Huntington disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance mode of inheritance and poor prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. It is caused by cytosine-adenine-guanine (CAG) trinucleotide repeats in the huntingtin gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics (HTT). The most common clinical presentation in adulthood is a movement disorder known as chorea: abrupt, involuntary movements of the face, trunk, and limbs. Psychiatric and cognitive features are also characteristic, and patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with HD are at an increased risk for suicide Suicide Suicide is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Patients with chronic medical conditions or psychiatric disorders are at increased risk of suicidal ideation, attempt, and/or completion. The patient assessment of suicide risk is very important as it may help to prevent a serious suicide attempt, which may result in death. Suicide throughout the course of the disease. The diagnosis is primarily clinical, often with a positive family history Family History Adult Health Maintenance followed by genetic confirmation. Management by an interdisciplinary team is supportive, with the goal of maintaining quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life. Treatment of depression, agitation Agitation A feeling of restlessness associated with increased motor activity. This may occur as a manifestation of nervous system drug toxicity or other conditions. St. Louis Encephalitis Virus, and psychosis is the 1st priority for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with Huntington disease over the treatment of chorea.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Huntington disease (HD) is an inherited and progressive neurodegenerative disorder that causes a choreiform movement disorder, unsteady gait Gait Manner or style of walking. Neurological Examination, and depression.
Huntington disease is caused by an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance genetic alteration in the huntingtin gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics (HTT) present on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 4p.
HD is caused by CAG trinucleotide repeats in the HTT gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics.
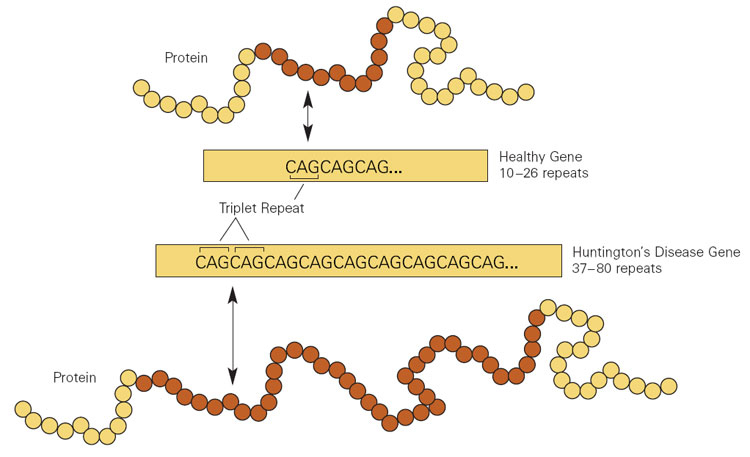
Cytosine-adenine-guanine (CAG) repeat expansion in the huntingtin gene (HTT) resulting in Huntington disease
Image: “Huntington’s disease patient” by National Institute of Standards and Technology. License: Public Domain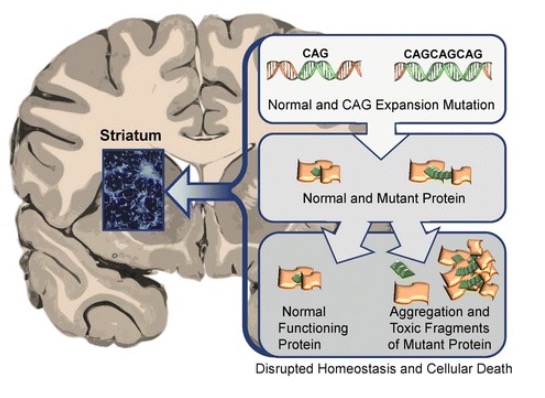
Abnormal HTT proteins’ toxic effect on the striatum in Huntington disease leading to neurodegeneration and death of the affected neurons
Image: “Neuronal changes in Huntington disease” by Jaenisch R, Zhang F, Gage F. License: CC BY 4.0Huntington disease affects generations of family members and typically spans several decades. The symptoms can be motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology, cognitive, and behavioral.
Management of HD includes medical and psychological support to manage symptoms and maintain quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life. Treatment of depression, agitation Agitation A feeling of restlessness associated with increased motor activity. This may occur as a manifestation of nervous system drug toxicity or other conditions. St. Louis Encephalitis Virus, and psychosis is the 1st priority for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with HD over the treatment of chorea.