Goodpasture syndrome, also known as anti-glomerular basement membrane Basement membrane A darkly stained mat-like extracellular matrix (ecm) that separates cell layers, such as epithelium from endothelium or a layer of connective tissue. The ecm layer that supports an overlying epithelium or endothelium is called basal lamina. Basement membrane (bm) can be formed by the fusion of either two adjacent basal laminae or a basal lamina with an adjacent reticular lamina of connective tissue. Bm, composed mainly of type IV collagen; glycoprotein laminin; and proteoglycan, provides barriers as well as channels between interacting cell layers. Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy (TBMN) (GBM) disease, is an autoimmune disease characterized by circulating antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions directed against glomerular and alveolar basement membranes. The autoantibodies Autoantibodies Antibodies that react with self-antigens (autoantigens) of the organism that produced them. Blotting Techniques are thought to be generated in response to an inciting stimulus in genetically predisposed individuals. Affected individuals present with symptoms of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is a syndrome of severe glomerular disease with progressive loss of kidney function within weeks to months. Histologically, crescents (the proliferation of epithelial cells and the infiltration of monocytes/macrophages in the Bowman space) are found in the glomeruli and arise from immunologic injury. Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis and alveolar hemorrhage. Constitutional symptoms Constitutional Symptoms Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis such as malaise Malaise Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus, chills Chills The sudden sensation of being cold. It may be accompanied by shivering. Fever, fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, arthralgia Arthralgia Pain in the joint. Rheumatic Fever, and weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery may also be present. Detection of anti-GBM antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions and renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis findings of crescentic glomerulonephritis with linear IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis deposition along the basement membranes provide the diagnosis. Management includes plasmapheresis Plasmapheresis Procedure whereby plasma is separated and extracted from anticoagulated whole blood and the red cells retransfused to the donor. Plasmapheresis is also employed for therapeutic use. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and immunosuppressants Immunosuppressants Immunosuppressants are a class of drugs widely used in the management of autoimmune conditions and organ transplant rejection. The general effect is dampening of the immune response. Immunosuppressants. Renal transplantation is an option in individuals who develop end-stage renal disease.
Last updated: Aug 15, 2025
Goodpasture syndrome (anti-glomerular basement membrane Basement membrane A darkly stained mat-like extracellular matrix (ecm) that separates cell layers, such as epithelium from endothelium or a layer of connective tissue. The ecm layer that supports an overlying epithelium or endothelium is called basal lamina. Basement membrane (bm) can be formed by the fusion of either two adjacent basal laminae or a basal lamina with an adjacent reticular lamina of connective tissue. Bm, composed mainly of type IV collagen; glycoprotein laminin; and proteoglycan, provides barriers as well as channels between interacting cell layers. Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy (TBMN) (GBM) disease) is a type II hypersensitivity caused by circulating autoantibodies Autoantibodies Antibodies that react with self-antigens (autoantigens) of the organism that produced them. Blotting Techniques directed against an intrinsic antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination in the glomerular and alveolar basement membranes. Goodpasture syndrome is a small vessel vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Rarely, individuals may present with concurrent ANCA-associated vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
Definitive diagnosis is made when anti-GBM antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions are identified in either the serum or on a renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis. Individuals should be evaluated for the antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions when symptoms and/or urinalysis Urinalysis Examination of urine by chemical, physical, or microscopic means. Routine urinalysis usually includes performing chemical screening tests, determining specific gravity, observing any unusual color or odor, screening for bacteriuria, and examining the sediment microscopically. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children findings suggest nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome, and/or if the individual presents with signs of pulmonary hemorrhage.
Chest imaging may show evidence of alveolar hemorrhage.
