Hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease are vascular neoplasms Neoplasms New abnormal growth of tissue. Malignant neoplasms show a greater degree of anaplasia and have the properties of invasion and metastasis, compared to benign neoplasms. Benign Bone Tumors of the CNS. Hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease are rare and are often associated with von Hippel-Lindau disease von Hippel-Lindau disease Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominant genetic condition resulting from a deletion or mutation in the VHL gene. Individuals diagnosed with VHL disease have tumors and cysts in various parts of their bodies and may present with hemangioblastomas, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), pheochromocytoma, endolymphatic sac tumors of the middle ear, pancreatic tumors, and papillary cystadenomas of the epididymis or the broad ligament. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease (VHL). The most common presentation is a headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess and, depending on the size and location of the tumor Tumor Inflammation, patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may present with sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology deficits and motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology weakness. Imaging is the main diagnostic method, with histopathologic evaluation required for definitive diagnosis. Surgery is often indicated in the management of hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease, though depending on the size, number, and location of the tumors, radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy may also be warranted. Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is usually good in solitary hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease, but tumors associated with VHL are often associated with a worse prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas and a higher risk of recurrence.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease are rare, slow-growing, benign Benign Fibroadenoma, highly vascular neoplasms Neoplasms New abnormal growth of tissue. Malignant neoplasms show a greater degree of anaplasia and have the properties of invasion and metastasis, compared to benign neoplasms. Benign Bone Tumors of the CNS that have a high association with von Hippel-Lindau disease von Hippel-Lindau disease Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease is an autosomal dominant genetic condition resulting from a deletion or mutation in the VHL gene. Individuals diagnosed with VHL disease have tumors and cysts in various parts of their bodies and may present with hemangioblastomas, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), pheochromocytoma, endolymphatic sac tumors of the middle ear, pancreatic tumors, and papillary cystadenomas of the epididymis or the broad ligament. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease (VHL), which is an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance condition characterized by a variety of benign Benign Fibroadenoma and malignant tumors.
| Categories | Specific tumors |
|---|---|
| Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS |
|
| Meningeal tumors |
|
| Sellar region tumors |
|
| Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum | Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum |
| Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification (5x more common than primary brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification tumors) | Most commonly arising from: |
| Peripheral tumors |
|
Hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease grow attached to the pia mater Pia mater The innermost layer of the three meninges covering the brain and spinal cord. It is the fine vascular membrane that lies under the arachnoid and the dura mater. Meninges: Anatomy (innermost meningeal layer)
Although the sporadic Sporadic Selective IgA Deficiency hemangiomas do not have a clear pathogenesis, the VHL-associated hemangiomas are thought to be caused by a mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the VHL gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics. Up to 50% of sporadic Sporadic Selective IgA Deficiency hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease have mutations or deletions in the VHL gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics as well.
Symptom development is caused by:
Symptoms depend on the location and progression of the tumor Tumor Inflammation. The most common symptoms observed are:
| Sporadic Sporadic Selective IgA Deficiency hemangioblastoma | VHL-associated hemangioblastoma |
|---|---|
| Presents as solitary tumor Tumor Inflammation | Multiple tumors along the neuraxis |
| Usually occurs in the 3rd or 4th decade of life | Diagnosed at a younger age (2nd decade) |
| Commonly presents as an isolated tumor Tumor Inflammation in the cerebellum Cerebellum The cerebellum, Latin for “little brain,” is located in the posterior cranial fossa, dorsal to the pons and midbrain, and its principal role is in the coordination of movements. The cerebellum consists of 3 lobes on either side of its 2 hemispheres and is connected in the middle by the vermis. Cerebellum: Anatomy | 50% of the tumors are located at the spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy, 40% at the cerebellum Cerebellum The cerebellum, Latin for “little brain,” is located in the posterior cranial fossa, dorsal to the pons and midbrain, and its principal role is in the coordination of movements. The cerebellum consists of 3 lobes on either side of its 2 hemispheres and is connected in the middle by the vermis. Cerebellum: Anatomy, and 10% at the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification stem. |
Complications usually occur because of an increase in the size of the tumor Tumor Inflammation (> 1.5 cm), causing compression Compression Blunt Chest Trauma, or because of spontaneous hemorrhage:
While the primary diagnostic tool is imaging, the gold standard of diagnosis requires histopathology from a biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma specimen.
The entire neural axis should be imaged to rule out multiple lesions, which are common in cases of VHL.
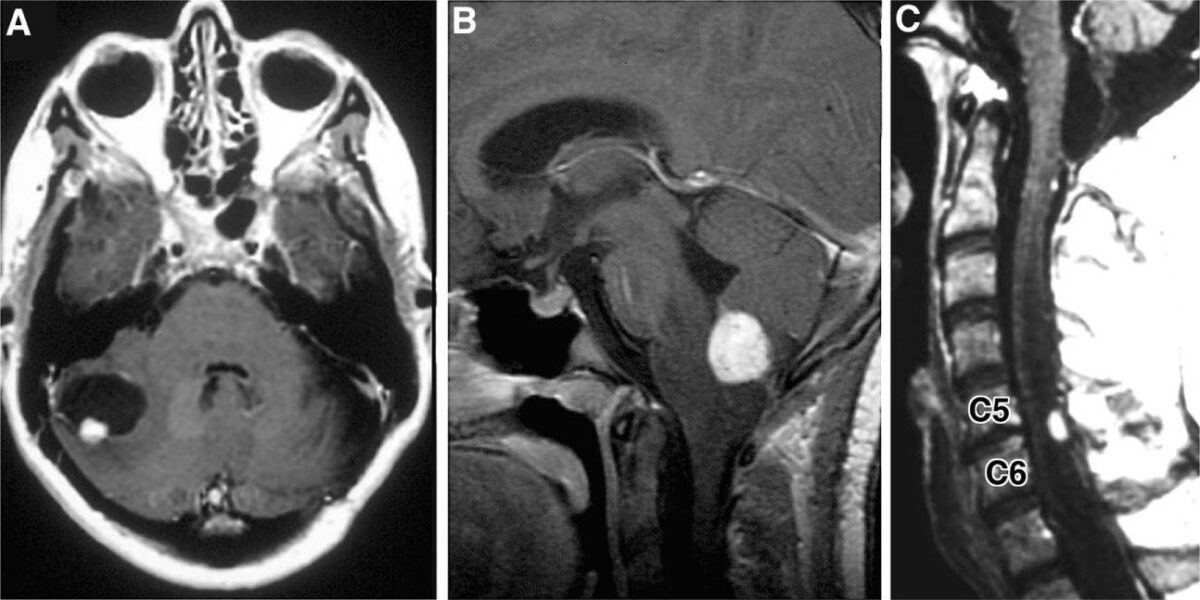
Radiographic images of hemangioblastomas:
A: Axial, contrast-enhanced, T1-weighted MRI showing cerebellar hemangioblastoma with contrast-enhancing mural nodule and peritumoral cyst
B: Sagittal, contrast-enhanced, T1-weighted MRI revealing contrast-enhancing medullary hemangioblastoma with surrounding vasogenic edema
C: Sagittal, contrast-enhanced, T1-weighted MRI with contrast-enhancing posterior/dorsal hemangioblastoma with associated syrinx
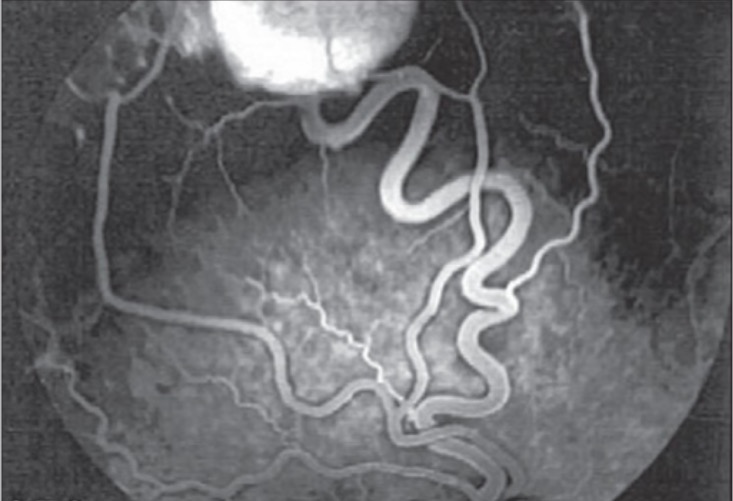
Fluorescein angiogram of right eye showing a temporal superior retinal hemangioblastoma with the feeder artery and draining vein
Image: “Fluorescein angiogram of right eye” by Vitreoretinal Division, Department of Ophthalmology, Al-Hussein Hospital, King Hussein Medical Center, Amman, Jordan. License: CC BY 2.0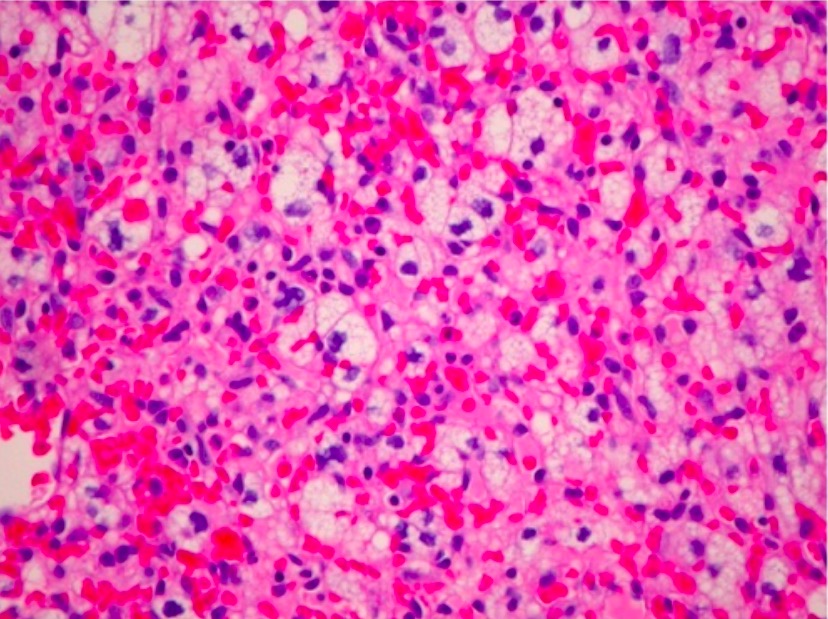
H&E photomicrograph of a hemangioblastoma of the optic nerve (unusual location) revealing a markedly vascular tumor with lipidized stromal cells (×200)
Image: “Optic nerve hemangioblastoma” by Department of Surgery, Division of Neurosurgery, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL 35294, USA. License: CC BY 3.0Surgical resection is the primary approach to treating hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease. Adjuvant Adjuvant Substances that augment, stimulate, activate, potentiate, or modulate the immune response at either the cellular or humoral level. The classical agents (freund’s adjuvant, bcg, corynebacterium parvum, et al.) contain bacterial antigens. Some are endogenous (e.g., histamine, interferon, transfer factor, tuftsin, interleukin-1). Their mode of action is either non-specific, resulting in increased immune responsiveness to a wide variety of antigens, or antigen-specific, i.e., affecting