Humoral adaptive immunity is an integral part of the adaptive immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs, which mounts a highly specific defense against pathogens but takes a longer time to respond (compared to the innate immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs). Humoral immunity is the arm Arm The arm, or "upper arm" in common usage, is the region of the upper limb that extends from the shoulder to the elbow joint and connects inferiorly to the forearm through the cubital fossa. It is divided into 2 fascial compartments (anterior and posterior). Arm: Anatomy of the immune system Immune system The body's defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs protecting the extracellular fluids of the lymphatics ( lymph Lymph The interstitial fluid that is in the lymphatic system. Secondary Lymphatic Organs), interstitium, and circulatory system ( plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products) from microbial contamination mediated through soluble molecules. The B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions play a major role, producing antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions or immunoglobulins Immunoglobulins Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions. Arising from the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis, B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions originate from the common lymphoid progenitor and undergo stages to assemble the B cell receptor B cell receptor Lymphocytes: Histology. To become fully functional, activation follows, and this can be T cell–dependent (which produces memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment cells) or T cell–independent (producing a short-lived response). When activated, B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions go through processes enhancing antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination affinity, class switching, and differentiation to plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cells and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment cells. Plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cells produce the antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, while memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions respond to reinfection. There are different immunoglobulin isotypes, generally providing immune protection through complement activation Complement Activation The sequential activation of serum complement proteins to create the complement membrane attack complex. Factors initiating complement activation include antigen-antibody complexes, microbial antigens, or cell surface polysaccharides. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, opsonization, neutralization of toxins or viruses Viruses Minute infectious agents whose genomes are composed of DNA or RNA, but not both. They are characterized by a lack of independent metabolism and the inability to replicate outside living host cells. Virology, and induction of cell lysis.
Last updated: Sep 8, 2022
The immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses Viruses Minute infectious agents whose genomes are composed of DNA or RNA, but not both. They are characterized by a lack of independent metabolism and the inability to replicate outside living host cells. Virology to parasites. The components of the system are interconnected by blood and the lymphatic circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment.
2 lines of defense Lines of Defense Inflammation (that overlap):
| Innate immunity Innate immunity The capacity of a normal organism to remain unaffected by microorganisms and their toxins. It results from the presence of naturally occurring anti-infective agents, constitutional factors such as body temperature and immediate acting immune cells such as natural killer cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation | Adaptive immunity | |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics Genetics Genetics is the study of genes and their functions and behaviors. Basic Terms of Genetics | Germline encoded | Gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics rearrangements involved in lymphocyte development |
| Immune response | Nonspecific | Highly specific |
| Timing of response | Immediate (minutes to hours) | Develops over a longer period of time |
| Memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment response | Without memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment response | With memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment response, which responds quickly upon recognition of antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination |
| Recognition of pathogen | Pattern recognition receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (PRRs) such as TLRs recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns Sepsis and Septic Shock ( PAMPs PAMPs Sepsis and Septic Shock). |
|
| Components |
|
|
Responding to microbial invaders is the responsibility of the immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs. Often, the innate immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs has the capability to contain the pathogens, but invaders have evolved means to evade innate immunity Innate immunity The capacity of a normal organism to remain unaffected by microorganisms and their toxins. It results from the presence of naturally occurring anti-infective agents, constitutional factors such as body temperature and immediate acting immune cells such as natural killer cells. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation. The next line of defense is the adaptive immune system Immune system The body’s defense mechanism against foreign organisms or substances and deviant native cells. It includes the humoral immune response and the cell-mediated response and consists of a complex of interrelated cellular, molecular, and genetic components. Primary Lymphatic Organs.
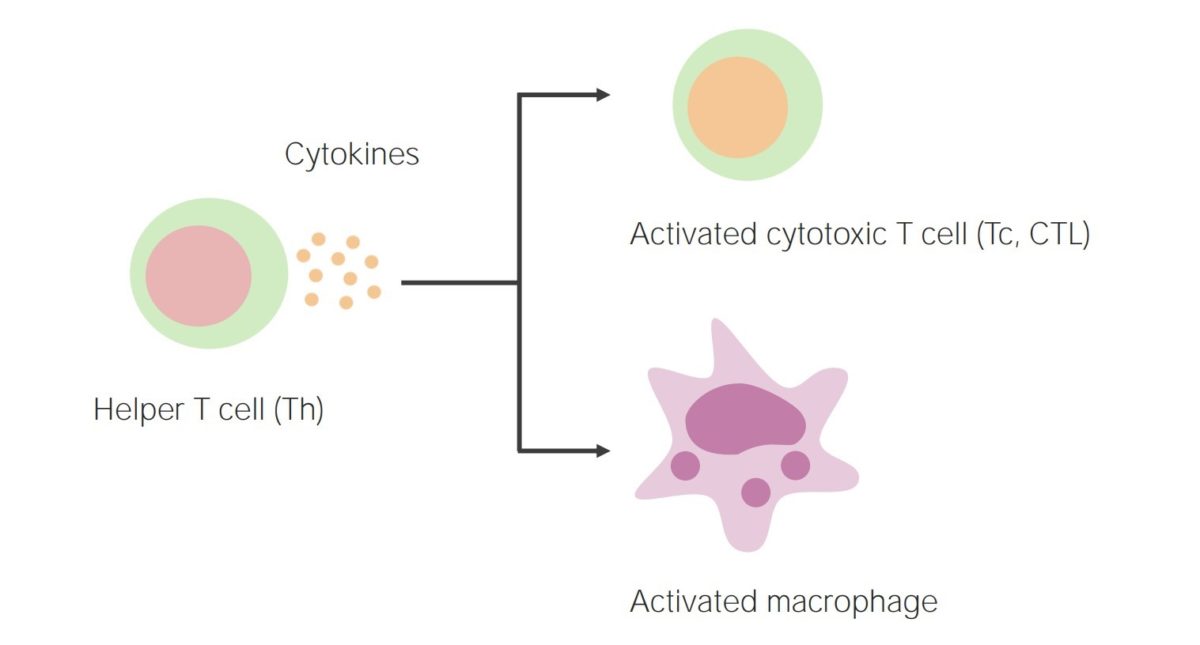
Cell-mediated immunity:
Activation of helper T cells results in the release of cytokines, thereby activating cytotoxic T cells and phagocytes (such as macrophages).
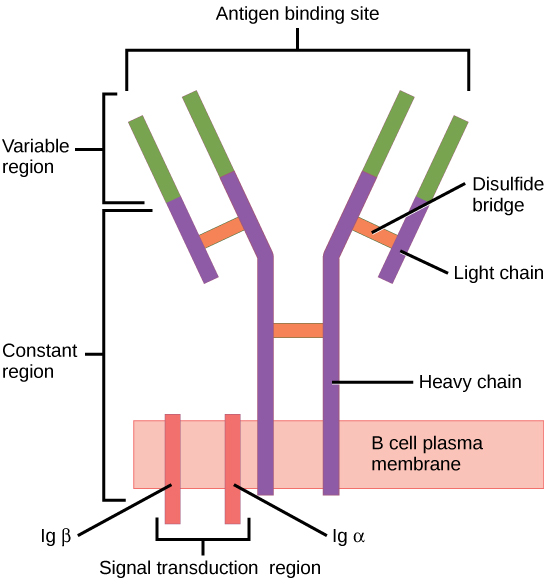
The B cell receptor (BCR) consists of the Ig molecule and the signaling molecule:
Ig contains 2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains linked by a disulfide bridge. The membrane-bound Ig is anchored to the cell surface.
Steps needed for the B cell to function:
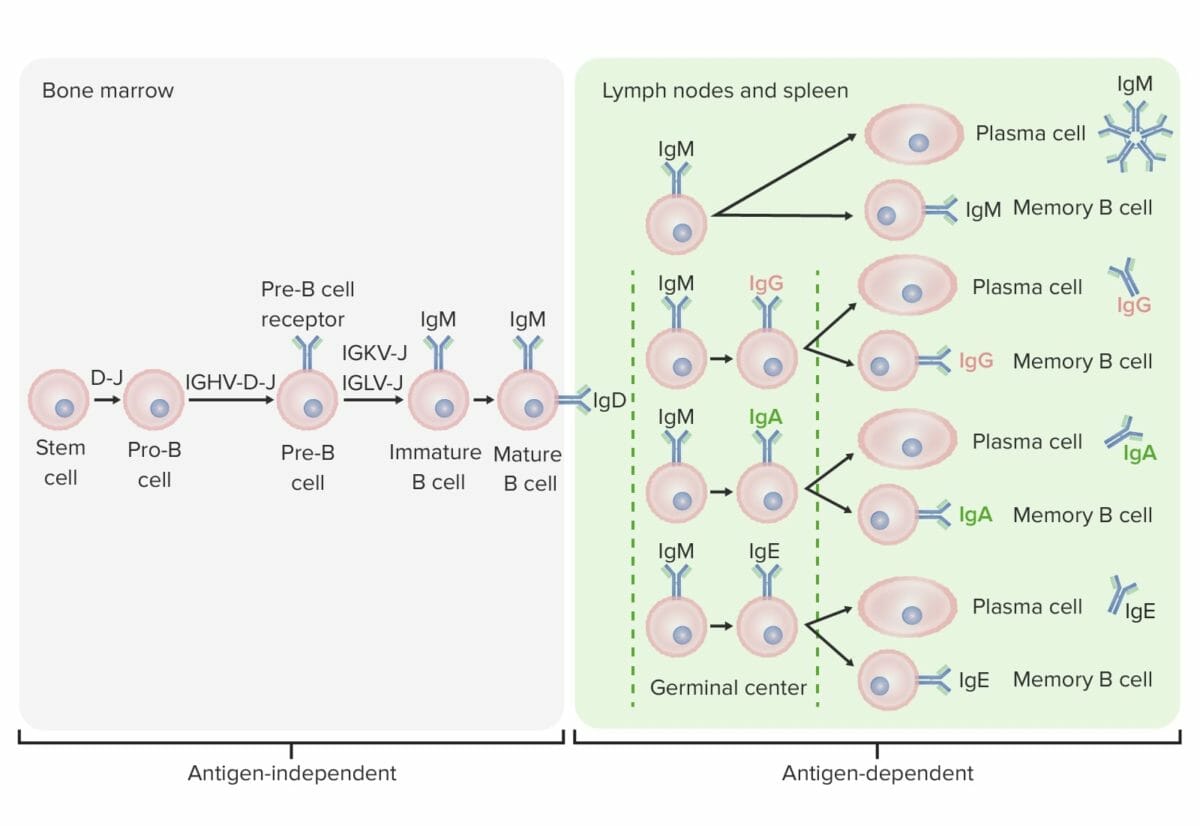
Differentiation stages of the B cell:
In antigen-independent stages, B-cell production starts with the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC), which becomes a common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) and then a pre-pro-B cell or B-progenitor cell. The next steps include gene rearrangement to assemble the Ig molecule. Ig heavy chains start with rearrangement of diversity and joining segments to form the pro-B cell. In the next step (pre-B cell), Ig heavy-chain recombination (variable, diversity, joining) is completed and the pre-B-cell receptor is formed. Light-chain (kappa (κ) or lambda (λ)) rearrangement occurs, resulting in the expression of a complete IgM-antibody molecule by an immature B cell. Formation of the mature B cell (naive) with both IgM and IgD follows.
Antigen-dependent stages take place in secondary lymphoid tissues. Once the mature B cell produce IgM and IgD, a class switch can take place to make IgE, IgG, and IgA. B cells are activated and become plasma cells or memory cells.
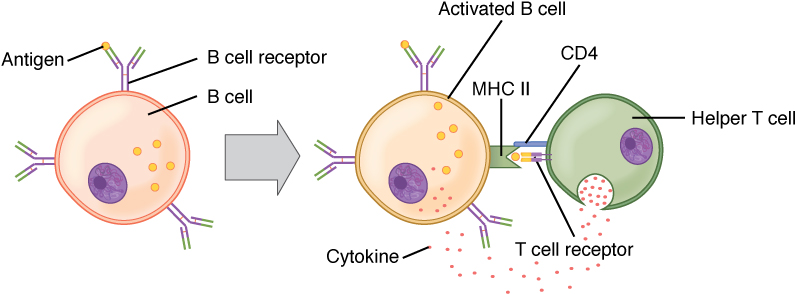
B cell activation (T cell dependent):
Circulating antigen interacts with the Bcell receptor (BCR) of the B cell. The antigen is endocytosed and degraded, and the peptide components are complexed with cell surface MHC II molecules. T follicular helper (Tfh) cells (specialized CD4+ T helper cells) recognize and bind the antigen–MHC II complex. Cytokines are released by the Tfh cells, leading to B cell activation and proliferation. Activated B cells enter the germinal centers, where they continue the process, leading to differentiation.
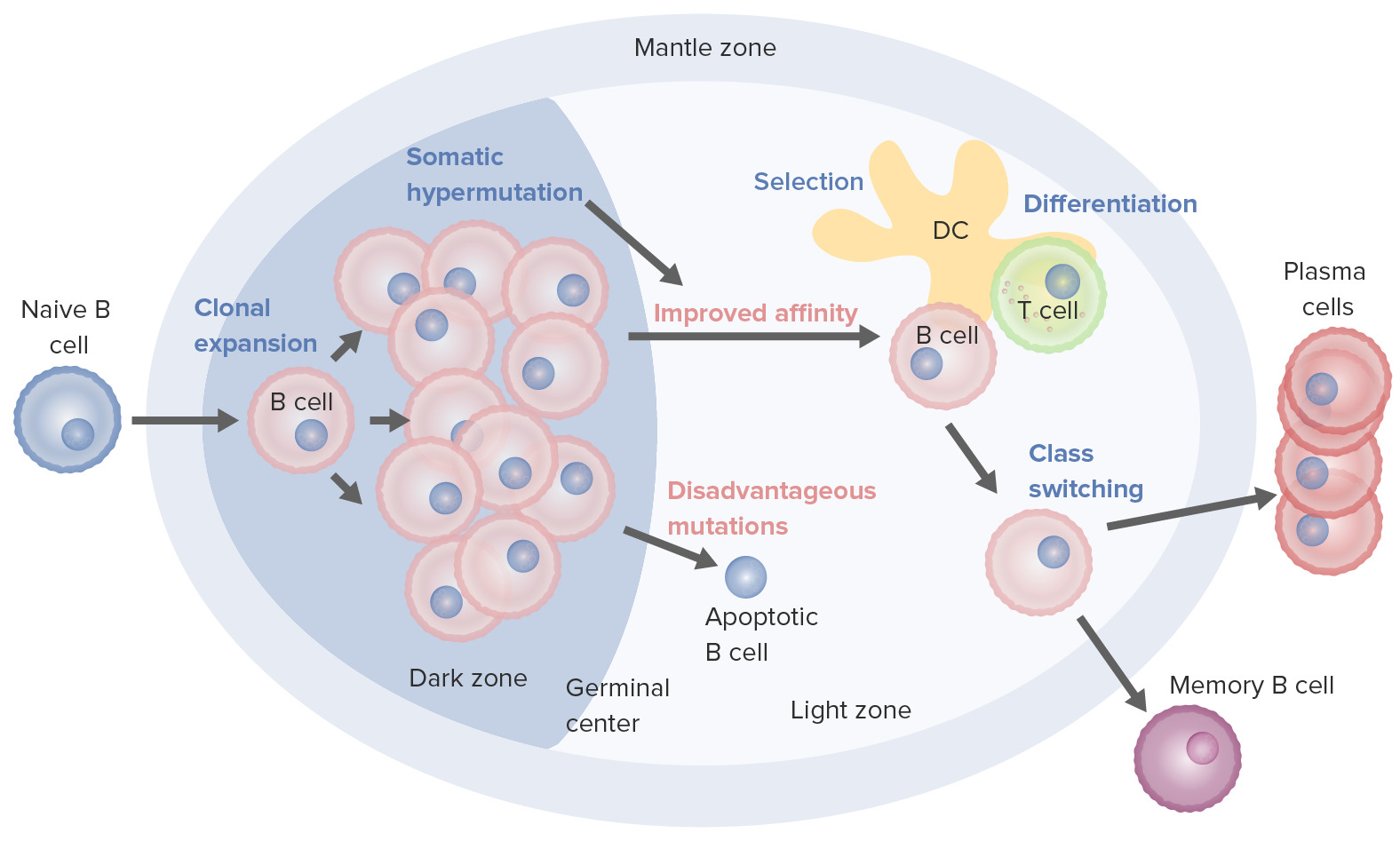
B cell activation and maturation processes taking place in the germinal center:
On activation, the B cell moves from the mantle zone and enters the germinal center. B cell proliferation (clonal expansion) takes place, and antibody affinity to the antigen is enhanced through the process of somatic hypermutation. Repeated cycles of proliferation and hypermutation fine-tune the B cell receptor. However, not all B cells continue to differentiate, especially if the affinity is weak. Apoptosis follows if the antigen–antibody binding is not optimized. Those with strong affinity survive (selection) with the help of survival signals from follicular dendritic cells and T cells. These selected B cells move on to class switching and differentiation into plasma cells or memory cells.
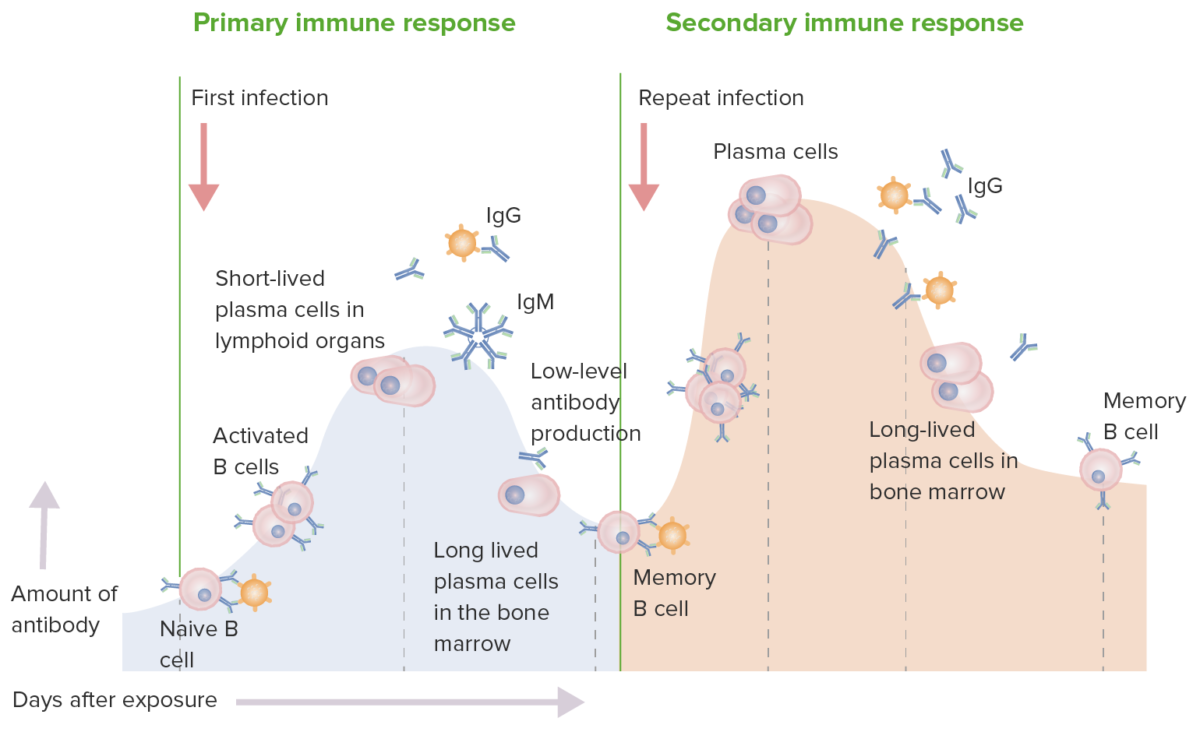
Primary and secondary immune response:
In a primary immune response, naive B cells are stimulated by antigen. B cell activation and then differentiation into antibody-secreting cells occur. The antibodies are specific for the eliciting antigen. The production of IgM is followed by IgG. While there is an immune response, the production is low-level. In the secondary immune response, the same antigen stimulates memory B cells, leading to the production of greater quantities of specific antibodies that are produced in the primary response. The production and release of IgG also occur earlier.
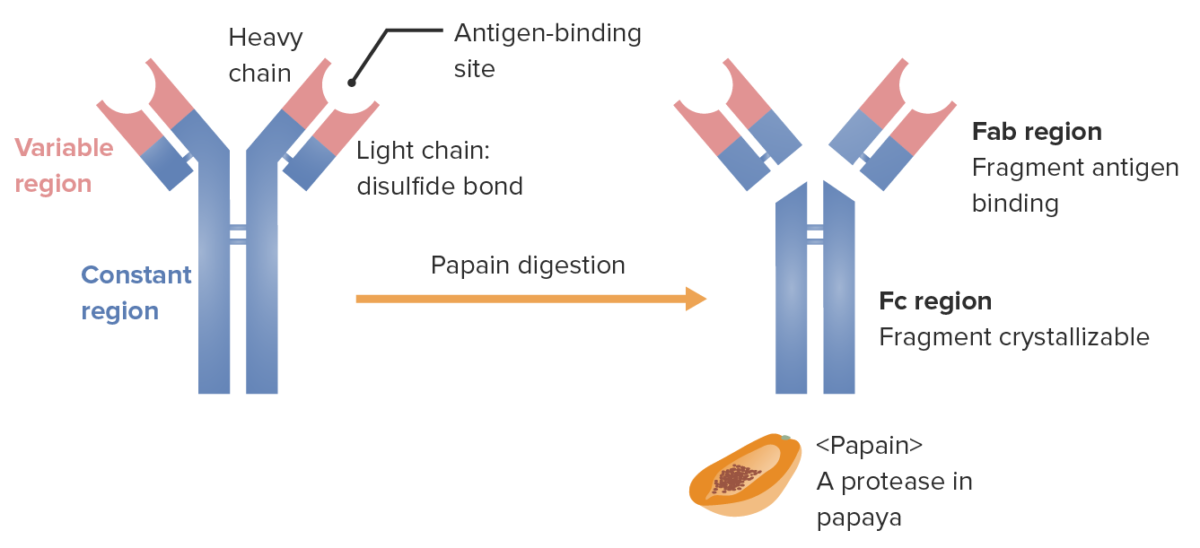
Fragments of the immunoglobulin (determined by location where the enzyme papain splits the Ig):
The Fab (fragment antigen-binding) region contains the variable regions (red) and parts of the constant region (blue) of both heavy and light chains. The Fc (fragment crystallizable) region contains the remaining part (tail) of the antibody (constant region of the heavy chain only).
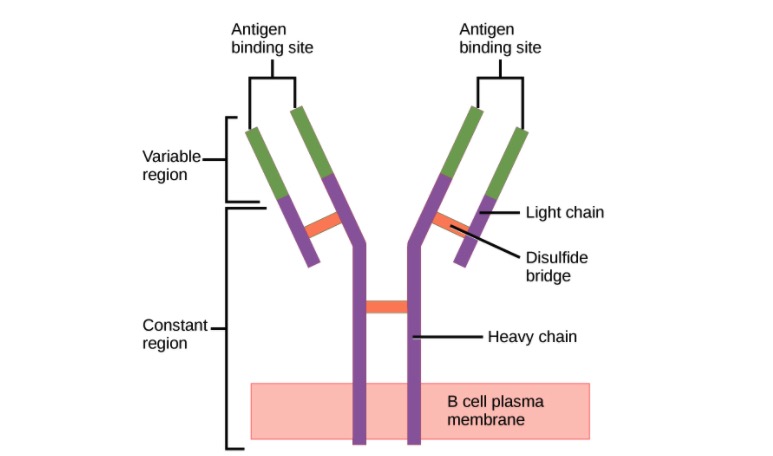
Structure of the antibody (regions):
An antibody has a unique variable region (formed by heavy and light chains) capable of binding a different antigen and a constant region (formed by heavy chains).
Protection against infectious agents and their products by:
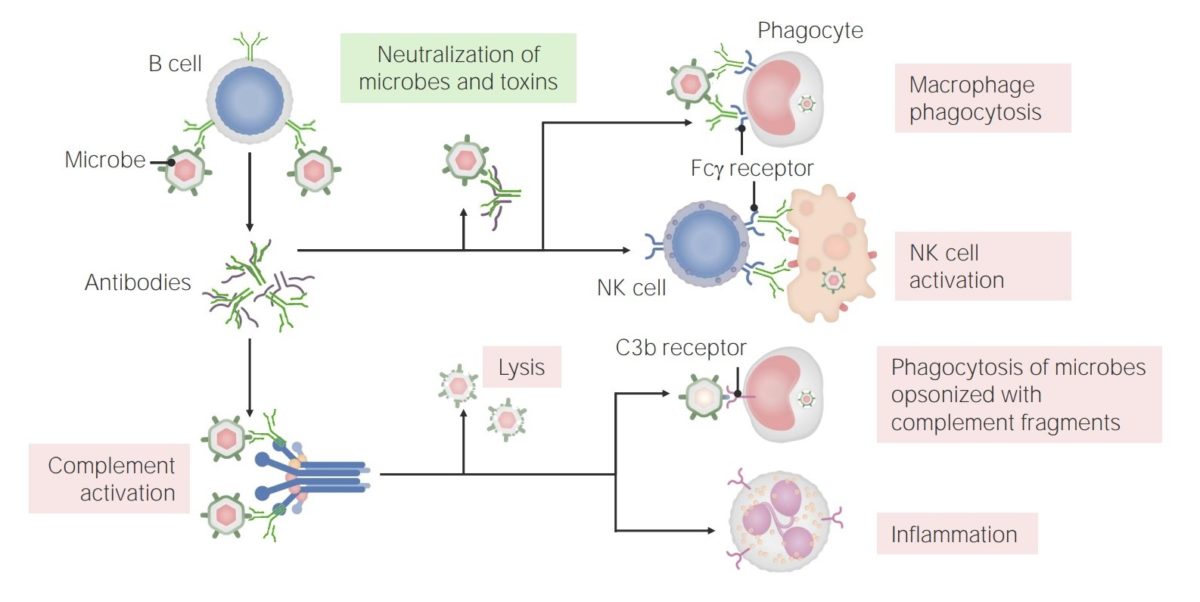
The functions of antibodies:
Antibodies have multiple roles in immunity, including neutralization (of microbes and toxins), promotion of phagocytosis, and NK cell activation. In addition, antibodies have a role in complement activation, which can lead to direct microbe lysis, opsonization and phagocytosis, and recruitment/activation of neutrophils.