Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection Sexually Transmitted Infection Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections that spread either by vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or oral sex. Symptoms and signs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, dysuria, skin lesions (e.g., warts, ulcers) on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some infections can lead to infertility and chronic debilitating disease. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) ( STI STI Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are infections that spread either by vaginal intercourse, anal sex, or oral sex. Symptoms and signs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, dysuria, skin lesions (e.g., warts, ulcers) on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some infections can lead to infertility and chronic debilitating disease. Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)) caused by the gram-negative bacteria gram-negative bacteria Bacteria which lose crystal violet stain but are stained pink when treated by gram's method. Bacteriology Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria ( N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria). Gonorrhea may be asymptomatic but commonly manifests as cervicitis or urethritis Urethritis Inflammation involving the urethra. Similar to cystitis, clinical symptoms range from vague discomfort to painful urination (dysuria), urethral discharge, or both. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) with less common presentations such as proctitis Proctitis Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum, the distal end of the large intestine. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis is a common inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva. It can be classified into infectious (mostly viral) and noninfectious conjunctivitis, which includes allergic causes. Patients commonly present with red eyes, increased tearing, burning, foreign body sensation, and photophobia. Conjunctivitis, or pharyngitis Pharyngitis Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the back of the throat (pharynx). Pharyngitis is usually caused by an upper respiratory tract infection, which is viral in most cases. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, and hoarseness. Pharyngitis. Without antibiotic treatment, complications can occur. Complications for men may include epididymitis Epididymitis Epididymitis and orchitis are characterized by acute inflammation of the epididymis and the testicle, respectively, due to viral or bacterial infections. Patients typically present with gradually worsening testicular pain and scrotal swelling along with systemic symptoms such as fever, depending on severity. Epididymitis and Orchitis, prostatitis Prostatitis Prostatitis is inflammation or an irritative condition of the prostate that presents as different syndromes: acute bacterial, chronic bacterial, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain, and asymptomatic. Bacterial prostatitis is easier to identify clinically and the management (antibiotics) is better established. Prostatitis, balanitis Balanitis Inflammation of the head of the penis, glans penis. Penile Anomalies and Conditions, and periurethral abscess Abscess Accumulation of purulent material in tissues, organs, or circumscribed spaces, usually associated with signs of infection. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Women may develop pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is defined as a polymicrobial infection of the upper female reproductive system. The disease can affect the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and adjacent structures. Pelvic inflammatory disease is closely linked with sexually transmitted diseases, most commonly caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Gardnerella vaginalis. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, which can cause perihepatitis and fertility issues. Disseminated gonococcal infection is associated with fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, dermatitis Dermatitis Any inflammation of the skin. Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema), tenosynovitis, septic arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis, and (rarely) endocarditis Endocarditis Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease involving the inner lining (endometrium) of the heart, most commonly affecting the cardiac valves. Both infectious and noninfectious etiologies lead to vegetations on the valve leaflets. Patients may present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever and fatigue. Endocarditis or meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis. Gonorrhea diagnosis is made by microscopy, culture, or nucleic acid amplification Nucleic acid amplification Laboratory techniques that involve the in-vitro synthesis of many copies of DNA or RNA from one original template. Septic Arthritis tests. Management generally involves ceftriaxone Ceftriaxone A broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic and cefotaxime derivative with a very long half-life and high penetrability to meninges, eyes and inner ears. Cephalosporins, but treatment with doxycycline should be pursued if a coinfection with Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia trachomatis Type species of Chlamydia causing a variety of ocular and urogenital diseases. Chlamydia (C. trachomatis) is not excluded.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
Gonorrhea is caused by the pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae Neisseria gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria ( N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria):
Risk factors:
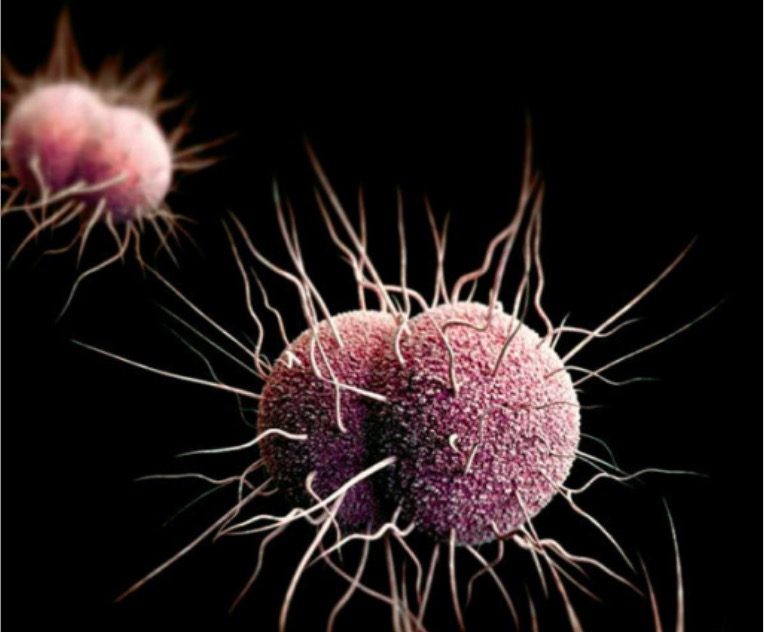
A 3-dimensional (3D) computer-generated image of N. gonorrhoeae bacteria:
Typical diplococci and multiple pili
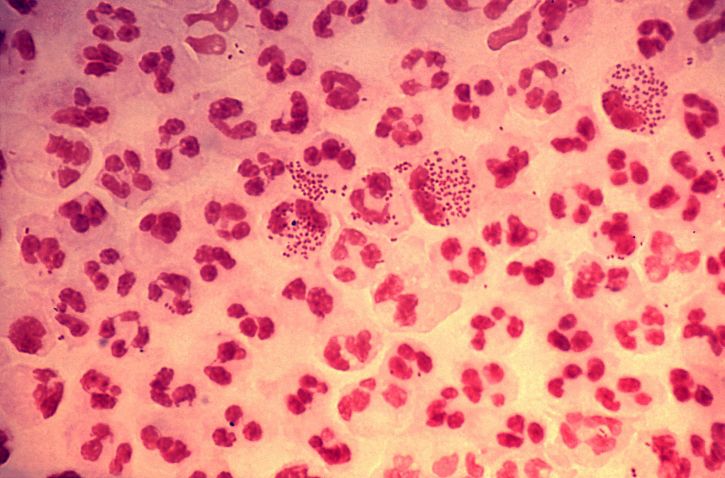
Gram stain of purulent exudate containing N. gonorrhoeae:
N. gonorrhoeae are seen as gram-negative diplococci. As seen here, the bacteria usually provoke a marked neutrophilic response with several neutrophils containing many phagocytized bacteria. Although not present in the image, gram staining would also reveal the bacteria within infected epithelial cells.
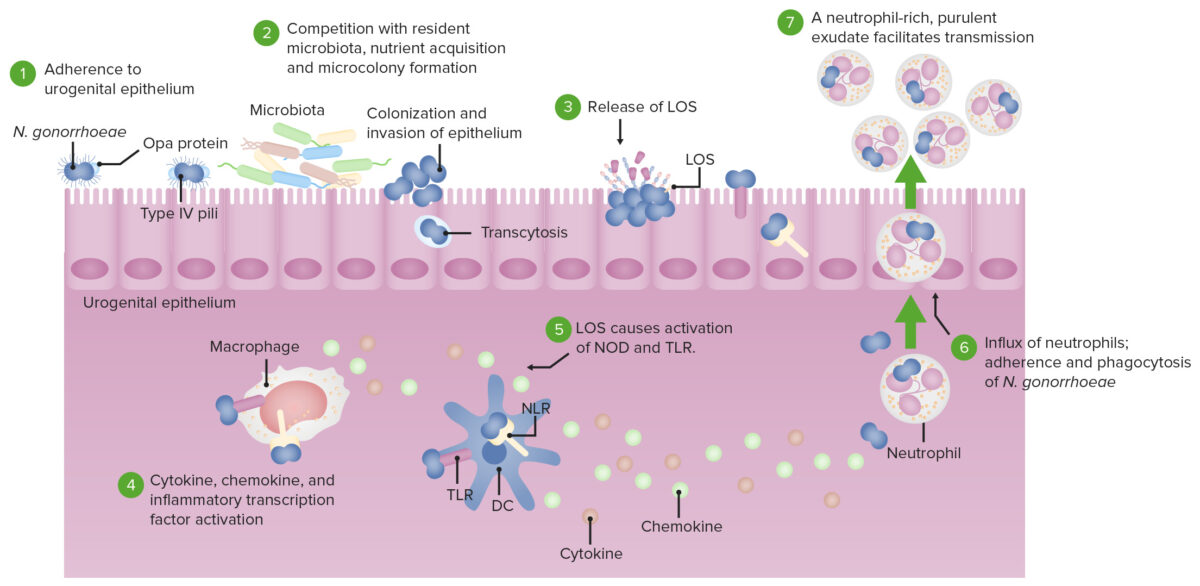
Pathogenesis of N. gonorrhoeae:
DC: dendritic cell
LOS: lipooligosaccharide
TLR: toll-like receptor
NOD: nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein
NLR: NOD-like receptor
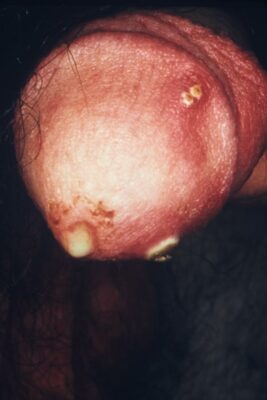
Purulent penile discharge due to urogenital gonorrhea infection
Image: “4065” by CDC. License: Public Domain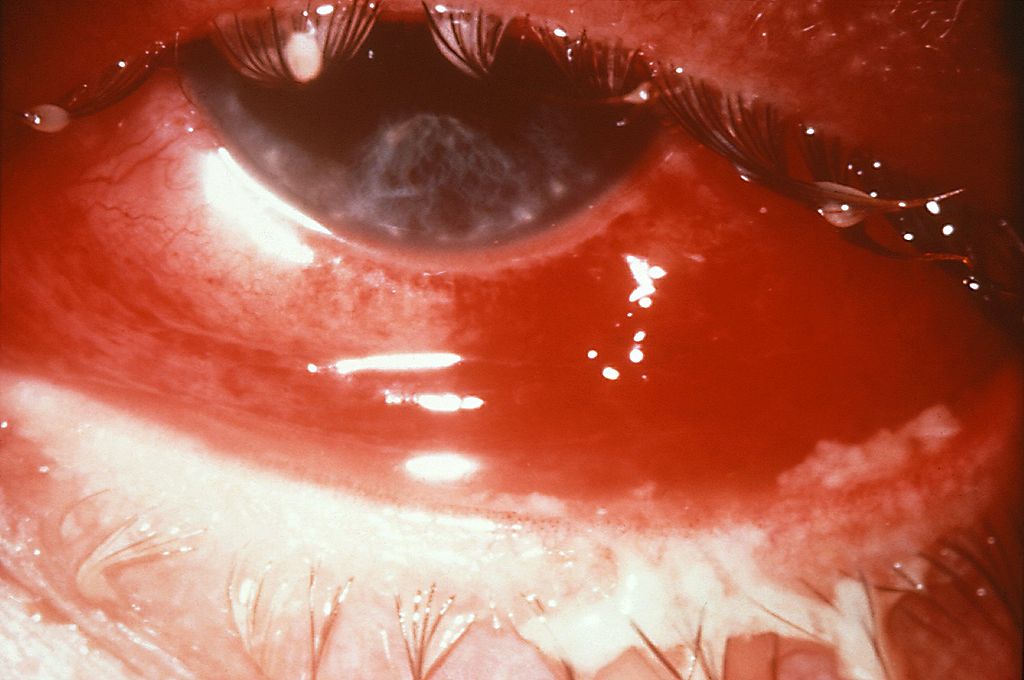
Hyperemia, chemosis, and purulent discharge due to gonococcal conjunctivitis:
The patient developed partial blindness as a result of the infection.
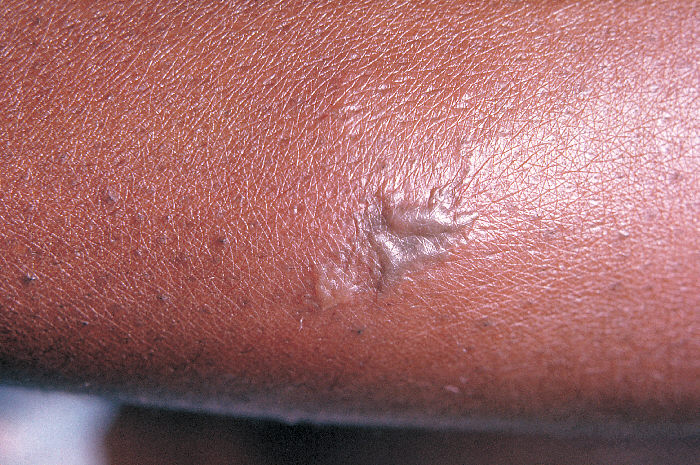
Close-up view of a gonococcal lesion on the skin of a patient’s arm:
A gray pustule associated with disseminated gonococcal infection
Newborn Newborn An infant during the first 28 days after birth. Physical Examination of the Newborn infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease:

A newborn presenting with gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum, caused by a maternally transmitted gonococcal infection.
Image: “Gonococcal ophthalmia neonatorum” by CDC/J. Pledger. License: Public DomainAfter the neonatal period:
In addition to the laboratory evaluations above, the following testing may be performed in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship suspected of having disseminated gonococcal infection:
Antibiotic management:
Additional measures: