Gynecomastia is a benign Benign Fibroadenoma proliferation of male breast glandular ductal tissue, usually bilateral, caused by increased estrogen Estrogen Compounds that interact with estrogen receptors in target tissues to bring about the effects similar to those of estradiol. Estrogens stimulate the female reproductive organs, and the development of secondary female sex characteristics. Estrogenic chemicals include natural, synthetic, steroidal, or non-steroidal compounds. Ovaries: Anatomy activity, decreased testosterone Testosterone A potent androgenic steroid and major product secreted by the leydig cells of the testis. Its production is stimulated by luteinizing hormone from the pituitary gland. In turn, testosterone exerts feedback control of the pituitary LH and FSH secretion. Depending on the tissues, testosterone can be further converted to dihydrotestosterone or estradiol. Androgens and Antiandrogens activity, or medications. The condition is common and physiological in neonates, adolescent boys, and elderly men. Some cases are pathological or secondary to chronic liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease, kidney disease, or hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism Hypersecretion of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland. Elevated levels of thyroid hormones increase basal metabolic rate. Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism. The majority of cases are asymptomatic and do not need treatment.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Asymptomatic gynecomastia is common enough that it could almost be considered a normal condition, with a trimodal age distribution.
Gynecomastia is classified into 3 major groups: physiological, pathological, and idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis.
To recall the causes of gynecomastia, remember CODES:
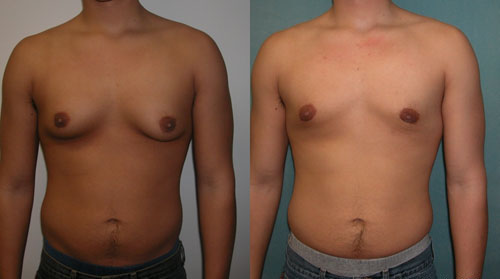
Physiological gynecomastia in an adolescent male
Image: “Adolescent Gynecomastia corrected by surgery protocol” by David Andrew Copeland, Dr. Mordcai Blau. License: GNU Free Documentation LicenseThe following conditions are differential diagnoses for gynecomastia: