Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a potentially reversible cause of acute kidney injury that develops secondary to liver disease. The main cause of HRS is splanchnic vasodilation with resultant decreased arterial volume and subsequent renal vasoconstriction, resulting in hypoperfusion of the kidneys. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship typically present with edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation or anuria Anuria Absence of urine formation. It is usually associated with complete bilateral ureteral (ureter) obstruction, complete lower urinary tract obstruction, or unilateral ureteral obstruction when a solitary kidney is present. Acute Kidney Injury, and ascites Ascites Ascites is the pathologic accumulation of fluid within the peritoneal cavity that occurs due to an osmotic and/or hydrostatic pressure imbalance secondary to portal hypertension (cirrhosis, heart failure) or non-portal hypertension (hypoalbuminemia, malignancy, infection). Ascites in the setting of acute or chronic liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy injury. Hepatorenal syndrome is considered a diagnosis of exclusion. Treatment is with agents that cause systemic vasoconstriction Vasoconstriction The physiological narrowing of blood vessels by contraction of the vascular smooth muscle. Vascular Resistance, Flow, and Mean Arterial Pressure and, therefore, improve renal perfusion. This includes octreotide Octreotide A potent, long-acting synthetic somatostatin octapeptide analog that inhibits secretion of growth hormone and is used to treat hormone-secreting tumors; diabetes mellitus; hypotension, orthostatic; hyperinsulinism; hypergastrinemia; and small bowel fistula. Antidiarrheal Drugs and midodrine Midodrine An ethanolamine derivative that is an adrenergic alpha-1 agonist. It is used as a vasoconstrictor agent in the treatment of hypotension. Sympathomimetic Drugs. Most cases of hepatorenal syndrome have a poor prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Hepatorenal syndrome is associated with portal hypertension Portal hypertension Portal hypertension is increased pressure in the portal venous system. This increased pressure can lead to splanchnic vasodilation, collateral blood flow through portosystemic anastomoses, and increased hydrostatic pressure. There are a number of etiologies, including cirrhosis, right-sided congestive heart failure, schistosomiasis, portal vein thrombosis, hepatitis, and Budd-Chiari syndrome. Portal Hypertension due to:
The classification system of hepatorenal syndrome was recently updated:
Trigger Trigger The type of signal that initiates the inspiratory phase by the ventilator Invasive Mechanical Ventilation factors are any interventions or conditions that cause arterial hypovolemia Hypovolemia Sepsis in Children:
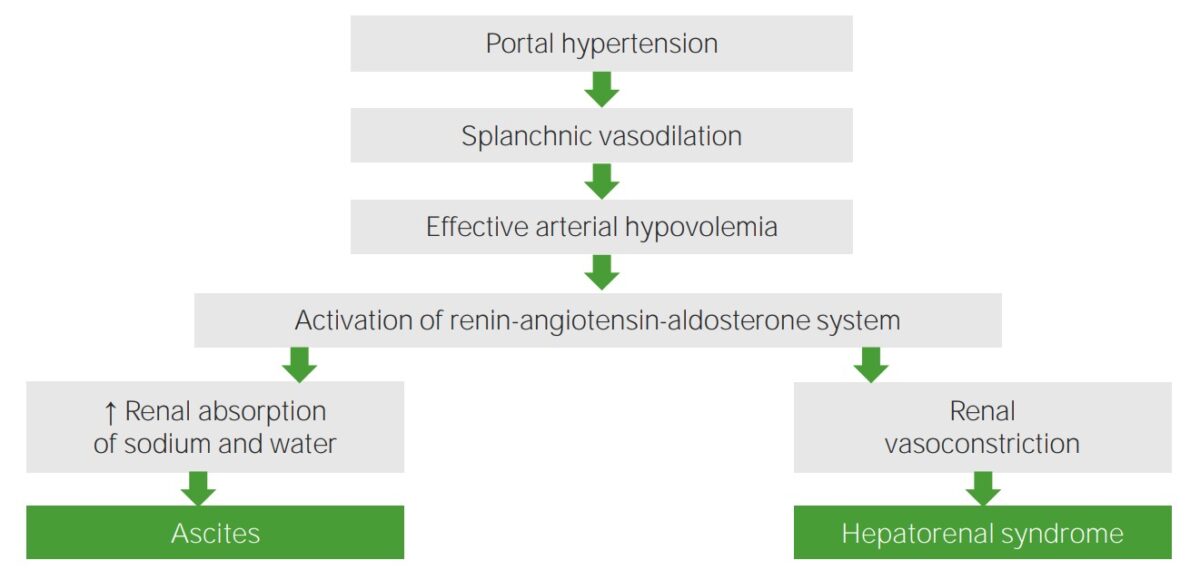
Pathophysiology of hepatorenal syndrome
Image by Lecturio.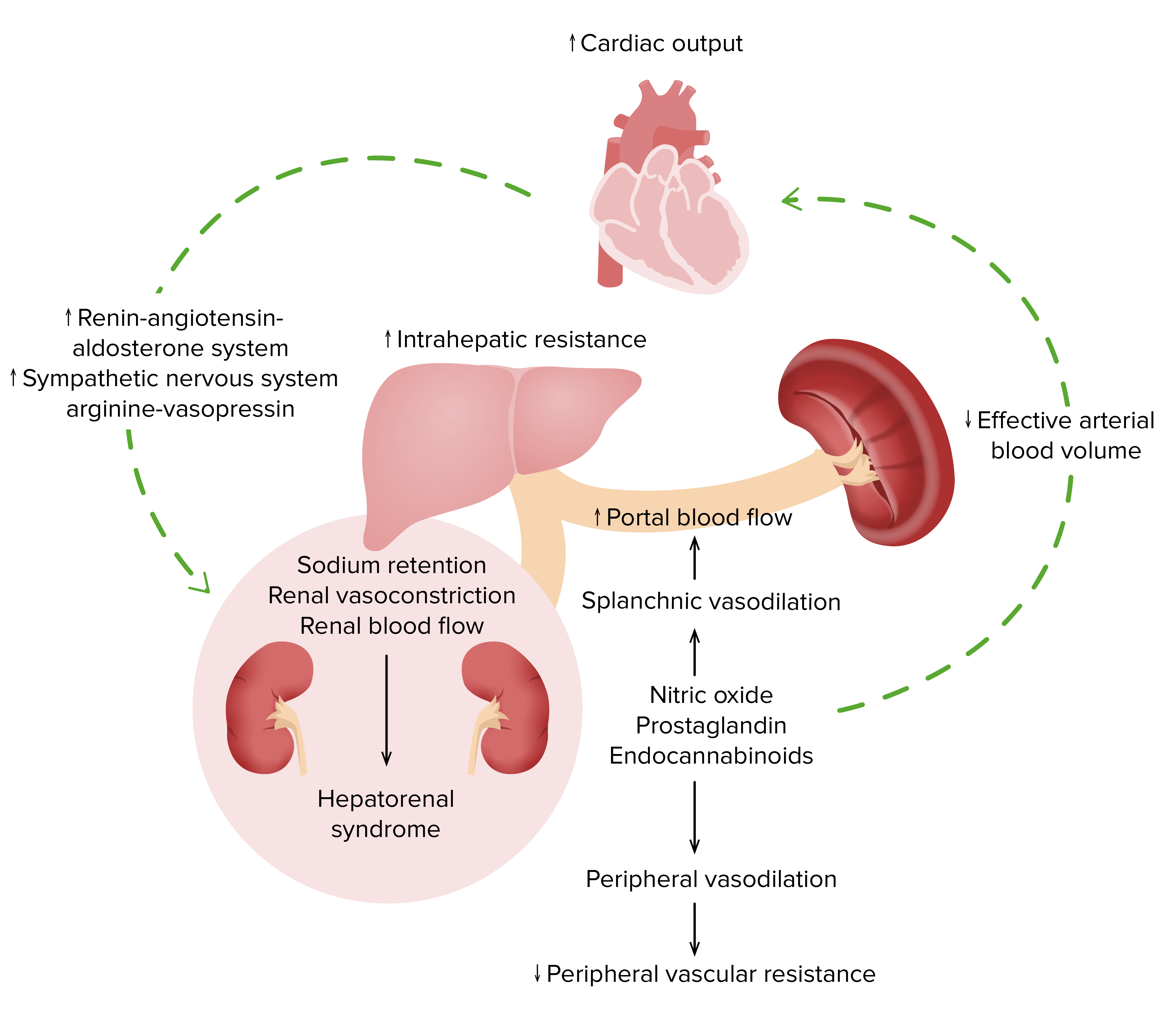
Pathophysiology of hepatorenal syndrome
Image by Lecturio.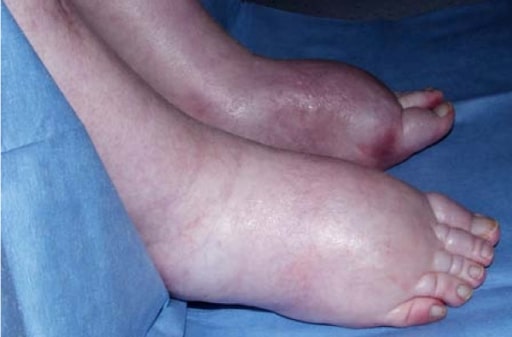
Lower extremity edema due to fluid retention in a patient with hepatorenal syndrome
Image: “Itraconazole associated quadriparesis and edema” by National Aspergillosis Centre, Education and Research Centre, University Hospital of South Manchester (Wythenshawe Hospital), Southmoor Road, Manchester M23 9LT, UK. License: CC BY 2.0The goal of therapy is improvement in liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy function.
Pre-renal disease: presents with similar laboratory findings (↑ serum creatinine and ↑BUN:Cr ratio) and similar urine findings (low sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia excretion in urine). Hepatorenal syndrome can be differentiated from pre-renal disease through an IV fluid challenge. Giving fluids improves pre-renal failure but not HRS.