Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum (HL) is a malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax of B lymphocytes B lymphocytes Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions originating in the lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 - 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy. The pathognomonic histologic finding of HL is a Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg ( HRS HRS Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of hrs is hypovolemia, often as a result of forced diuresis or drainage of ascites. This leads to renal vasoconstriction resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Hepatorenal Syndrome) cell (giant multinucleated B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions with eosinophilic inclusions). The disease presents most commonly with lymphadenopathy Lymphadenopathy Lymphadenopathy is lymph node enlargement (> 1 cm) and is benign and self-limited in most patients. Etiologies include malignancy, infection, and autoimmune disorders, as well as iatrogenic causes such as the use of certain medications. Generalized lymphadenopathy often indicates underlying systemic disease. Lymphadenopathy ( neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess most commonly involved), night sweats Night sweats Tuberculosis, weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery, fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, and at times, splenomegaly Splenomegaly Splenomegaly is pathologic enlargement of the spleen that is attributable to numerous causes, including infections, hemoglobinopathies, infiltrative processes, and outflow obstruction of the portal vein. Splenomegaly and hepatomegaly. Diagnostic testing includes lymph Lymph The interstitial fluid that is in the lymphatic system. Secondary Lymphatic Organs node histologic analysis showing HRS HRS Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of hrs is hypovolemia, often as a result of forced diuresis or drainage of ascites. This leads to renal vasoconstriction resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Hepatorenal Syndrome cells, blood tests, and CT and PET PET An imaging technique that combines a positron-emission tomography (PET) scanner and a ct X ray scanner. This establishes a precise anatomic localization in the same session. Nuclear Imaging scanning. HL is managed with chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma and radiotherapy. The prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas has improved significantly with the advent of chemotherapeutic regimens.
Last updated: Jun 30, 2025
Hodgkin lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum (HL) is a monoclonal B-cell lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum (neoplasm) originating in lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 – 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy in which the malignant Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg ( HRS HRS Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of hrs is