Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses DNA Viruses Viruses whose nucleic acid is DNA. Virology belonging to the Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2 family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are commonly contracted during childhood. Both HHV-6B and HHV-7 cause a common childhood illness known as roseola infantum (also known as roseola or 6th disease). Roseola is a self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children disease that presents with high fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, followed by a diffuse, rose-pink maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination rash Rash Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. The diagnosis is clinical, and management is supportive.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
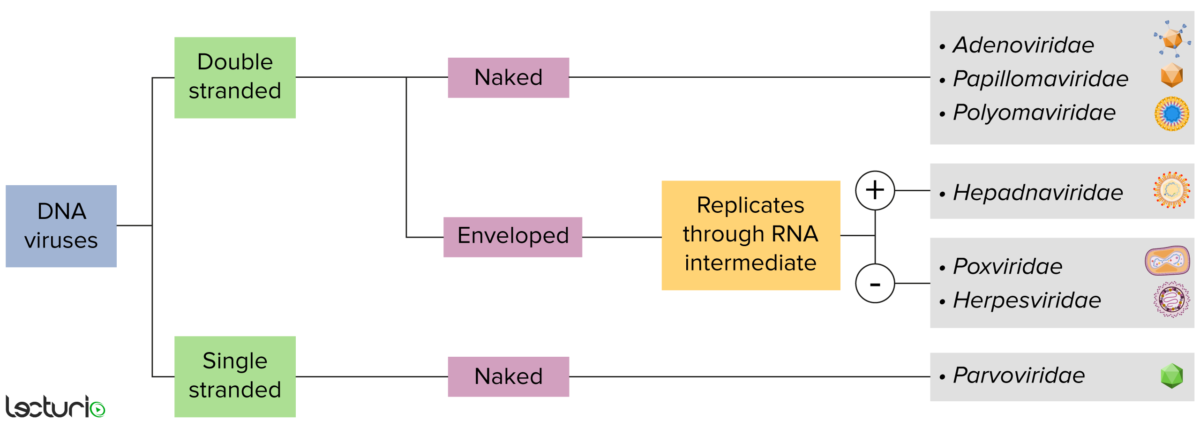
Identification of DNA viruses:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. Viruses with a DNA genome can be further characterized as single or double stranded. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane, which is usually taken from the host cell. If the coat is absent, however, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Some enveloped viruses translate DNA into RNA before incorporating into the genome of the host cell.
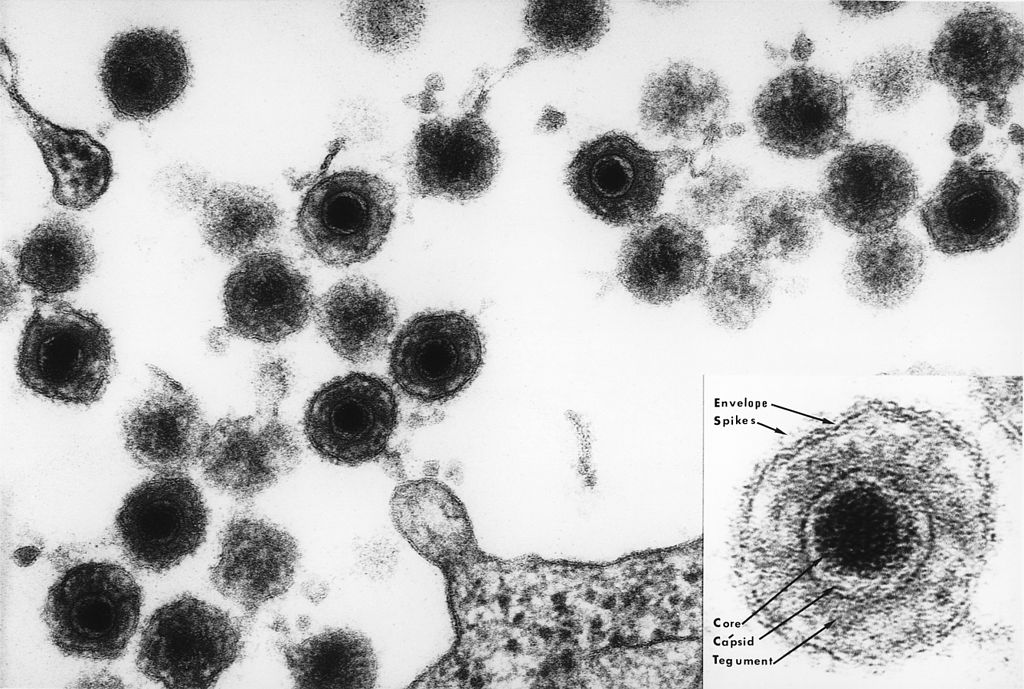
Electron micrograph of HHV-6 virions
Image: “Electron micrograph of one of the HHV6 species” by Bernard Kramarsky. License: Public DomainThe clinical relevance of HHV-6A is not entirely known.
