Herbicides are chemical substances used to kill or control the growth of unwanted plants Plants Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic. Important herbicides that can affect humans include paraquat, Agent Orange, glyphosate, and organophosphates. Different types of herbicides result in different clinical manifestations and have various toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation levels. Paraquat ingestion is associated with multiorgan damage within a few hours and is fatal in large amounts. In contrast, glyphosate typically has low toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation, but if a significant volume is ingested, serious adverse effects occur. Organophosphates, which are broadly used as pesticides, produce a cholinergic toxidrome Toxidrome A toxidrome describes a group of signs, symptoms, and/or characteristic effects associated with exposure to a particular substance or class of substances. General Principles of Toxidromes. Agent Orange, containing 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin, a human carcinogen, carries both short-term (e.g., chloracne, liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation) and long-term (e.g., cancers) complications. Exposure can be dermal or via inhalation or ingestion. In general, early detection is important to prevent serious sequelae. Initial management consists of stabilizing the patient and decontamination. An antidote Antidote An antidote is a substance that counteracts poisoning or toxicity. Substances that can cause poisoning include heavy metals (from occupation, treatments, or diet), alcohols, environmental toxins, and medications. Antidotes of Common Poisonings is given, if available. Treatment of herbicide poisoning revolves around supportive care that depends on the involved organ system.
Last updated: Apr 14, 2025
Herbicides are substances that are used to kill or control the growth of unwanted plants Plants Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic.
Paraquat:
Rules in the United States:
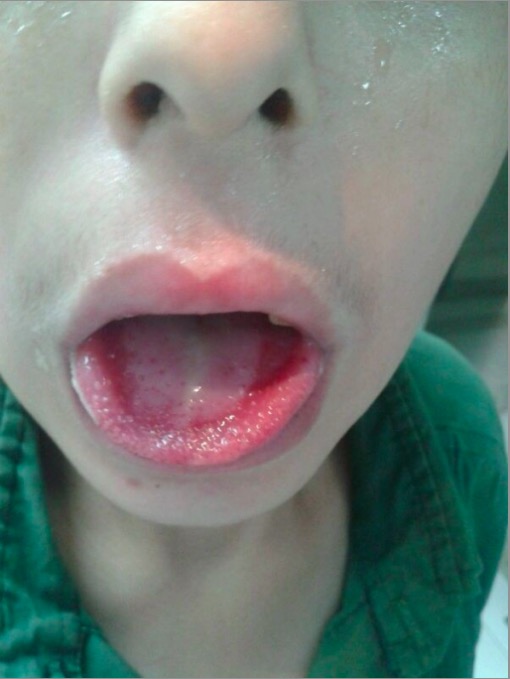
Paraquat intoxication:
Exudative ulcerated tongue and edematous lip in a patient with intentional paraquat ingestion
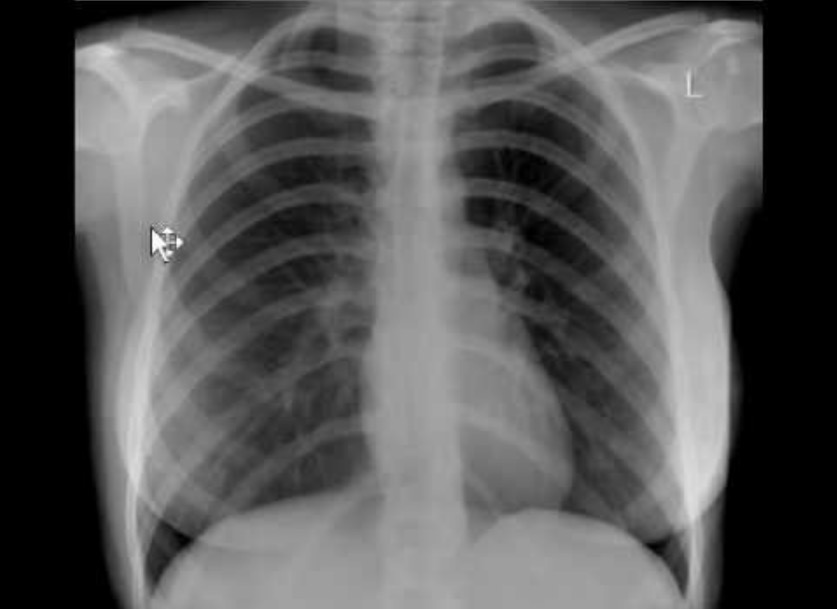
Paraquat intoxication:
Posteroanterior (PA) chest X-ray showing mild bilateral patchy consolidation, especially in hilum
Agent Orange:
Acute:
Chronic:
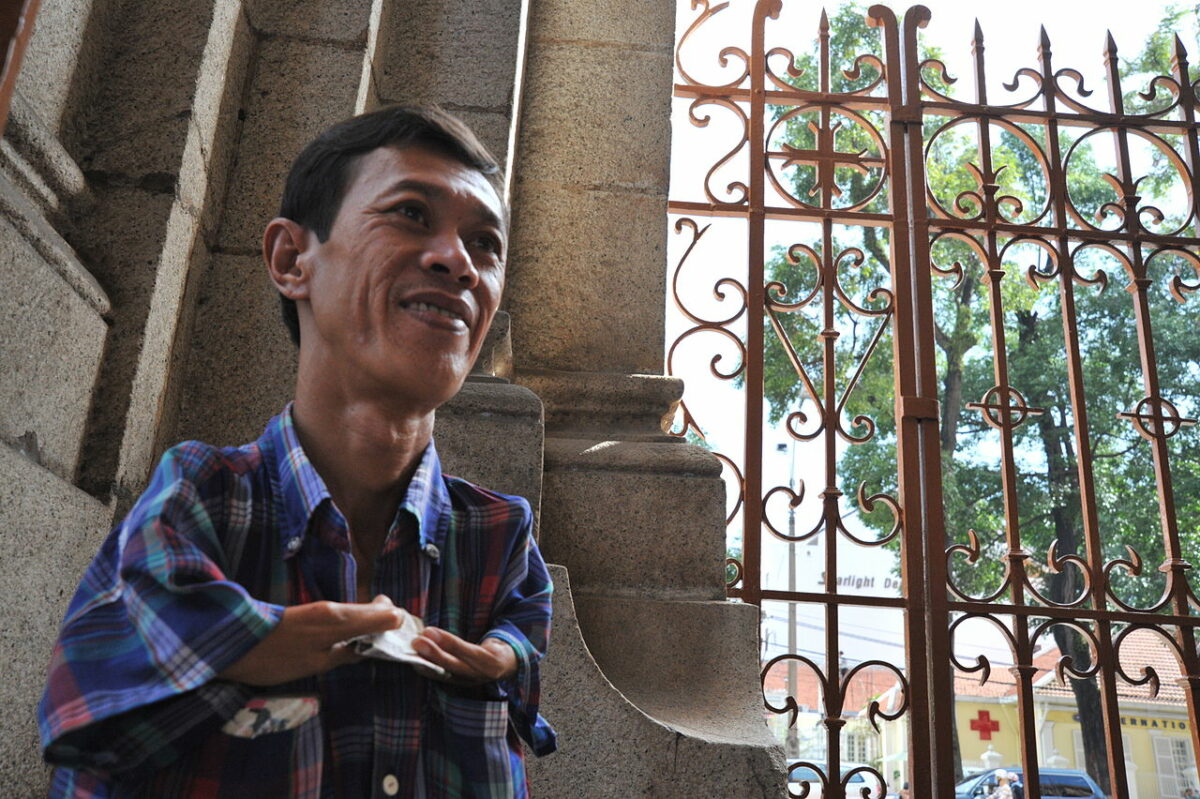

A person with birth deformities associated with prenatal exposure to Agent Orange
Image: “A person with birth deformities associated with prenatal exposure to Agent Orange” by Emilio Labrador. License: CC BY 2.0
Chloracne in a herbicide production worker:
Almost every follicular orifice on the face and neck is affected with comedones, papules, and cyst-like lesions.
Glyphosate:
Mild to moderate toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation:
Severe toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation:
Organophosphates:
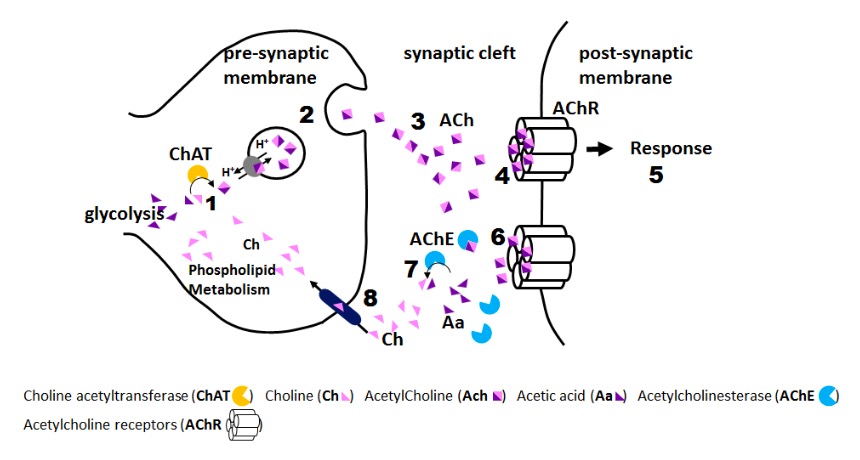
Pesticide/herbicide effect (organophosphate):
1: Pesticide accumulation in synaptic cleft
2: Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by pesticide
3: Constant activation of acetylcholine receptors
SLUDGE BBB BBB Specialized non-fenestrated tightly-joined endothelial cells with tight junctions that form a transport barrier for certain substances between the cerebral capillaries and the brain tissue. Nervous System: Histology (muscarinic effects):
DUMBELS (muscarinic effects):