Horner syndrome is a condition resulting from an interruption of the sympathetic innervation of the eyes. The syndrome is usually idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis but can be directly caused by head and neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess trauma, cerebrovascular disease, or a tumor Tumor Inflammation of the CNS. Horner syndrome is classified as 1st-order (central), 2nd-order (preganglionic), or 3rd-order (postganglionic) based on the location of the lesion along the sympathetic pathway. Partial ptosis Ptosis Cranial Nerve Palsies, miosis Miosis Pupil: Physiology and Abnormalities, and facial anhidrosis are the classical signs of Horner syndrome, making up a characteristic triad. Other associated neurologic signs may also be present depending on the location of the lesion and can aid in determining the cause. The syndrome is diagnosed by using cocaine Cocaine An alkaloid ester extracted from the leaves of plants including coca. It is a local anesthetic and vasoconstrictor and is clinically used for that purpose, particularly in the eye, ear, nose, and throat. It also has powerful central nervous system effects similar to the amphetamines and is a drug of abuse. Cocaine, like amphetamines, acts by multiple mechanisms on brain catecholaminergic neurons; the mechanism of its reinforcing effects is thought to involve inhibition of dopamine uptake. Local Anesthetics, apraclonidine Apraclonidine Glaucoma, or hydroxyamphetamine eye drops. Management of Horner syndrome requires treatment of the underlying condition.
Last updated: Jan 31, 2023
Horner syndrome, also known as oculosympathetic paresis Paresis A general term referring to a mild to moderate degree of muscular weakness, occasionally used as a synonym for paralysis (severe or complete loss of motor function). In the older literature, paresis often referred specifically to paretic neurosyphilis. ‘general paresis’ and ‘general paralysis’ may still carry that connotation. Bilateral lower extremity paresis is referred to as paraparesis. Spinal Disk Herniation, is a condition resulting from the interruption of the sympathetic innervation to the eyes. The syndrome is characterized by the classic triad of:
Horner syndrome can result from a lesion anywhere on the 3-neuron sympathetic pathway supplying the eye. The nerve supply starts from the posterolateral hypothalamus Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is a collection of various nuclei within the diencephalon in the center of the brain. The hypothalamus plays a vital role in endocrine regulation as the primary regulator of the pituitary gland, and it is the major point of integration between the central nervous and endocrine systems. Hypothalamus and ends as the long ciliary nerves that supply the iris dilator and Müller muscles (superior tarsal muscle).
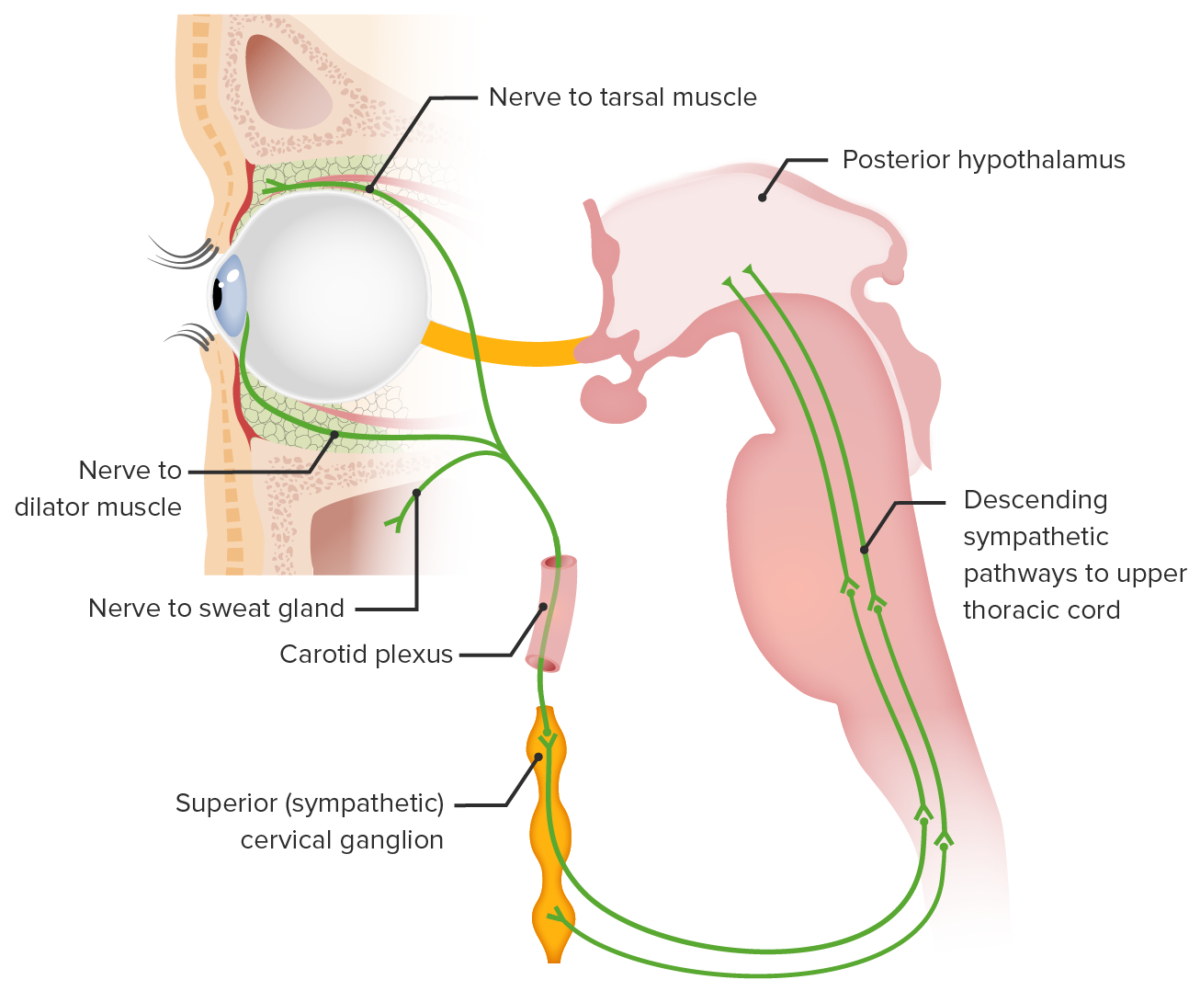
The neural circuitry involved in Horner syndrome:
1) Posterior hypothalamic sympathetic fibers synapse at the ciliospinal center of Budge (C8–T2).
2) Preganglionic fibers traverse the brachial plexus to synapse at the superior cervical ganglion.
3) Postganglionic fibers ascend in the carotid sheath to innervate the target structures.
Most cases of Horner syndrome are idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis. Of the identified causes, the etiology depends on the location of the lesion. The causes vary between adult and pediatric populations.
Horner syndrome is the result of the disruption of the sympathetic supply to the eye. The symptoms depend on the location of the lesion, and the severity depends on the severity of denervation.
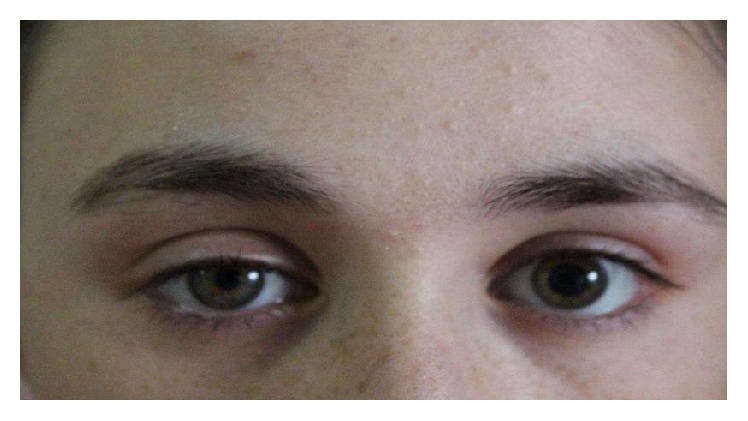
Right-sided miosis and ptosis suggestive of Horner syndrome
Image: “Myosis and eyelid ptosis were noted on the right side” by Case Reports in Endocrinology. License: CC BY 4.0