply of blood to the myocardium exists due to a stenosis of the coronary arteries, typically from atherosclerosis. Coronary Heart Disease, and mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status |
| Moderate |
|
Strong association with risk of clinical stroke, subclinical stroke, cognitive decline, coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease Coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease, describes a situation in which an inadequate supply of blood to the myocardium exists due to a stenosis of the coronary arteries, typically from atherosclerosis. Coronary Heart Disease, and mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status |
| Malignant | Signs of moderate retinopathy Retinopathy Degenerative changes to the retina due to hypertension. Alport Syndrome plus optic disc Optic disc The portion of the optic nerve seen in the fundus with the ophthalmoscope. It is formed by the meeting of all the retinal ganglion cell axons as they enter the optic nerve. Eye: Anatomy swelling Swelling Inflammation | Strong association with mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status |
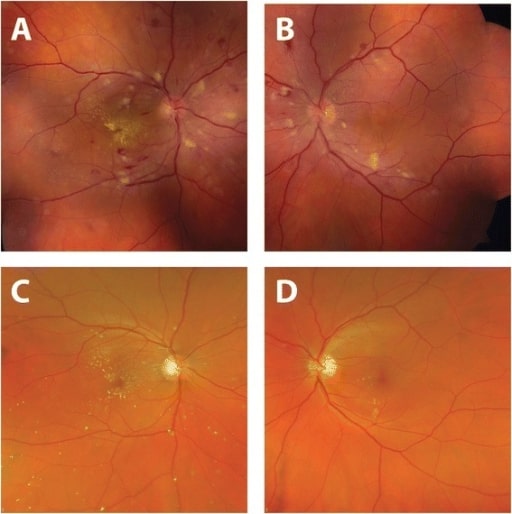
Improvement in fundus appearance after hypertension treatment.
Fundus photographs taken at time of presentation (A, B): Arteriolar narrowing, retinal hemorrhages, cotton-wool spots, and hard exudates (on the right) are noted.
Four months after diagnosis and treatment of systemic hypertension (C, D): Normalization of blood pressure resulted in the resolution of retinal hemorrhages and cotton-wool spots.
There is interval improvement in hard exudates in the right eye with a residual macular star.