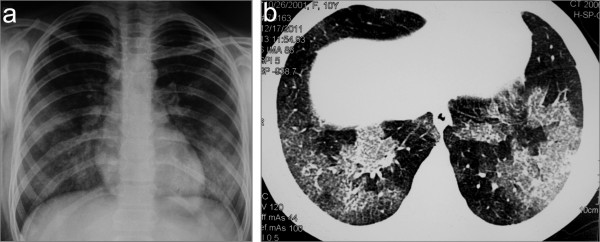
Chest imaging in a child with concurrent Goodpasture syndrome and ANCA vasculitis: chest X-ray (a) and CT scan (b) showing bilateral lung infiltrates as a result of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
Image: “Chest X-ray (a) and CT scan (b) showing bilateral lung infiltrates as a result of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage” by Bogdanović R, Minić P, Marković-Lipkovski J, Stajić N, Savić N, Rodić M. License: CC BY 2.0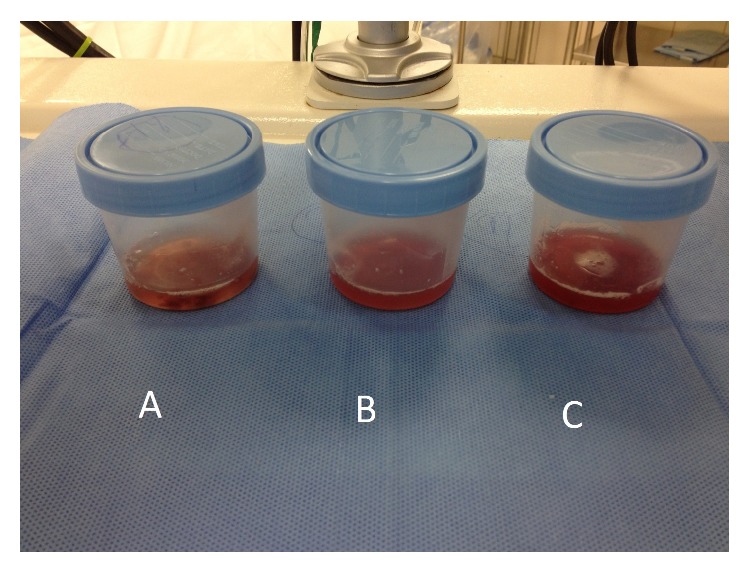
Bronchoalveolar fluid samples become progressively more hemorrhagic in diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and may be seen in individuals with Goodpasture syndrome.
Image: “Bronchoalveolar fluid showed evidence of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (A–C)” by Ijaz M, Abbas N, Lvovsky D. License: CC BY 3.0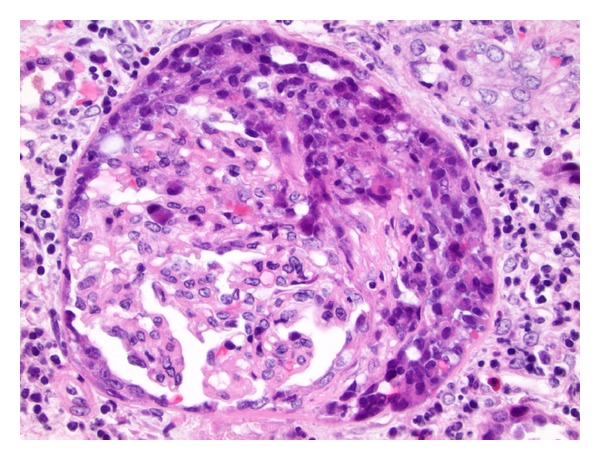
An H&E-stained section showing crescentic glomerulonephritis in Goodpasture syndrome:
Moderate interstitial inflammation and mild fibrosis can be seen.
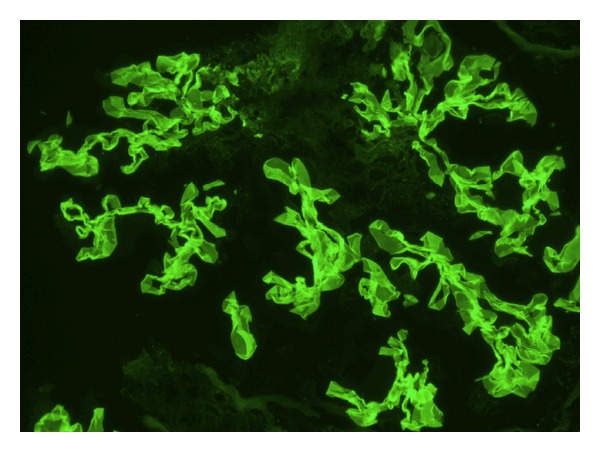
Immunofluorescence staining showing linear anti-glomerular basement membrane IgG deposition consistent with Goodpasture syndrome.
Image: “Immunofluorescence staining shows linear GBM staining for IgG consistent with Goodpasture’s disease” by Muqeet Adnan M, Morton J, Hashmi S, Abdul Mujeeb S, Kern W, Cowley BJ. License: CC BY 3.0