A glucagonoma is a glucagon-secreting neuroendocrine tumor Tumor Inflammation that originates from the α-cells in the pancreatic islets. Most glucagonomas are malignant, and many of them are part of the autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance condition known as multiple endocrine neoplasia Multiple endocrine neoplasia Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes are autosomal dominant inherited conditions characterized by 2 or more hormone-producing tumors involving the endocrine organs. There are different types of MEN, namely MEN1-4. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (MEN 1). Elevated levels of glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions lead to increased gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the process of making glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors. This metabolic pathway is more than just a reversal of glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis provides the body with glucose not obtained from food, such as during a fasting period. The production of glucose is critical for organs and cells that cannot use fat for fuel. Gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis Glycogenolysis The release of glucose from glycogen by glycogen phosphorylase (phosphorolysis). The released glucose-1-phosphate is then converted to glucose-6-phosphate by phosphoglucomutase before entering glycolysis. Glycogenolysis is stimulated by glucagon or epinephrine via the activation of phosphorylase kinase. Glycogen Metabolism, resulting in an increase in free glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance in the bloodstream and the depletion of fat and amino acid Amino acid Amino acids (AAs) are composed of a central carbon atom attached to a carboxyl group, an amino group, a hydrogen atom, and a side chain (R group). Basics of Amino Acids stores. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship often present with diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, a characteristic rash Rash Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever called necrolytic migratory erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion, weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, deep vein thrombosis Thrombosis Formation and development of a thrombus or blood clot in the blood vessel. Epidemic Typhus, and neuropsychiatric symptoms. Laboratory findings demonstrate an elevated glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions level, and imaging shows a pancreatic mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast. Management is usually supportive and includes glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions inhibition with octreotide Octreotide A potent, long-acting synthetic somatostatin octapeptide analog that inhibits secretion of growth hormone and is used to treat hormone-secreting tumors; diabetes mellitus; hypotension, orthostatic; hyperinsulinism; hypergastrinemia; and small bowel fistula. Antidiarrheal Drugs (a somatostatin Somatostatin A 14-amino acid peptide named for its ability to inhibit pituitary growth hormone release, also called somatotropin release-inhibiting factor. It is expressed in the central and peripheral nervous systems, the gut, and other organs. SRIF can also inhibit the release of thyroid-stimulating hormone; prolactin; insulin; and glucagon besides acting as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. In a number of species including humans, there is an additional form of somatostatin, srif-28 with a 14-amino acid extension at the n-terminal. Gastrointestinal Secretions analog). Surgical resection is attempted if disease is localized, though this is frequently palliative. Chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma and targeted molecular agents are also used in advanced disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A glucagonoma is a glucagon-secreting tumor Tumor Inflammation arising from the α cells in the pancreatic islets and is sometimes seen in the context of MEN 1.
Secreted by the α cells in the pancreatic islets, glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions’s role is to make energy readily available by producing glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance and halting its storage.
Glucagonomas are uncommon, but 10%–20% of those that are found are associated with MEN 1.
The presentation of glucagonomas can be confused with that of many other conditions, and the ultimate diagnosis of most cases is not confirmed until there has been metastatic spread of the disease.
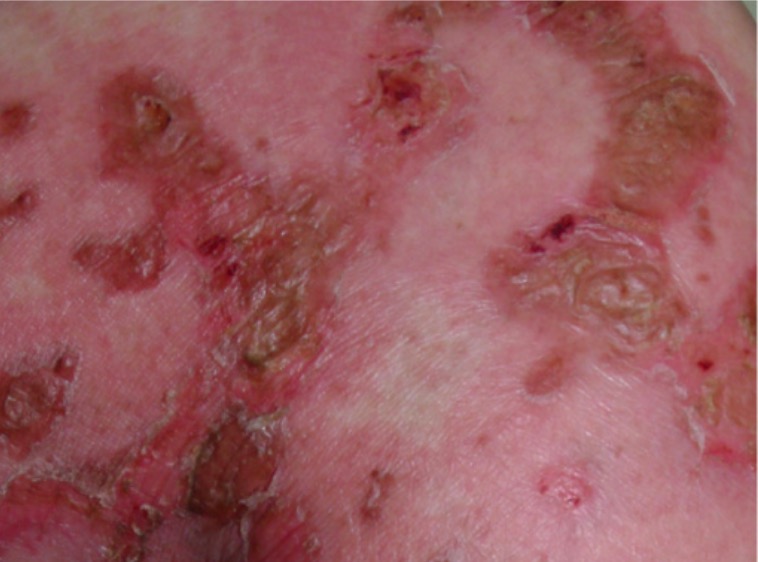
Necrolytic migratory erythema (NME) is a cutaneous manifestation often (but not exclusively) seen with glucagonomas. NME is described as areas of well-demarcated erythematous plaques, with fragile blisters and erosions.
Image: “Necrolytic Migratory Erythema” by Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University School of Medicine, No, 277, Yanta West Road, 710061 Xi’an, Shaanxi, P,R, China. License: CC BY 4.0To recall the clinical manifestations of a glucagonoma, remember the 6 Ds:
The diagnosis of glucagonoma is made on the basis of a combination of history, exam, elevated glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions levels, and imaging showing a pancreatic mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast. Staging Staging Methods which attempt to express in replicable terms the extent of the neoplasm in the patient. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis malignant disease is also an important part of the diagnostic process, since metastases are often present at diagnosis.
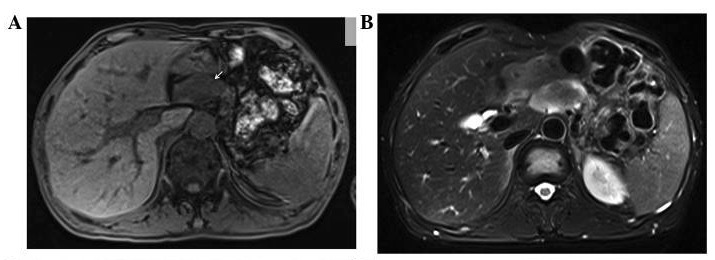
MRI of a patient with glucagonoma:
A: low signal intensity of the lesion on the T1-weighted image (arrow)
B: slightly high signal intensity of the lesion
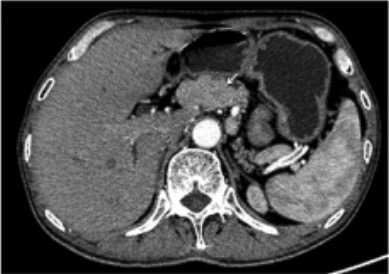
CT scan showing a mass in the neck of the pancreas, diagnosed as a glucagonoma
Image: “Glucagonoma” by Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Center, Qilu Hospital, First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong 250012, P.R. China. License: CC BY 3.0, cropped by Lecturio.