Haemophilus is a genus of Gram-negative coccobacilli, all of whose strains require at least 1 of 2 factors for growth ( factor V Factor V Heat- and storage-labile plasma glycoprotein which accelerates the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin in blood coagulation. Factor V accomplishes this by forming a complex with factor Xa, phospholipid, and calcium (prothrombinase complex). Hemostasis [ NAD NAD+ A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-diphosphate coupled to adenosine 5'-phosphate by pyrophosphate linkage. It is found widely in nature and is involved in numerous enzymatic reactions in which it serves as an electron carrier by being alternately oxidized (NAD+) and reduced (NADH). Pentose Phosphate Pathway] and factor X Factor X Storage-stable glycoprotein blood coagulation factor that can be activated to factor Xa by both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. A deficiency of factor X, sometimes called stuart-prower factor deficiency, may lead to a systemic coagulation disorder. Hemostasis [heme]); therefore, it is most often isolated on chocolate agar, which can supply both factors. The most common pathogenic species is H. influenzae, which is transmitted through respiratory droplets Droplets Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox and can cause epiglottitis Epiglottitis Epiglottitis (or "supraglottitis") is an inflammation of the epiglottis and adjacent supraglottic structures. The majority of cases are caused by bacterial infection. Symptoms are rapid in onset and severe. Epiglottitis, meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis, otitis media, and pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia. H. ducreyi is transmitted through sexual contact and is the cause of chancroid Chancroid Chancroid is a highly transmissible STD caused by Haemophilus ducreyi. The disease presents with painful ulcer(s) on the genital tract (termed chancroid or "soft chancre"). Up to 50% of patients will develop painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. Chancroid, a type of genital ulcer.
Last updated: Oct 30, 2024
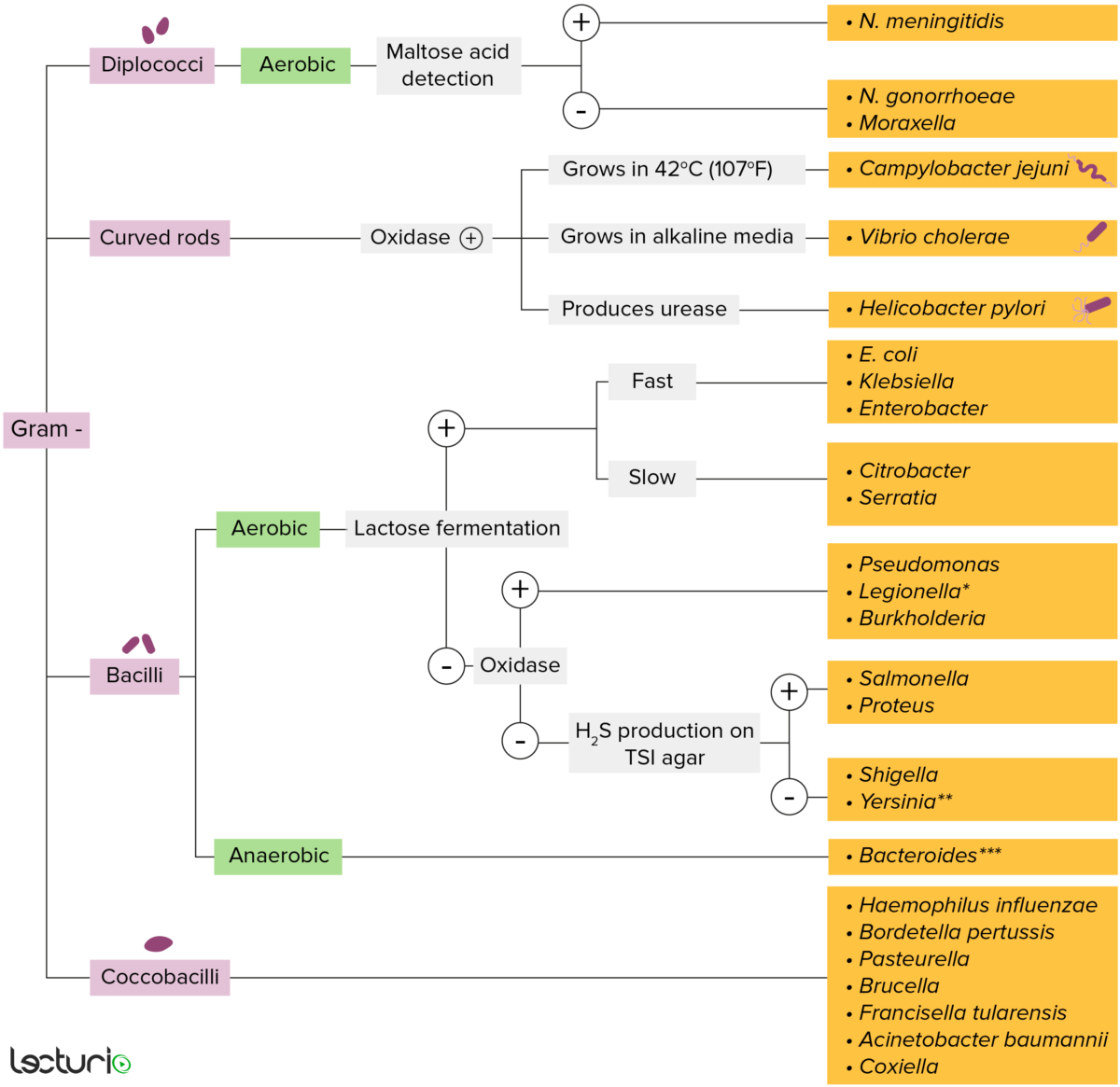
Gram-negative bacteria:
Most bacteria can be classified according to a lab procedure called Gram staining.
Bacteria with cell walls that have a thin layer of peptidoglycan do not retain the crystal violet stain utilized in Gram staining. These bacteria do, however, retain the safranin counterstain and thus appear as pinkish-red on the stain, making them gram negative. These bacteria can be further classified according to morphology (diplococci, curved rods, bacilli, and coccobacilli) and their ability to grow in the presence of oxygen (aerobic versus anaerobic). The bacteria can be more narrowly identified by growing them on specific media (triple sugar iron (TSI) agar) where their enzymes can be identified (urease, oxidase) and their ability to ferment lactose can be tested.
* Stains poorly on Gram stain
** Pleomorphic rod/coccobacillus
*** Require special transport media
General characteristics of Haemophilus species:
Virulence Virulence The degree of pathogenicity within a group or species of microorganisms or viruses as indicated by case fatality rates and/or the ability of the organism to invade the tissues of the host. The pathogenic capacity of an organism is determined by its virulence factors. Proteus factors of Haemophilus species:
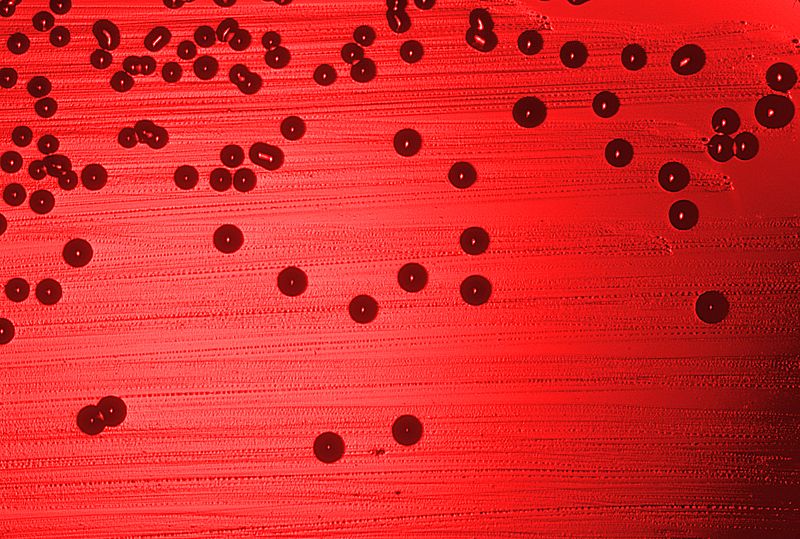
Haemophilus influenzae bacteria cultured on a blood agar plate.
Image: “Haemophilus influenzae 01” by CDC. License: Public Domain| Pathogen | Population at risk | Symptoms | |
|---|---|---|---|
| H. influenzae | Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis |
|
Predominantly caused by strains with the type B capsule Capsule An envelope of loose gel surrounding a bacterial cell which is associated with the virulence of pathogenic bacteria. Some capsules have a well-defined border, whereas others form a slime layer that trails off into the medium. Most capsules consist of relatively simple polysaccharides but there are some bacteria whose capsules are made of polypeptides. Bacteroides |
| Otitis Media | Children and adults |
|
|
| Epiglottitis Epiglottitis Epiglottitis (or “supraglottitis”) is an inflammation of the epiglottis and adjacent supraglottic structures. The majority of cases are caused by bacterial infection. Symptoms are rapid in onset and severe. Epiglottitis | Children 2–7 years old |
|
|
| Pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia | Elderly, patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Pulmonary disease Diseases involving the respiratory system. Blastomyces/Blastomycosis ( COPD COPD Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease characterized by progressive, largely irreversible airflow obstruction. The condition usually presents in middle-aged or elderly persons with a history of cigarette smoking. Signs and symptoms include prolonged expiration, wheezing, diminished breath sounds, progressive dyspnea, and chronic cough. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)) | Typical presentation: blood-tinged sputum |
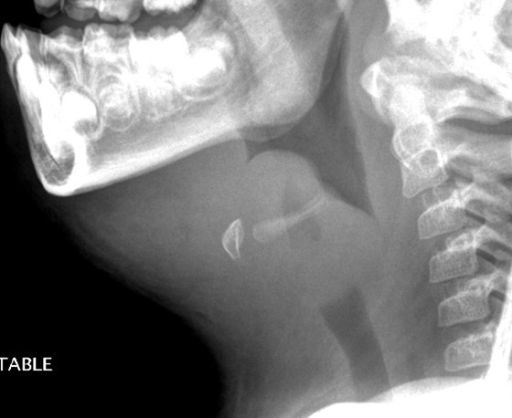
A lateral neck radiograph showing epiglottitis and complete obstruction of the airways in a 5-year-old girl. The condition is commonly caused by the Haemophilus influenzae bacteria.
Image: “Acute epiglottitis as the initial presentation of pediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus” by Charuvanij S et al. License: CC BY 2.0To help remember the common clinical manifestations of H. influenzae, use the following mnemonic:
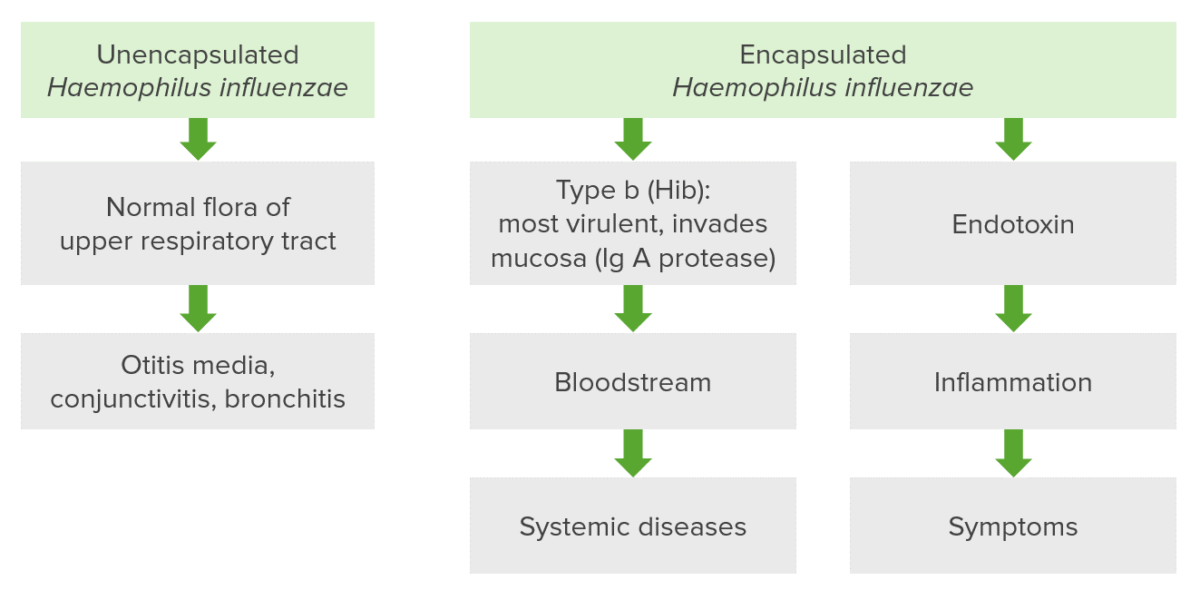
Mnemonic:
Haemophilus ducreyi is so painful that you do cry.
Haemophilus ducreyi bacteria, the causative agent of chancroid, stained with gentian violet.