A hip fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures is a disruption in the cortex of the femur at the hip joint Hip joint The hip joint is a ball-and-socket joint formed by the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis. The hip joint is the most stable joint in the body and is supported by a very strong capsule and several ligaments, allowing the joint to sustain forces that can be multiple times the total body weight. Hip Joint: Anatomy, either between the trochanters (intertrochanteric) or at the femoral neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess. Hip fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures is a serious injury and can result in life-threatening complications. The causes include high-energy impact due to trauma such as in motor vehicle accidents Motor Vehicle Accidents Spinal Cord Injuries, or low-energy trauma Low-Energy Trauma Toddler’s Fractures (falls) in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis. The clinical presentation includes groin Groin The external junctural region between the lower part of the abdomen and the thigh. Male Genitourinary Examination pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, tenderness on palpation Palpation Application of fingers with light pressure to the surface of the body to determine consistency of parts beneath in physical diagnosis; includes palpation for determining the outlines of organs. Dermatologic Examination, immobility, and deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs of the lower limbs. Diagnosis is made clinically and by imaging studies. Definitive management is usually surgical, but depends on the type of fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures and status of the patient.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A hip fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures is a disruption in the cortex of the femur at the femoroacetabular (hip) joint, either between the greater and lesser trochanters (intertrochanteric) or at the femoral neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess.
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint made up of the femoral head and acetabulum (socket). Blood supply to the femoral head is from the circumflex artery.
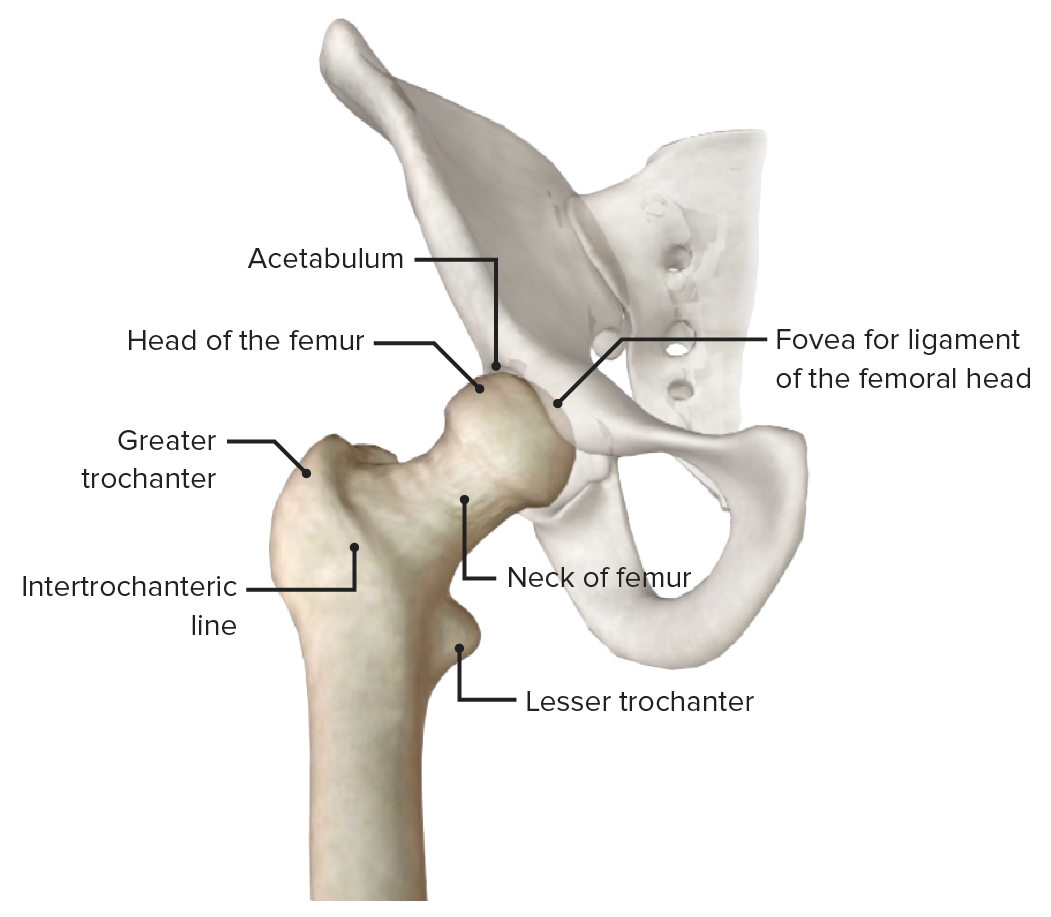
Anterior view of the hip joint (pelvis faded), featuring the bony landmarks of the proximal end of the femur
Image by BioDigital, edited by Lecturio
Anterior and posterior views of the hip joint featuring the extra-articular ligaments
Image by Lecturio.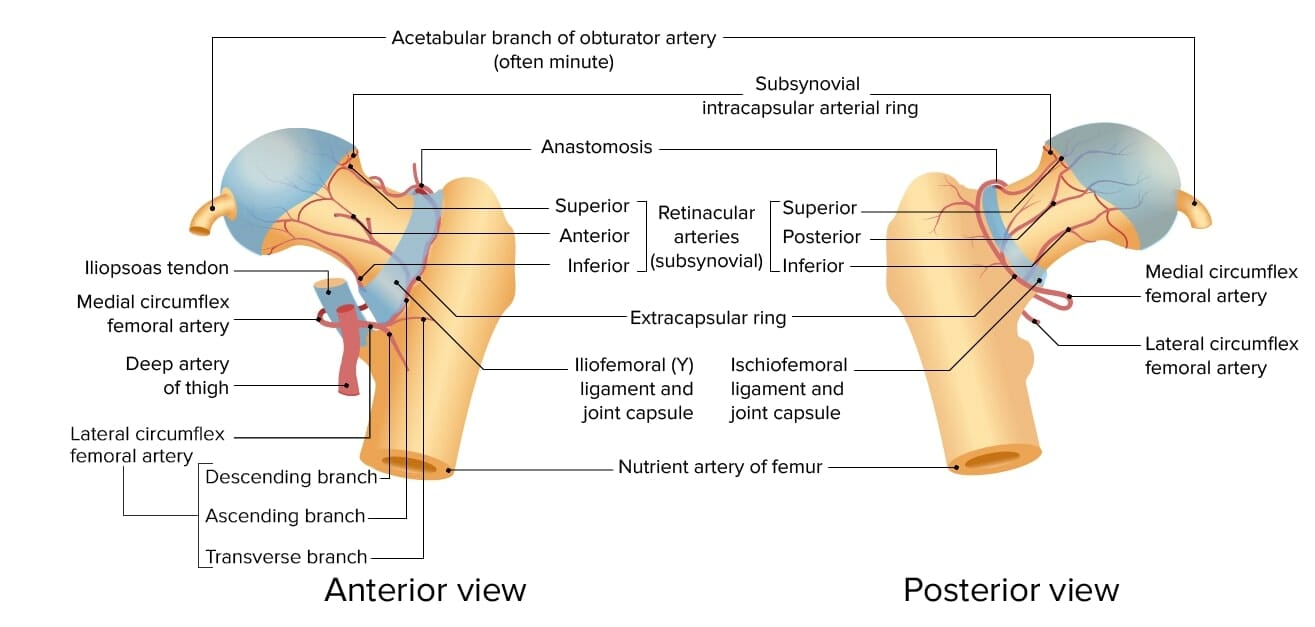
Blood supply of the femoral head and neck
Image by Lecturio.Hip fractures are classified by anatomic location and fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures type. Recognizing these fractures is important for surgical management.
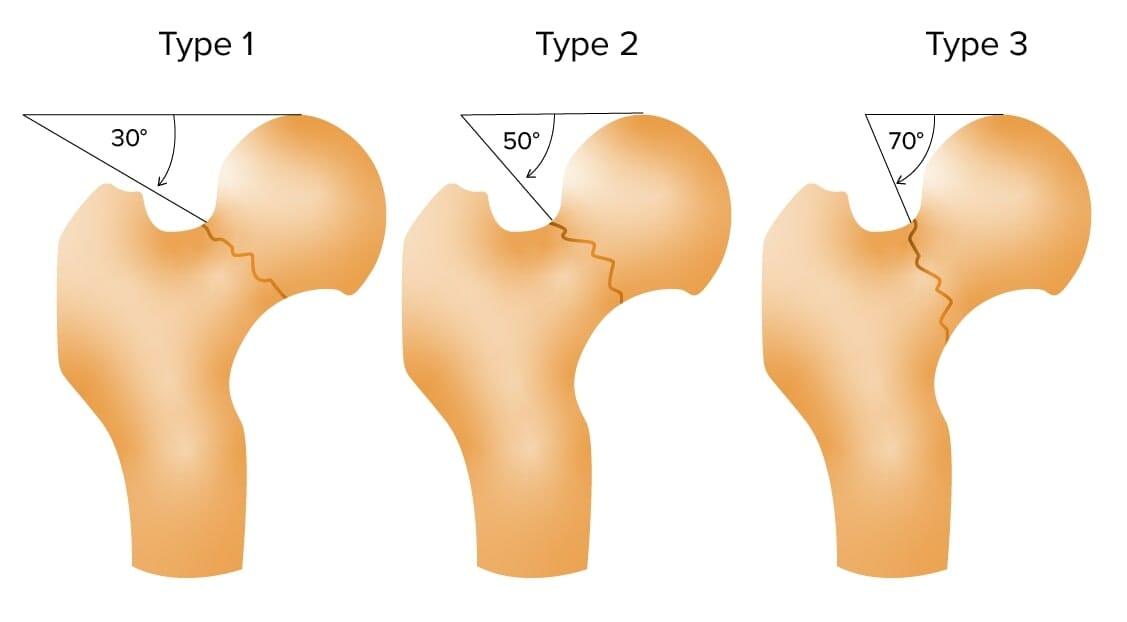
Pauwel classification of femoral neck fractures
Image by Lecturio.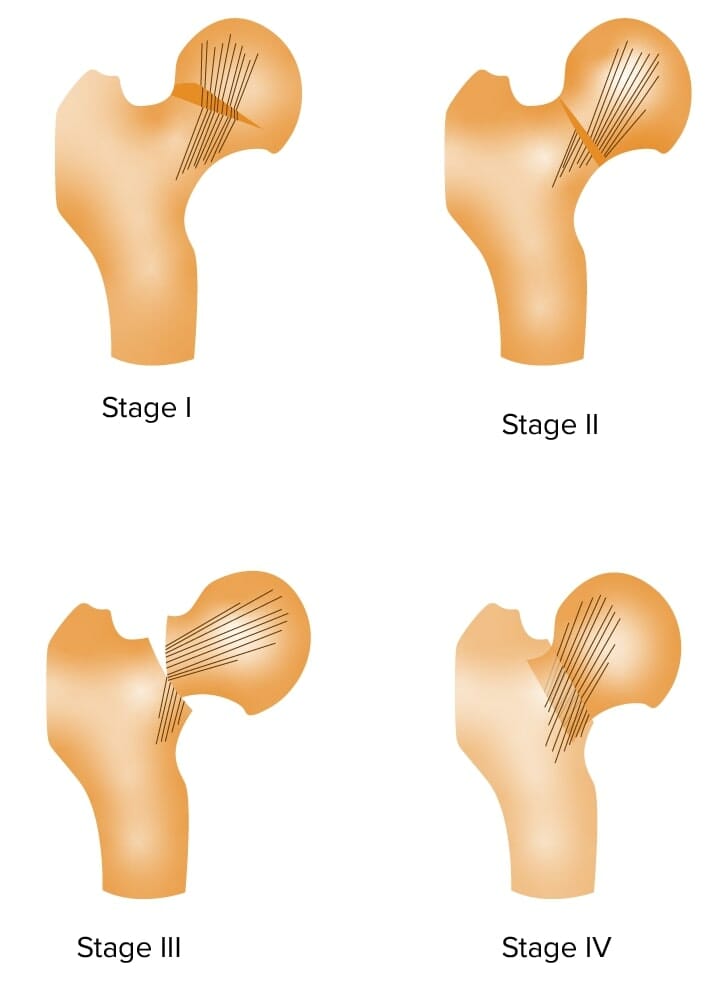
Garden classification of femoral neck fractures
Image by Lecturio.The general principle behind all fractures is that the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types is subjected to a load that overwhelms its bearing capacity, resulting in a loss of structural integrity.
The presentation of a patient with a hip fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures depends on the clinical situation.
The diagnosis of a hip fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures is made clinically and with diagnostic imaging. A hip fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures may be complicated by a dislocation depending on the degree of adduction Adduction Examination of the Upper Limbs at the time of impact, especially in motor vehicle accidents Motor Vehicle Accidents Spinal Cord Injuries.
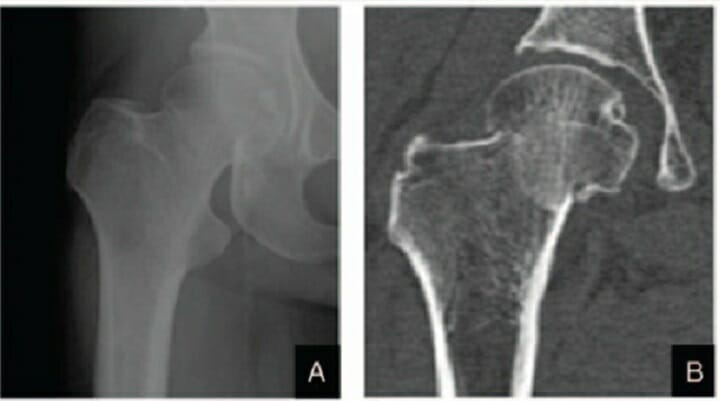
Garden stage I right femoral neck fracture:
A: Anteroposterior radiograph
B: Coronal CT scan
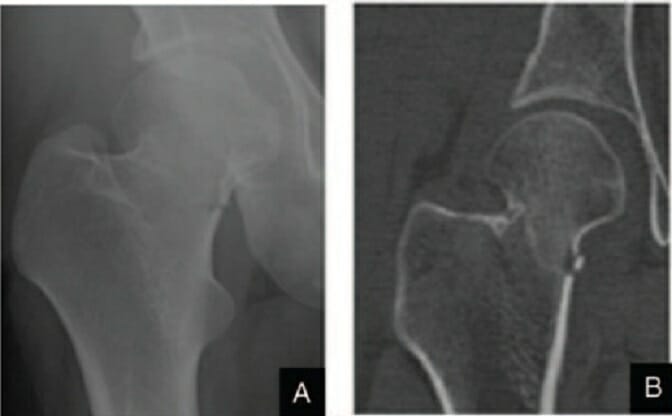
Garden stage II right femoral neck fracture:
A: Anteroposterior radiograph
B: Coronal CT scan
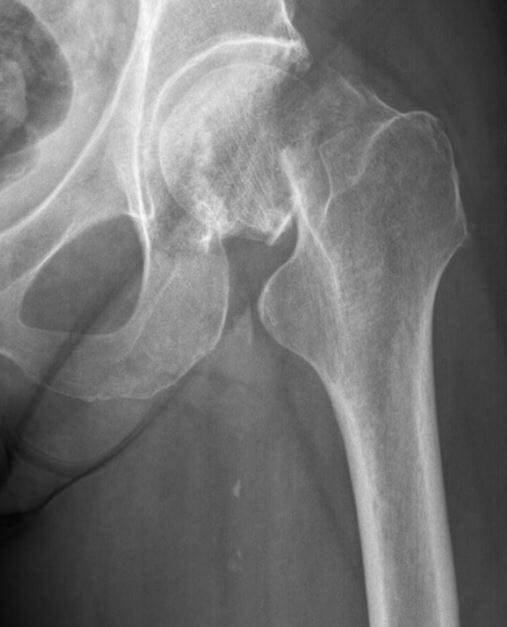
