Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia is the infection of the lung parenchyma, resulting from the spread of pathogens and accompanied by the host inflammatory response. This condition is the most common infectious cause of death. Multiple organisms cause pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia, including bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology (of which Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common), viruses Viruses Minute infectious agents whose genomes are composed of DNA or RNA, but not both. They are characterized by a lack of independent metabolism and the inability to replicate outside living host cells. Virology, and fungi Fungi A kingdom of eukaryotic, heterotrophic organisms that live parasitically as saprobes, including mushrooms; yeasts; smuts, molds, etc. They reproduce either sexually or asexually, and have life cycles that range from simple to complex. Filamentous fungi, commonly known as molds, refer to those that grow as multicellular colonies. Mycology. The infection can be acquired while hospitalized (hospital-acquired) or outside the hospital setting (community-acquired). Common symptoms include fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, chills Chills The sudden sensation of being cold. It may be accompanied by shivering. Fever, cough, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, and dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea. Chest X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests usually shows consolidation Consolidation Pulmonary Function Tests and/or infiltrates. Diagnosis can be made with clinical presentation and imaging, but in severe cases, microbiological testing (sputum and cultures, molecular testing) and routine blood tests are needed. Empiric treatment with antibiotics is recommended, with regimen depending on the setting, risk factors for multidrug-resistant organisms Multidrug-Resistant Organisms Multidrug-resistant Organisms and Nosocomial Infections, and individual comorbidities Comorbidities The presence of co-existing or additional diseases with reference to an initial diagnosis or with reference to the index condition that is the subject of study. Comorbidity may affect the ability of affected individuals to function and also their survival; it may be used as a prognostic indicator for length of hospital stay, cost factors, and outcome or survival. St. Louis Encephalitis Virus. Identification Identification Defense Mechanisms of the causative pathogen helps narrow down the antibiotics. Preventive measures include vaccinations (pneumococcal and influenza Influenza Influenza viruses are members of the Orthomyxoviridae family and the causative organisms of influenza, a highly contagious febrile respiratory disease. There are 3 primary influenza viruses (A, B, and C) and various subtypes, which are classified based on their virulent surface antigens, hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA). Influenza typically presents with a fever, myalgia, headache, and symptoms of an upper respiratory infection. Influenza Viruses/Influenza) and smoking Smoking Willful or deliberate act of inhaling and exhaling smoke from burning substances or agents held by hand. Interstitial Lung Diseases cessation.
Last updated: Sep 12, 2025
Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia is the infection of the lung parenchyma.
Classification based on the site where infection was acquired:[1,8]
Classification by etiology:[12,13]
General:
HAP:
VAP:
Signs and symptoms may include:[1]
With mechanical ventilation Ventilation The total volume of gas inspired or expired per unit of time, usually measured in liters per minute. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing, suggestive findings may include:[22]
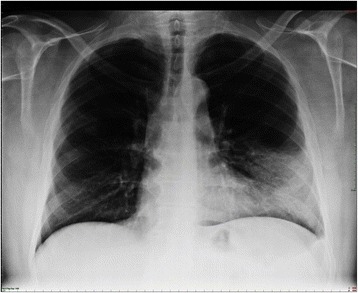
Lobar pneumonia. Dense infiltration in the left lower lobe has caused a silhouette of the left cardiac border (dashed line). Air bronchogram is a typical feature of consolidation.