hypovolemia, often as a result of forced diuresis or drainage of ascites. This leads to renal vasoconstriction resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Hepatorenal Syndrome) cells are mixed with a heterogeneous population of nonneoplastic inflammatory cells.
Based on WHO classification, HLs have the following types and subtypes according to immunophenotype and morphology.
Classic HL (95%):
Nodular lymphocyte–predominant HL (NLPHL):
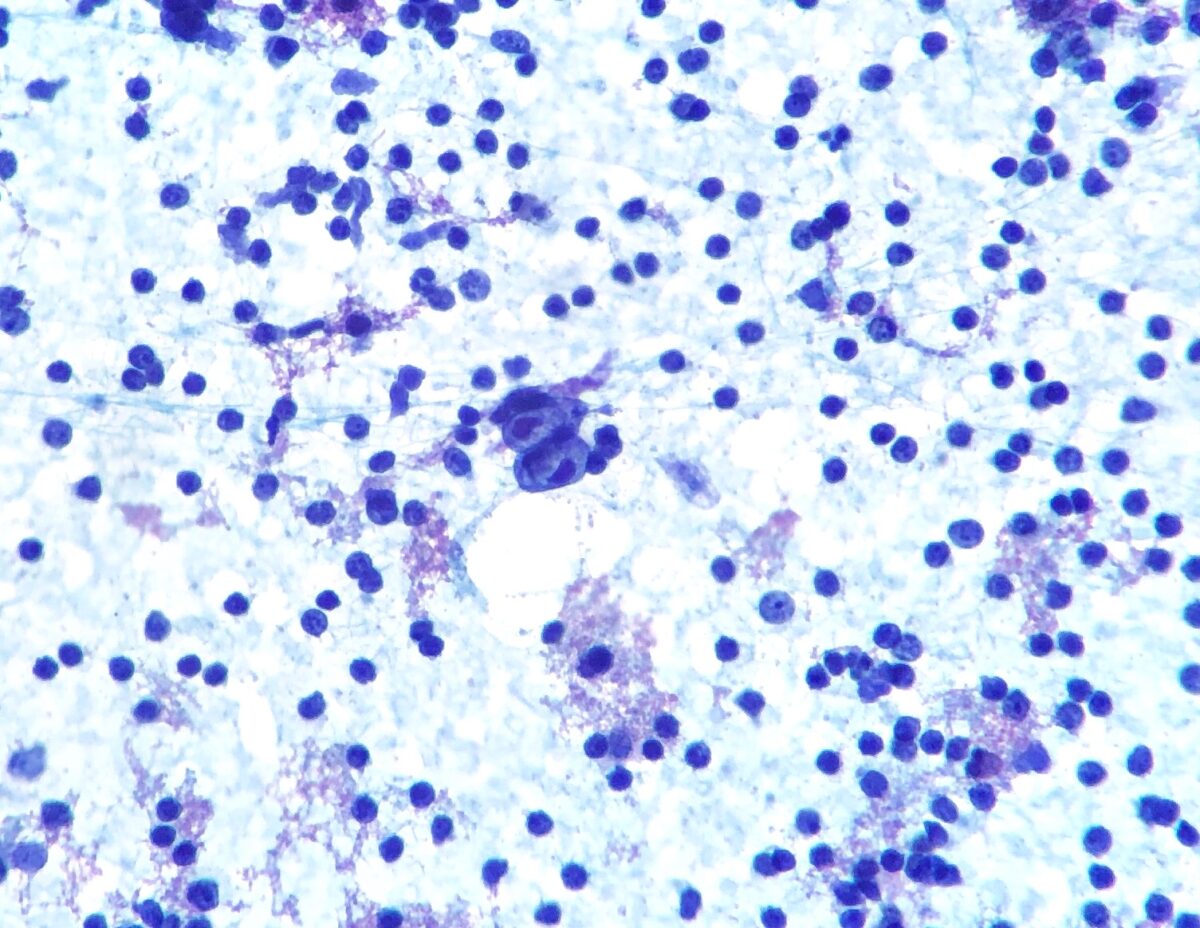
Hodgkin lymphoma:
Fine-needle aspiration of a lymph node showing Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cell (bilobed cell in the center)
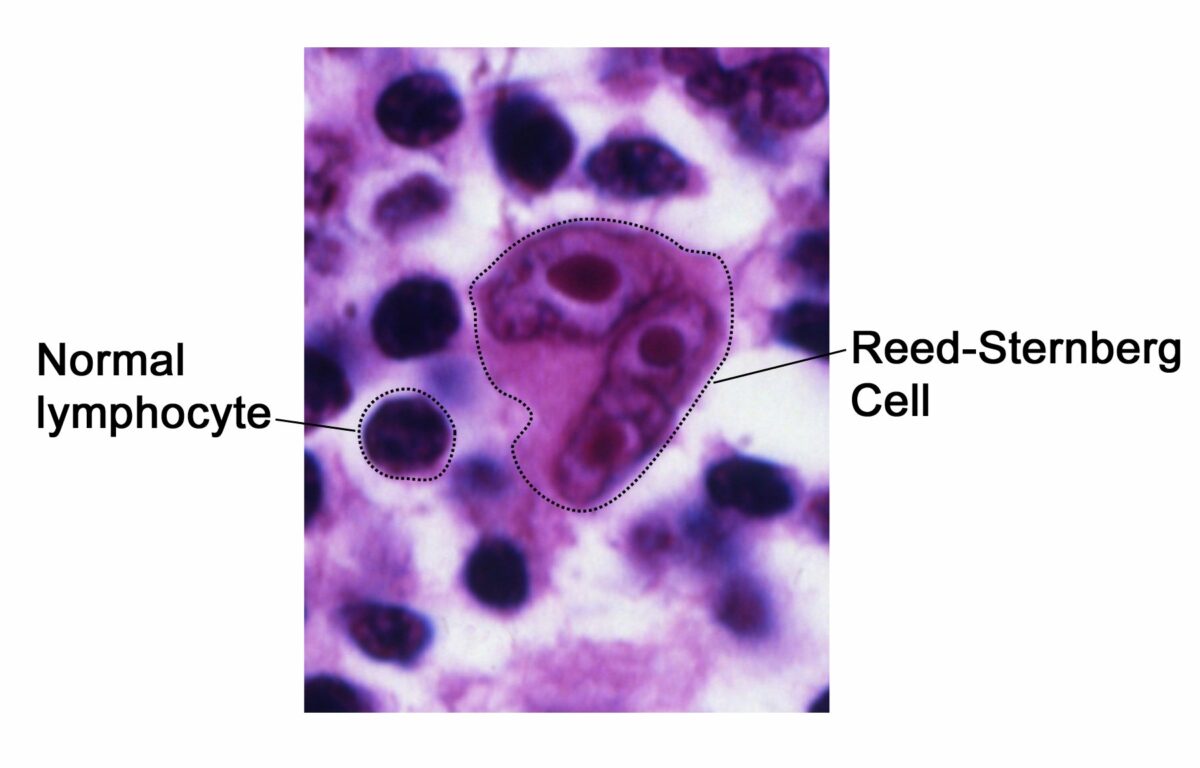
Pathognomonic histologic finding for Hodgkin lymphoma:
The Reed-Sternberg cell “owl-eyes”
Time course:
Most common presentations:
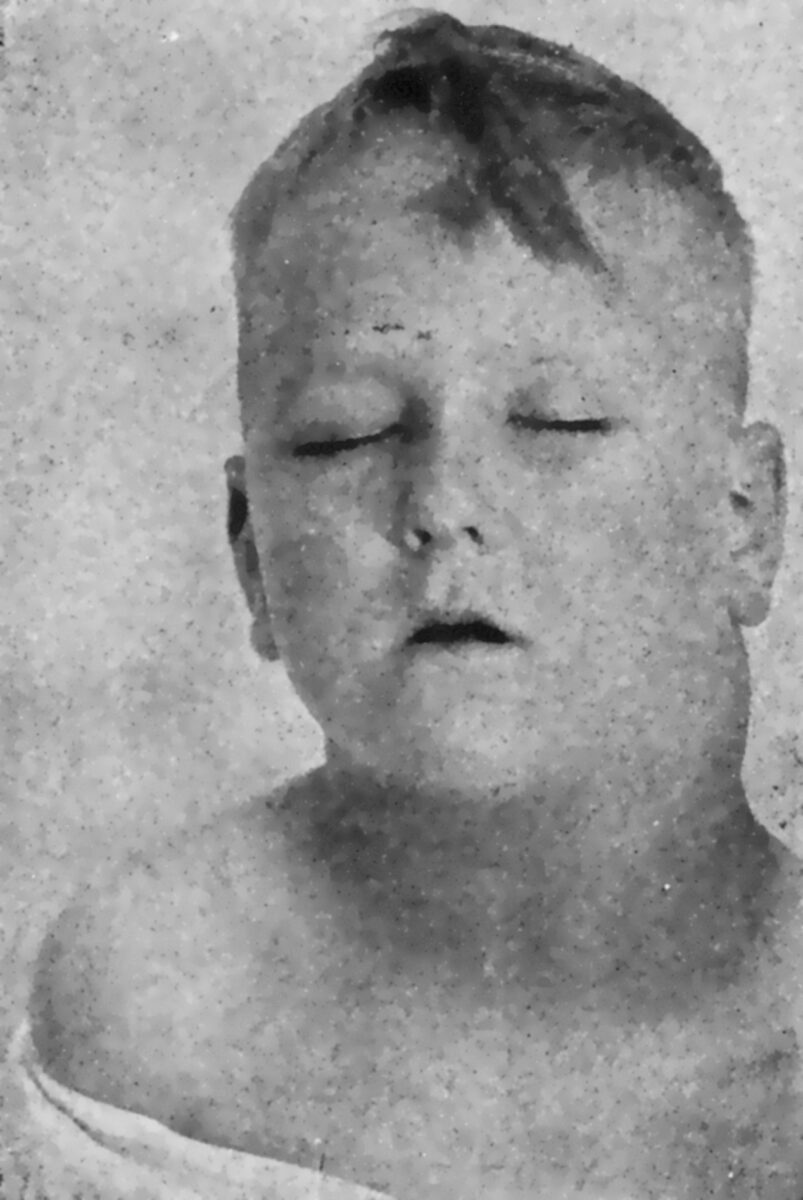
Hodgkin lymphoma:
Prominent cervical lymphadenopathy
“B” symptoms (constitutional) present in 40% of cases:
Other symptoms:
Laboratory studies:
Imaging:
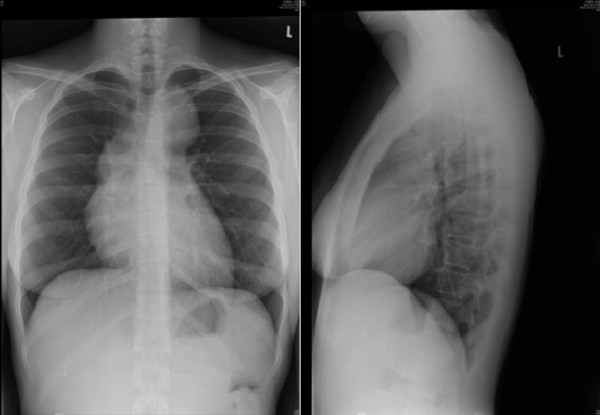
Hodgkin lymphoma. CXR showing mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
Image: “Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting with markedly elevated IgE: a case report” by Ellis AK, Waserman S. License: CC BY 2.0Biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma:
Staging Staging Methods which attempt to express in replicable terms the extent of the neoplasm in the patient. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis is based on the Ann Arbor classification.
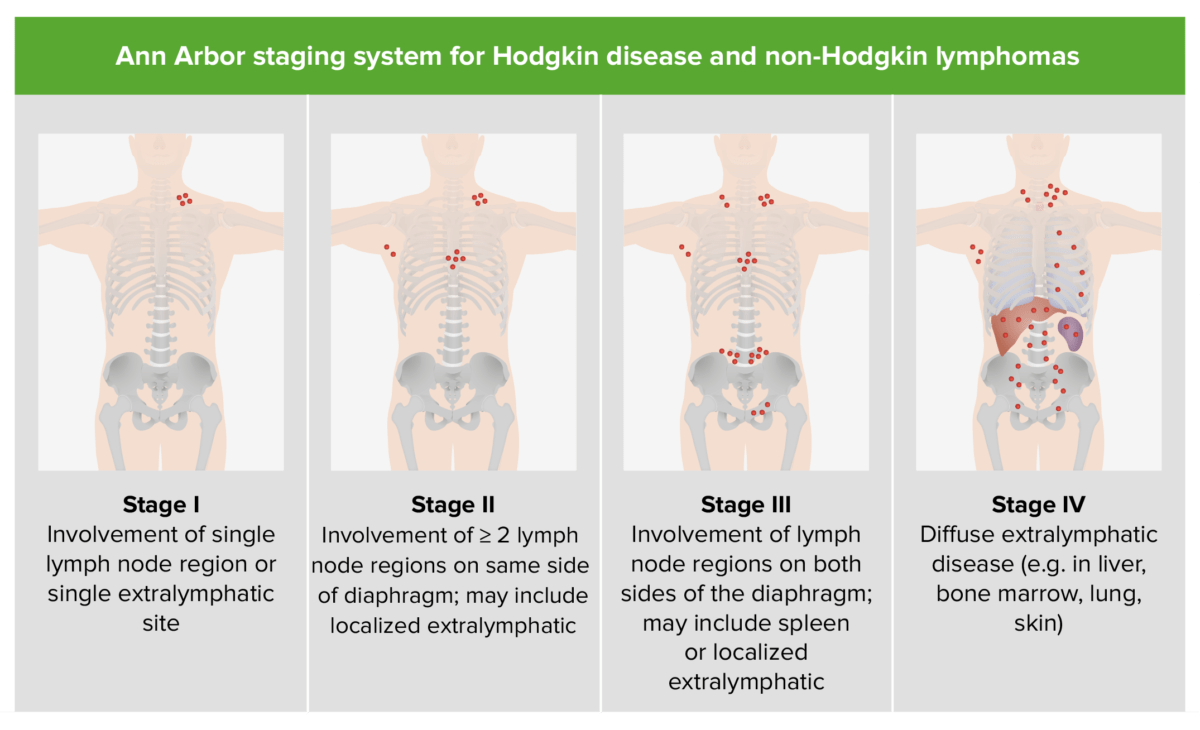
Staging of Hodgkin disease and NHL
Image by Lecturio.