Garden stage III right femoral neck fracture
Image: “Femoral Neck fracture” by Jillian Kazley. License: CC BY 4.0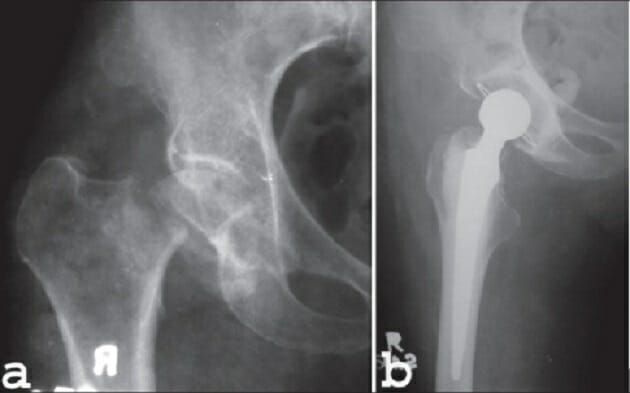
a: Anteroposterior radiograph of 60-year-old woman with Garden stage IV
b: Immediate postoperative anteroposterior radiograph of the same individual after total hip arthroplasty
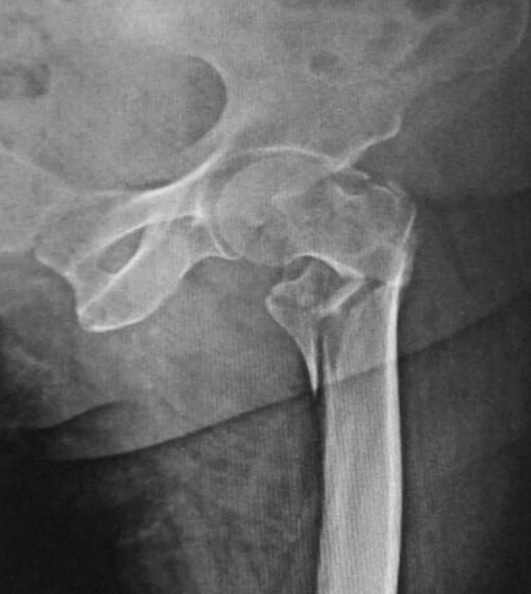
X-ray of a comminuted trochanteric hip fracture
Image: “X-ray of a comminuted hip fracture” by Rohan R. Memon, Drashtant Patel and Nishant Juva. License: CC BY 4.0Definitive management depends on the type of fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures and requires consultation with an orthopedic surgeon.
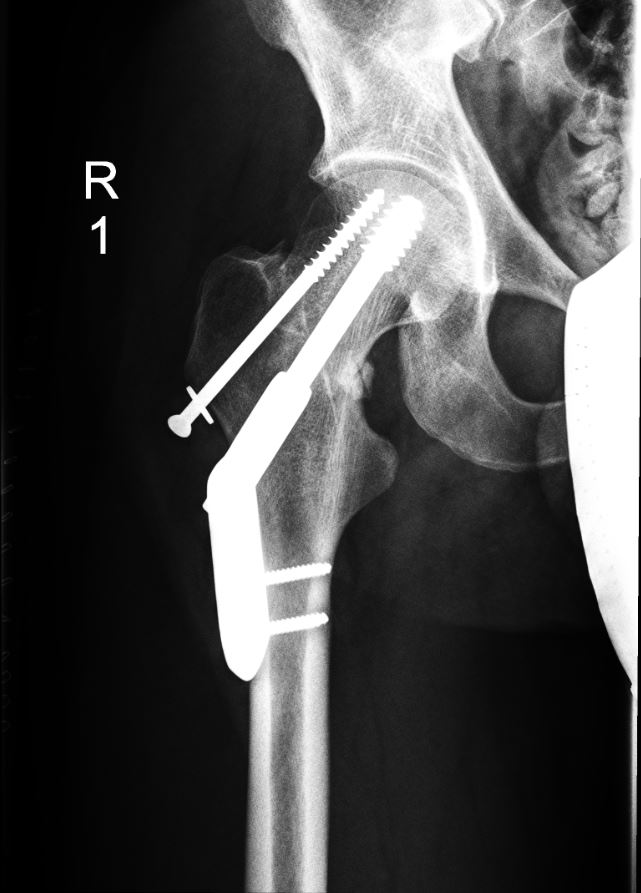
Unspecified displaced fracture of the right femur with surgical repair
Image: “Hip fractures with DHS 1” by Prof. Dr. med. Ralf Puls. License: CC BY 3.0