Gout medications include antiinflammatory and urate-lowering medications. Colchicine is an antiinflammatory medication that can be used for acute gout flares. The urate-lowering drug classes include the xanthine oxidase inhibitors, uricosuric agents, and uricases. These medications are beneficial for the prevention of gout exacerbations and work through a variety of mechanisms. Xanthine oxidase inhibitors are the most commonly used urate-lowering therapy; these work by inhibiting the enzyme necessary for the conversion of purines to uric acid. Uricosuric agents reduce reabsorption of uric acid by the proximal tubule, thereby increasing renal excretion. Lastly, the uricases are recombinant enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body's constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes that metabolize uric acid Uric acid An oxidation product, via xanthine oxidase, of oxypurines such as xanthine and hypoxanthine. It is the final oxidation product of purine catabolism in humans and primates, whereas in most other mammals urate oxidase further oxidizes it to allantoin. Nephrolithiasis to allantoin. In addition to gout Gout Gout is a heterogeneous metabolic disease associated with elevated serum uric acid levels (> 6.8 mg/dL) and abnormal deposits of monosodium urate in tissues. The condition is often familial and is initially characterized by painful, recurring, and usually monoarticular acute arthritis, or "gout flare," followed later by chronic deforming arthritis. Gout, urate-lowering treatment can also be used for other indications, such as the prevention of tumor lysis Tumor Lysis Tumor Lysis Syndrome syndrome and uric acid Uric acid An oxidation product, via xanthine oxidase, of oxypurines such as xanthine and hypoxanthine. It is the final oxidation product of purine catabolism in humans and primates, whereas in most other mammals urate oxidase further oxidizes it to allantoin. Nephrolithiasis nephrolithiasis Nephrolithiasis Nephrolithiasis is the formation of a stone, or calculus, anywhere along the urinary tract caused by precipitations of solutes in the urine. The most common type of kidney stone is the calcium oxalate stone, but other types include calcium phosphate, struvite (ammonium magnesium phosphate), uric acid, and cystine stones. Nephrolithiasis.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Colchicine is an alkaloid extracted from Colchicum autumnale (autumn crocus).
Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption:
Distribution:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
Gout Gout Gout is a heterogeneous metabolic disease associated with elevated serum uric acid levels (> 6.8 mg/dL) and abnormal deposits of monosodium urate in tissues. The condition is often familial and is initially characterized by painful, recurring, and usually monoarticular acute arthritis, or “gout flare,” followed later by chronic deforming arthritis. Gout:
Other indications include:
Caution should be used in individuals with:
The following could lead to increased levels of colchicine:
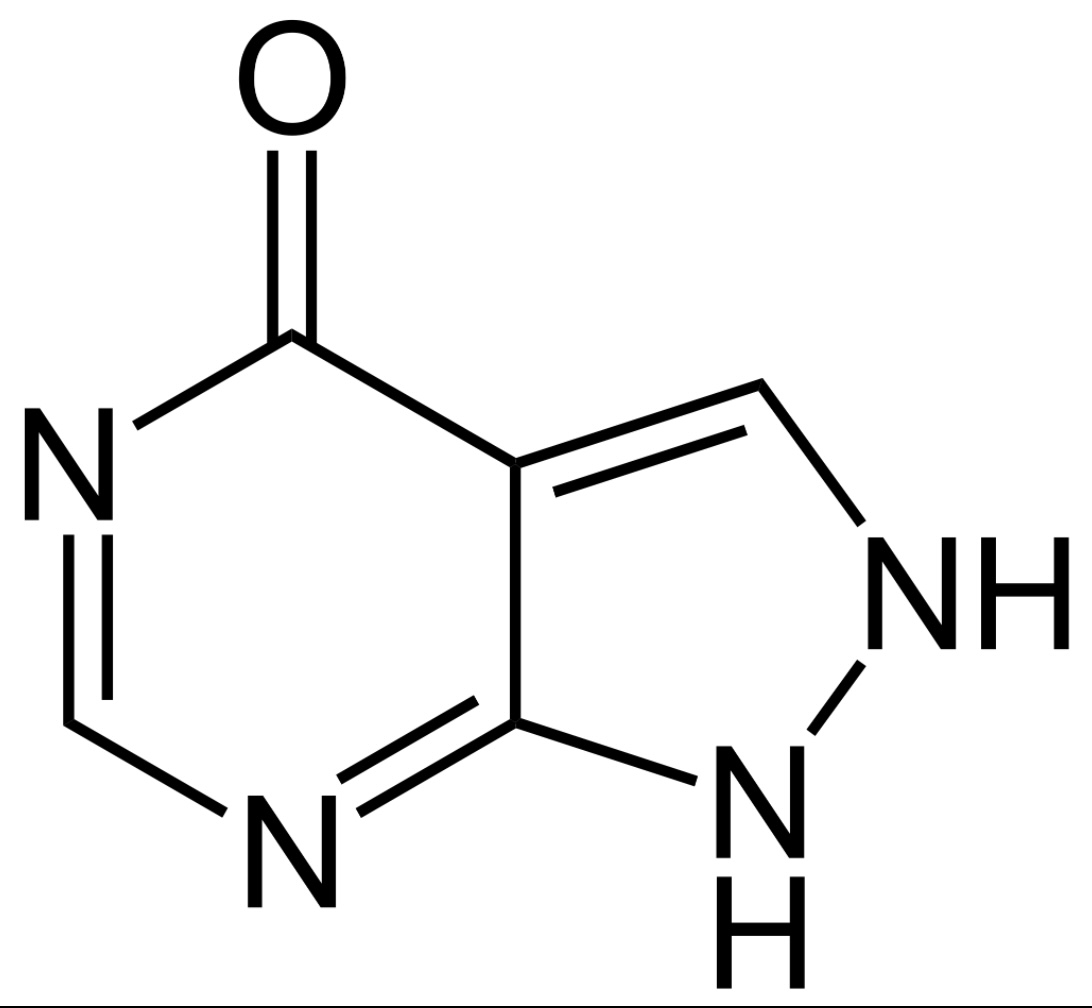
Chemical structure of allopurinol
Image: “Allopurinol” by Jü. License: Public Domain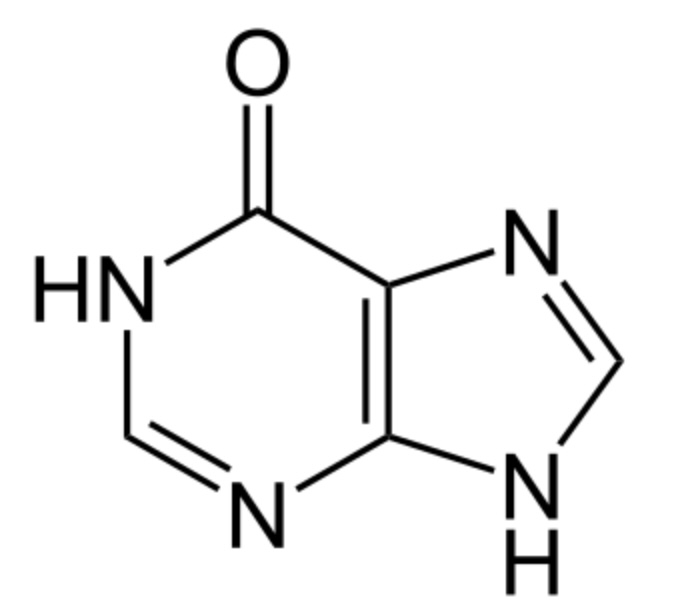
Chemical structure of hypoxanthine:
Note the similarity to allopurinol, a xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
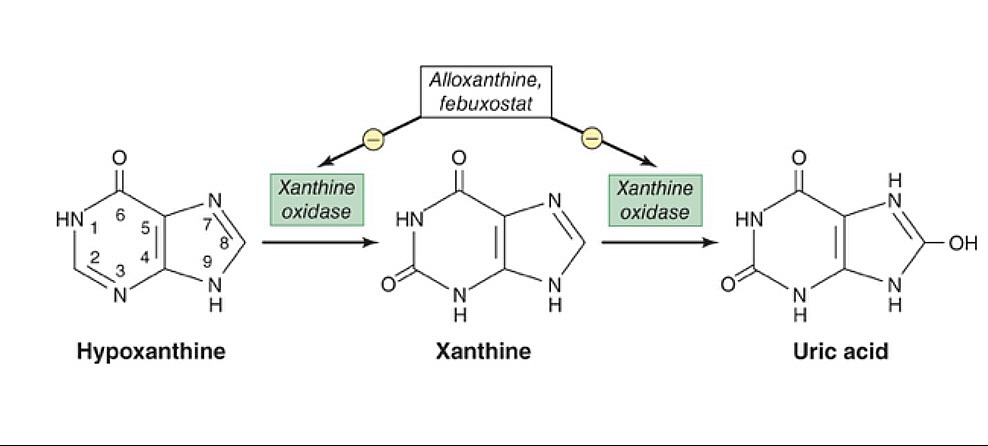
The xanthine oxidase inhibitors, allopurinol and febuxostat, prevent the conversion of hypoxanthine and xanthine to uric acid.
Image by Lecturio.| Medication | Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol | Well absorbed orally | Negligible protein-binding | Urine and feces | |
| Febuxostat | Highly protein-bound |
|
Allopurinol:
Febuxostat:
Allopurinol:
Febuxostat:
Xanthine oxidase Oxidase Neisseria inhibitors can lead to an increased concentration of 6-mercaptopurine 6-Mercaptopurine An antimetabolite antineoplastic agent with immunosuppressant properties. It interferes with nucleic acid synthesis by inhibiting purine metabolism and is used, usually in combination with other drugs, in the treatment of or in remission maintenance programs for leukemia. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy and azathioprine Azathioprine An immunosuppressive agent used in combination with cyclophosphamide and hydroxychloroquine in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. According to the fourth annual report on carcinogens, this substance has been listed as a known carcinogen. Immunosuppressants (which are metabolized by xanthine oxidase Oxidase Neisseria).
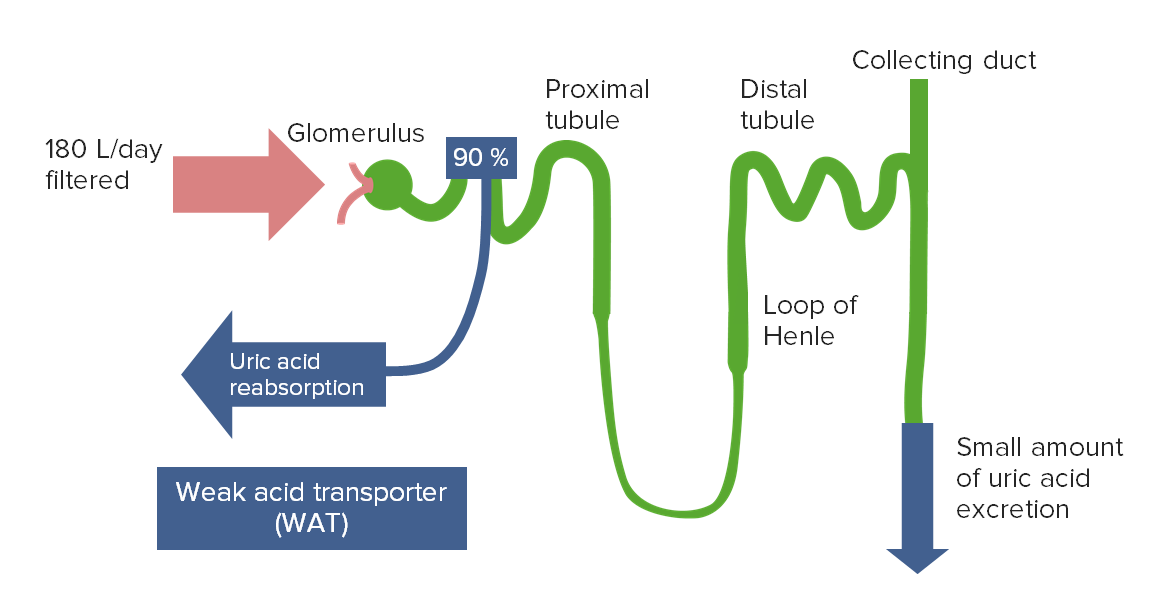
The majority of filtered uric acid is reabsorbed in the proximal tubule.
Image by Lecturio.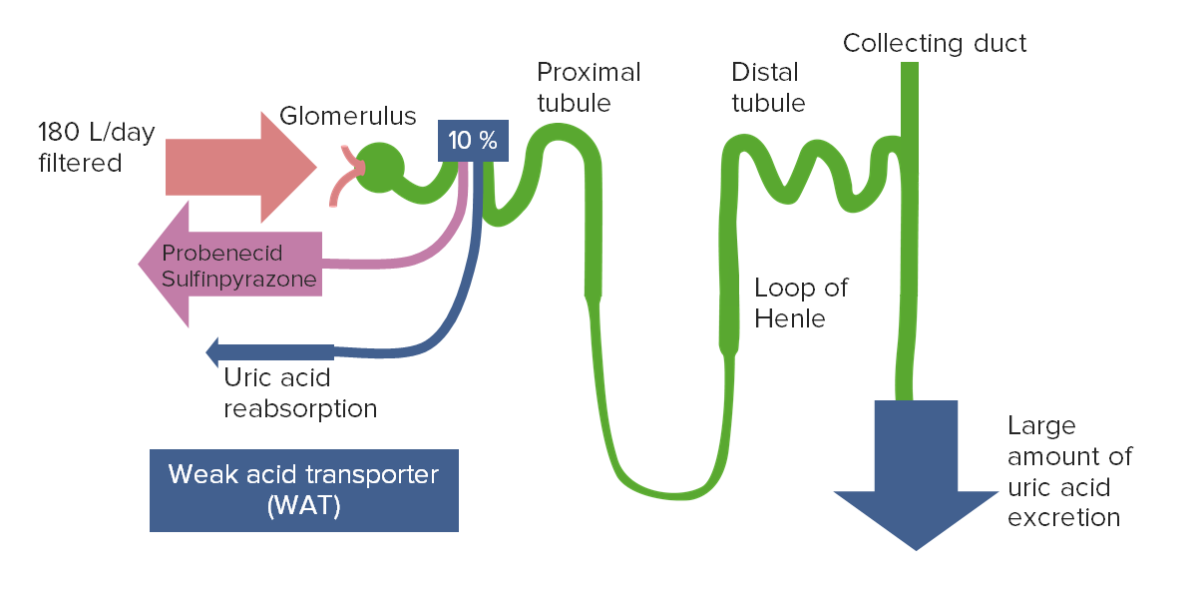
Uricosuric agents, such as probenecid, competitively inhibit the transporters responsible for uric acid reabsorption.
This leads to increased urinary excretion and decreased plasma uric acid levels.
| Medication | Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Probenecid | Rapid, well absorbed | Highly protein-bound | Hepatic | Urine |
| Lesinurad | Hepatic, cytochrome P450 Cytochrome P450 A superfamily of hundreds of closely related hemeproteins found throughout the phylogenetic spectrum, from animals, plants, fungi, to bacteria. They include numerous complex monooxygenases (mixed function oxygenases). In animals, these p450 enzymes serve two major functions: (1) biosynthesis of steroids, fatty acids, and bile acids; (2) metabolism of endogenous and a wide variety of exogenous substrates, such as toxins and drugs (biotransformation). They are classified, according to their sequence similarities rather than functions, into cyp gene families (>40% homology) and subfamilies (>59% homology). For example, enzymes from the cyp1, cyp2, and cyp3 gene families are responsible for most drug metabolism. Drug-Induced Liver Injury | Urine and feces |
Uricosuric agents are uncommonly used for the treatment of hyperuricemia Hyperuricemia Excessive uric acid or urate in blood as defined by its solubility in plasma at 37 degrees c; greater than 0. 42 mmol per liter (7. 0 mg/dl) in men or 0. 36 mmol per liter (6. 0 mg/dl) in women. Gout and chronic gout Chronic Gout Gout.
Probenecid:
Lesinurad:
The following drug interactions are associated with probenecid:
These medications are classified as recombinant urate oxidases (uricases).
The uricases metabolize uric acid Uric acid An oxidation product, via xanthine oxidase, of oxypurines such as xanthine and hypoxanthine. It is the final oxidation product of purine catabolism in humans and primates, whereas in most other mammals urate oxidase further oxidizes it to allantoin. Nephrolithiasis to allantoin, which is:
Pegloticase:
Rasburicase:
The uricases should not be used for individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase Pentose Phosphate Pathway ( G6PD G6PD Pentose Phosphate Pathway) deficiency (can precipitate severe hemolysis).