Humans are the reservoir Reservoir Animate or inanimate sources which normally harbor disease-causing organisms and thus serve as potential sources of disease outbreaks. Reservoirs are distinguished from vectors (disease vectors) and carriers, which are agents of disease transmission rather than continuing sources of potential disease outbreaks. Humans may serve both as disease reservoirs and carriers. Escherichia coli for HHV-6 and HHV-7.
HHV-6 and HHV-7 are transmitted through contact with saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy.
Human herpesvirus-6 infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are usually mild and occur during childhood. Most HHV-7 infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease are asymptomatic.
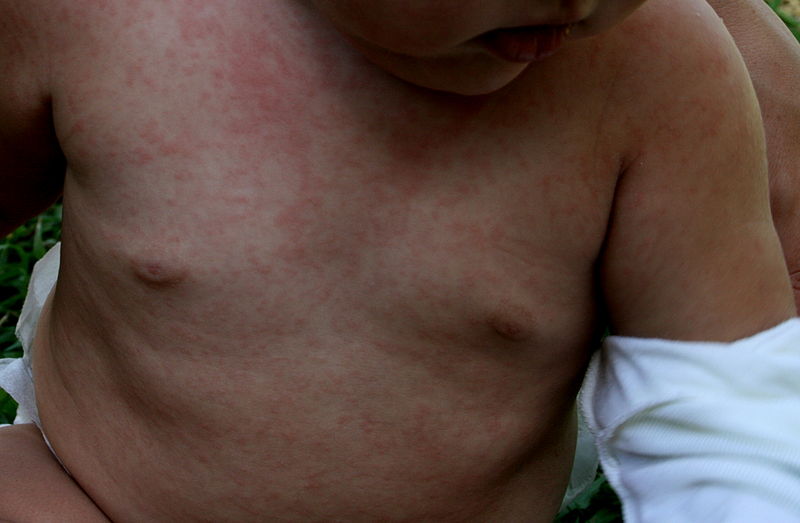
Erythematous maculopapular rash seen in roseola:
This rash is most commonly caused by human HHV-6B, and to a lesser extent, HHV-7.
The diagnosis is clinical, and testing is rarely indicated. An exception is made in the case of severe disease in immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis individuals (e.g., encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis, myocarditis Myocarditis Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the myocardium, which may occur alone or in association with a systemic process. There are numerous etiologies of myocarditis, but all lead to inflammation and myocyte injury, most often leading to signs and symptoms of heart failure. Myocarditis).
Treatment is generally not necessary, as symptoms are self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with severe disease may be given:
The following table compares the 9 herpesviruses considered endemic in humans; there are 115 different total known species of herpesviruses, grouped into 3 families:
| HHV | Common name | Primary target cells | Latency site | Clinical presentation* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (alpha group) |
HSV-1 | Mucoepithelial cells | Dorsal root ganglia |
|
|
2 (alpha group) |
HSV-2 |
|
||
|
3 (alpha group) |
VZV |
|
||
|
4 (gamma group) |
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus |
|
Memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions |
|
|
5 (beta group) |
CMV |
|
Hematopoietic progenitor cells in bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis |
|
|
6A, 6B (beta group) |
HHV-6 | T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified – cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions | Monocytes Monocytes Large, phagocytic mononuclear leukocytes produced in the vertebrate bone marrow and released into the blood; contain a large, oval or somewhat indented nucleus surrounded by voluminous cytoplasm and numerous organelles. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation | Roseola |
|
7 (beta group) |
HHV-7 | T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified – cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions | ||
|
8 (gamma group) |
Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus Kaposi sarcoma–associated herpesvirus Human herpesvirus 8, also known as kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, is a double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This uncommon oncogenic virus causes kaposi sarcoma (an AIDS-defining condition), primary effusion lymphomas, and multicentric castleman disease mainly in immunocompromised patients. Human Herpesvirus 8 |
|
B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions | Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions sarcoma |
| Number | Other names for the disease | Etiology | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st disease 1st disease Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus |
|
Measles Measles Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It is highly contagious and spreads by respiratory droplets or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular rash. Measles Virus morbillivirus Morbillivirus A genus of the family paramyxoviridae (subfamily paramyxovirinae) where the virions of most members have hemagglutinin but not neuraminidase activity. All members produce both cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusion bodies. Measles virus is the type species. Measles Virus |
|
| 2nd disease |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3rd disease 3rd disease An acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. The virus enters the respiratory tract via airborne droplet and spreads to the lymphatic system. Rubella Virus |
|
Rubella Rubella An acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. The virus enters the respiratory tract via airborne droplet and spreads to the lymphatic system. Rubella Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology |
|
| 4th disease |
|
Due to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess strains that make epidermolytic (exfoliative) toxin |
|
| 5th disease | Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion infectiosum | Erythrovirus or parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (Primate erythroparvovirus Erythroparvovirus Parvovirus B19 1) |
|
| 6th disease |
|
Human herpesvirus 6B or 7 |
|