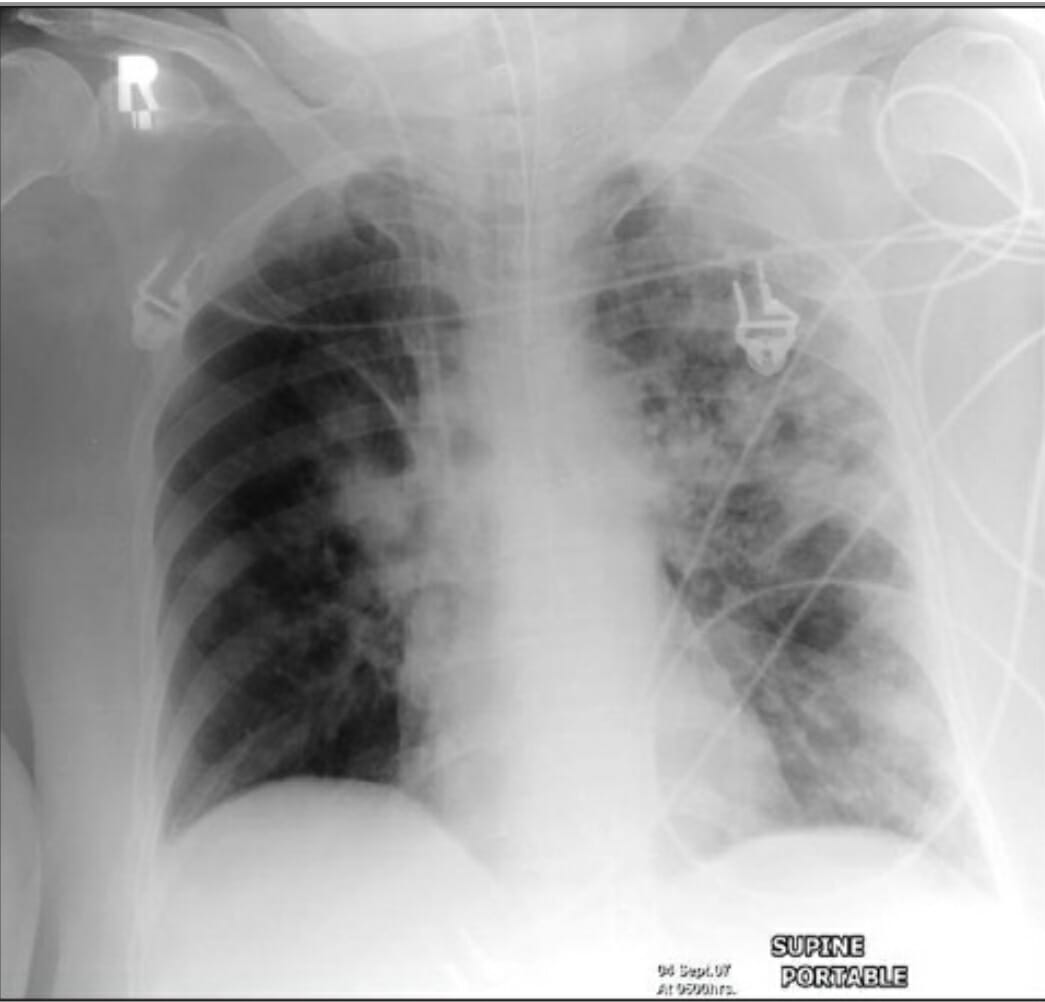
An AP supine radiograph of a patient on mechanical ventilation showing patchy consolidation in both lung fields (more prominent on the left) due to hospital-acquired pneumonia
Image: “Reading chest rediographs in the critically ill” by Khan AN, Al-Jahdali H, Al-Ghanem S, Gouda A. License: CC BY 2.0Recommendations may vary depending on practice location, regional epidemiology, and availability of drug therapy. The following is a summary derived largely from the ATS/IDSA guidelines. For detailed information, ATS/IDSA guidelines (US), UK guidelines, and European guidelines are available for review.
Empiric broad-spectrum Broad-Spectrum Fluoroquinolones antibiotics are given, with coverage for S.aureus, P. aeruginosa P. aeruginosa A species of gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria commonly isolated from clinical specimens (wound, burn, and urinary tract infections). It is also found widely distributed in soil and water. P. Aeruginosa is a major agent of nosocomial infection. Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella.
Deciding on treatment initiation:[8]
Deciding on the regimen:[8,18]
| Type of pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia | Risk factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HAP | Associated with ↑ mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status |
|
|
| Associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas, gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella, MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus |
|
||
| Associated with MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus |
|
||
| Associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella |
|
||
| VAP | Associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas, gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella, MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus |
|
|
| Associated with MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus |
|
||
| Associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella |
|
||
Antibiotic options:[1,8,18,20]
| Type of pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia | Clinical scenario | Recommended regimen |
|---|---|---|
| HAP | With risk factors associated with ↑ mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status | 2 antipseudomonal antimicrobial agents (different classes) + MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus coverage |
| With risk factors associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas, gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella, MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus | ||
| With risk factors associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella only | 2 antipseudomonal antimicrobial agents (different classes) | |
| With risk factors for MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus only | Single agent with antipseudomonal activity + MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus coverage | |
| No MDR risk factors or increased mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status | Single agent with MSSA and antipseudomonal activity | |
| VAP | With risk factors associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas, gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella, MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus | 2 antipseudomonal antimicrobial agents (different classes) + MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus coverage |
| With risk factors associated with MDR Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas and other gram-negative bacilli Bacilli Shigella only | 2 antipseudomonal antimicrobial agents (different classes) | |
| With risk factors for MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus only | Single agent with antipseudomonal activity + MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus coverage | |
| No MDR risk factors or site/hospital has ≤ 10% gram-negative isolates that are resistant to an agent (monotherapy) or ≤ 20% MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus | Single agent with MSSA and antipseudomonal activity |
| Class | Antibiotic choices* | Typical starting dose |
|---|---|---|
| Antipseudomonal beta-lactams | Piperacillin Piperacillin Semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, ampicillin derived ureidopenicillin antibiotic proposed for pseudomonas infections. It is also used in combination with other antibiotics. Penicillins– tazobactam Tazobactam A penicillanic acid and sulfone derivative and potent beta-lactamase inhibitor that enhances the activity of other anti-bacterial agents against beta-lactamase producing bacteria. Cephalosporins | 4.5 g IV every 6 hours |
| Cefepime Cefepime A fourth-generation cephalosporin antibacterial agent that is used in the treatment of infections, including those of the abdomen, urinary tract, respiratory tract, and skin. It is effective against pseudomonas aeruginosa and may also be used in the empiric treatment of febrile neutropenia. Cephalosporins | 2 g IV every 8 hours | |
| Ceftazidime Ceftazidime Semisynthetic, broad-spectrum antibacterial derived from cephaloridine and used especially for pseudomonas and other gram-negative infections in debilitated patients. Cephalosporins | 2 g IV every 8 hours | |
| Imipenem Imipenem Semisynthetic thienamycin that has a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity against gram-negative and gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, including many multiresistant strains. It is stable to beta-lactamases. Clinical studies have demonstrated high efficacy in the treatment of infections of various body systems. Its effectiveness is enhanced when it is administered in combination with cilastatin, a renal dipeptidase inhibitor. Carbapenems and Aztreonam | 500 mg IV every 6 hours | |
| Meropenem Meropenem A thienamycin derivative antibacterial agent that is more stable to renal dehydropeptidase I than imipenem, but does not need to be given with an enzyme inhibitor such as cilastatin. It is used in the treatment of bacterial infections, including infections in immunocompromised patients. Carbapenems and Aztreonam | 1 g IV every 8 hours | |
| Aztreonam Aztreonam The carbapenems and aztreonam are both members of the bactericidal beta-lactam family of antibiotics (similar to penicillins). They work by preventing bacteria from producing their cell wall, ultimately leading to bacterial cell death. Carbapenems and Aztreonam | 2 g IV every 8 hours | |
| Fluoroquinolones Fluoroquinolones Fluoroquinolones are a group of broad-spectrum, bactericidal antibiotics inhibiting bacterial DNA replication. Fluoroquinolones cover gram-negative, anaerobic, and atypical organisms, as well as some gram-positive and multidrug-resistant (MDR) organisms. Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin Ciprofloxacin A broad-spectrum antimicrobial carboxyfluoroquinoline. Fluoroquinolones | 400 mg IV every 8 hours |
| Levofloxacin Levofloxacin The l-isomer of ofloxacin. Fluoroquinolones | 750 mg IV daily | |
| Aminoglycosides Aminoglycosides Aminoglycosides are a class of antibiotics including gentamicin, tobramycin, amikacin, neomycin, plazomicin, and streptomycin. The class binds the 30S ribosomal subunit to inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. Unlike other medications with a similar mechanism of action, aminoglycosides are bactericidal. Aminoglycosides | Amikacin | 15–20 mg/kg IV daily |
| Gentamicin Gentamicin Aminoglycosides | 5–7 mg/kg IV daily | |
| Tobramycin | 5–7 mg/kg IV daily | |
| Glycopeptides Glycopeptides The glycopeptide antibiotics (GPAs) vancomycin and teicoplanin are inhibitors of bacterial cell wall synthesis and considered the last resort treatment of severe infections due to gram-positive bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus spp., and Clostridiodes difficile. Glycopeptides | Vancomycin Vancomycin Antibacterial obtained from streptomyces orientalis. It is a glycopeptide related to ristocetin that inhibits bacterial cell wall assembly and is toxic to kidneys and the inner ear. Glycopeptides |
Starting options:
|
| Oxazolidinones Oxazolidinones The oxazolidinones (linezolid and tedizolid) are bacterial protein synthesis inhibitors. Their unique binding site on the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S ribosome gives them zero cross-resistance with other antibiotics. Oxazolidinones | Linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones | 600 mg IV every 12 hours |
Deescalation and duration:[1,3,8,18,19]
Consultations:[18]
Diagnosis Codes:
These codes are used to diagnose pneumonias acquired in a healthcare setting.
Ventilator-associated pneumonia
Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia
Multidrug-resistant Organisms and Nosocomial Infections (VAP) is a specific and serious subtype of
hospital-acquired pneumonia
Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
Pneumonia in Children (HAP).
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | J95.851 | Ventilator associated pneumonia Ventilator associated pneumonia Serious inflammation of the lung in patients who required the use of pulmonary ventilator. It is usually caused by bacterial cross infection in hospitals. Pneumonia |
| ICD-10-CM | J15.9 | Unspecified bacterial pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia |
Evaluation & Workup:
This code is for obtaining a
bronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage
Washing out of the lungs with saline or mucolytic agents for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. It is very useful in the diagnosis of diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in immunosuppressed patients.
Pulmonary Fibrosis (BAL) specimen during a
bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy
Endoscopic examination, therapy or surgery of the bronchi.
Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia, which is an invasive method to obtain a lower respiratory tract sample for culture to identify the causative pathogen in VAP.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CPT | 31624 | Bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy Endoscopic examination, therapy or surgery of the bronchi. Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia; with bronchoalveolar lavage Bronchoalveolar lavage Washing out of the lungs with saline or mucolytic agents for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. It is very useful in the diagnosis of diffuse pulmonary infiltrates in immunosuppressed patients. Pulmonary Fibrosis |
Medications:
This code is for a
broad-spectrum
Broad-Spectrum
Fluoroquinolones, anti-pseudomonal antibiotic combination like
piperacillin
Piperacillin
Semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, ampicillin derived ureidopenicillin antibiotic proposed for pseudomonas infections. It is also used in combination with other antibiotics.
Penicillins/
tazobactam
Tazobactam
A penicillanic acid and sulfone derivative and potent beta-lactamase inhibitor that enhances the activity of other anti-bacterial agents against beta-lactamase producing bacteria.
Cephalosporins, which is a common choice for empiric treatment of HAP/VAP, often combined with
vancomycin
Vancomycin
Antibacterial obtained from streptomyces orientalis. It is a glycopeptide related to ristocetin that inhibits bacterial cell wall assembly and is toxic to kidneys and the inner ear.
Glycopeptides to cover for
MRSA
MRSA
A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins.
Staphylococcus.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 1148971 | Piperacillin Piperacillin Semisynthetic, broad-spectrum, ampicillin derived ureidopenicillin antibiotic proposed for pseudomonas infections. It is also used in combination with other antibiotics. Penicillins / Tazobactam Tazobactam A penicillanic acid and sulfone derivative and potent beta-lactamase inhibitor that enhances the activity of other anti-bacterial agents against beta-lactamase producing bacteria. Cephalosporins (ingredient) |
| RxNorm | 11124 | Vancomycin Vancomycin Antibacterial obtained from streptomyces orientalis. It is a glycopeptide related to ristocetin that inhibits bacterial cell wall assembly and is toxic to kidneys and the inner ear. Glycopeptides (ingredient) |