a restricted type of immune response to a narrow group of antigens. The therapeutic efficacy of many biological response modifiers is related to their antigen-specific immunoadjuvanticity. Vaccination therapies are commonly required in VHL-associated hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease, and options include radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy, endovascular embolization Embolization A method of hemostasis utilizing various agents such as gelfoam, silastic, metal, glass, or plastic pellets, autologous clot, fat, and muscle as emboli. It has been used in the treatment of spinal cord and intracranial arteriovenous malformations, renal arteriovenous fistulas, gastrointestinal bleeding, epistaxis, hypersplenism, certain highly vascular tumors, traumatic rupture of blood vessels, and control of operative hemorrhage. Gastrointestinal Bleeding, and antiangiogenic Antiangiogenic Macular Degeneration therapy.
Surgery is the primary definitive approach to treat hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease, as they are benign Benign Fibroadenoma, noninvasive tumors.
Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is good in most treated hemangioblastomas Hemangioblastomas A benign tumor of the nervous system that may occur sporadically or in association with von Hippel-Lindau disease. It accounts for approximately 2% of intracranial tumors, arising most frequently in the cerebellar hemispheres and vermis. Histologically, the tumors are composed of multiple capillary and sinusoidal channels lined with endothelial cells and clusters of lipid-laden pseudoxanthoma cells. Usually solitary, these tumors can be multiple and may also occur in the brain stem, spinal cord, retina, and supratentorial compartment. Cerebellar hemangioblastomas usually present in the third decade with intracranial hypertension, and ataxia. Von Hippel-Lindau Disease: