Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is any degree of impairment in the ability to apprehend sound as determined by audiometry Audiometry The testing of the acuity of the sense of hearing to determine the thresholds of the loWest intensity levels at which an individual can hear a set of tones. The frequencies between 125 and 8000 hz are used to test air conduction thresholds and the frequencies between 250 and 4000 hz are used to test bone conduction thresholds. Ménière Disease to be below normal hearing thresholds. Clinical presentation may occur at birth or as a gradual loss of hearing with age, including a short-term or sudden loss at any point. Diagnostic evaluation relies on history, physical examination (including otoscopic and tuning fork examinations), and audiology testing. Management is directed toward the underlying cause of the hearing loss to choose the appropriate course of treatment.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is any degree of impairment in the ability to apprehend sound as determined by audiometry Audiometry The testing of the acuity of the sense of hearing to determine the thresholds of the loWest intensity levels at which an individual can hear a set of tones. The frequencies between 125 and 8000 hz are used to test air conduction thresholds and the frequencies between 250 and 4000 hz are used to test bone conduction thresholds. Ménière Disease to be below normal hearing thresholds.
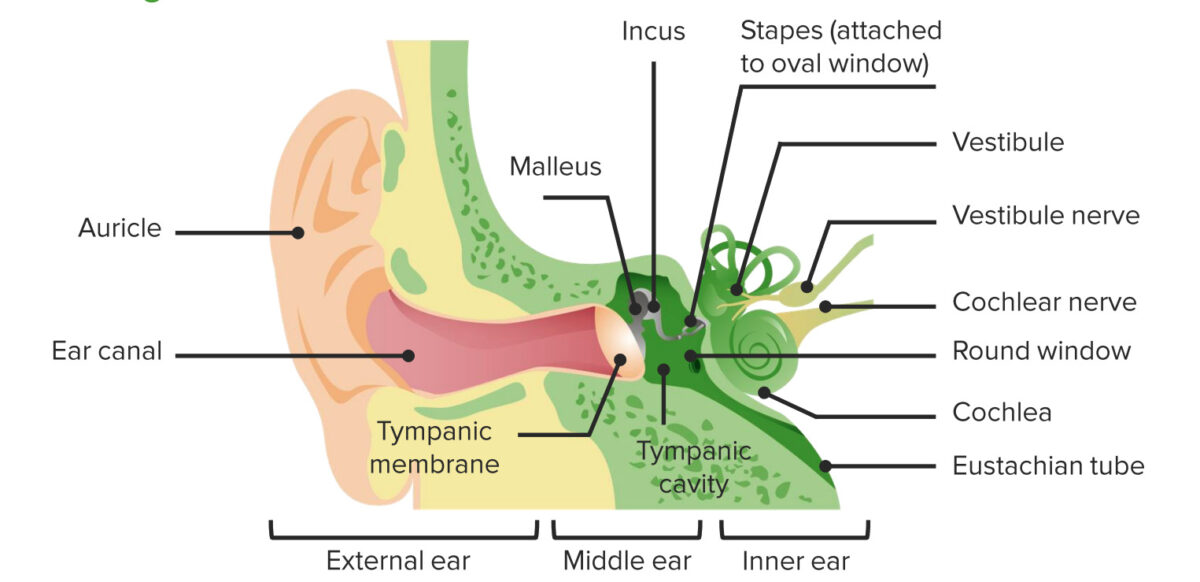
Diagram of the anatomy of the external, middle, and inner ear
Image by Lecturio.Conductive hearing loss (CHL):
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL):
Information to gather from the individual or caregiver regarding hearing loss:
An otoscope Otoscope Instruments designed to inspect or auscultate the ear. They are designed primarily to examine the outer ear canal and tympanic membrane by means of light and air under moderate pressure, as with a pneumatic otoscope. Head and Neck Examination is used to examine the outer and middle ear Middle ear The space and structures directly internal to the tympanic membrane and external to the inner ear (labyrinth). Its major components include the auditory ossicles and the eustachian tube that connects the cavity of middle ear (tympanic cavity) to the upper part of the throat. Acute Otitis Media and a tuning fork is used to determine the type of hearing loss.
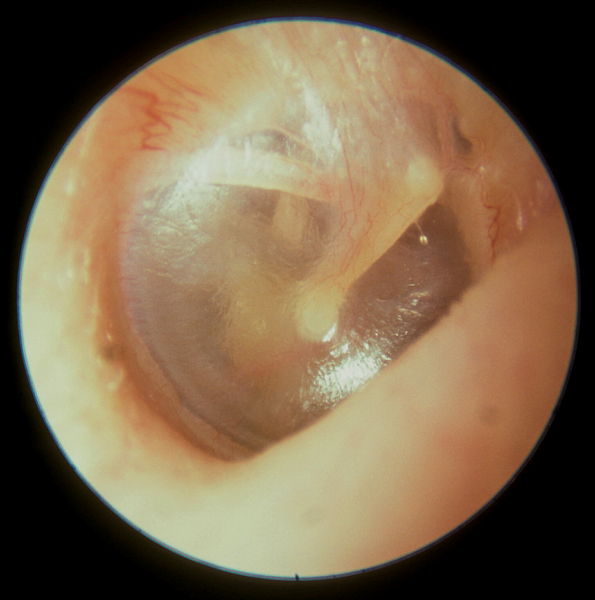
View of a normal tympanic membrane on an otoscopic exam:
Note the bony malleus attached to the tympanic membrane.
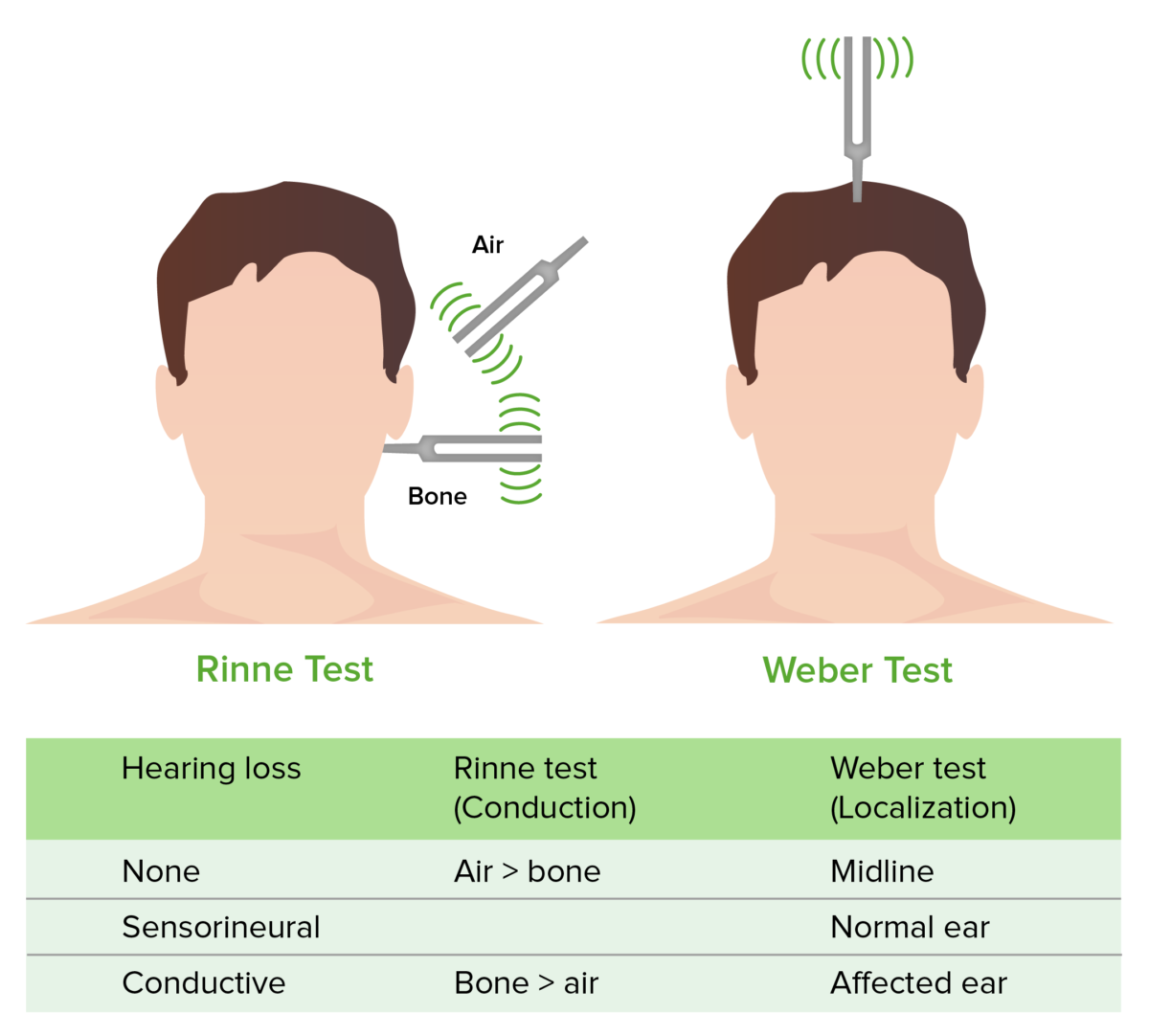
Weber and Rinne test
Image by Lecturio.Diagnosis of hearing loss is based on physiologic and audiometric testing. Lab testing and imaging may also be needed to rule out another pathology.
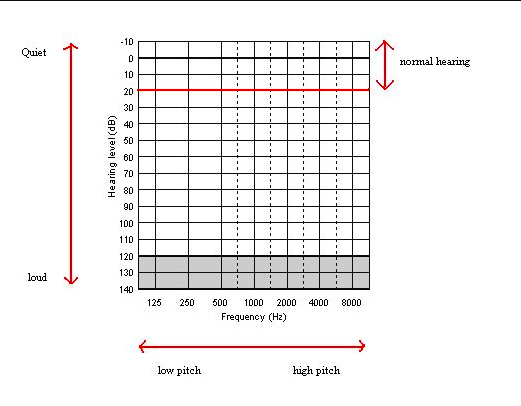
Audiogram chart
Image: “Audiogram” by Audiology6. License: Public DomainCommon conditions causing hearing loss: