Glandular epithelia, composed of epithelial tissue, are specialized structures that play a role in the production and release of enzymes, hormones, sweat, oil, and mucus in organisms. The secretion and release of these substances are prompted by either external or internal stimuli. Products of glandular epithelia are released either into ducts leading to the surface of the epithelium or into the blood. The main types of glands are exocrine and endocrine glands. The classification is based on the number and location of secreting cells and the type of secretions, among other factors.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
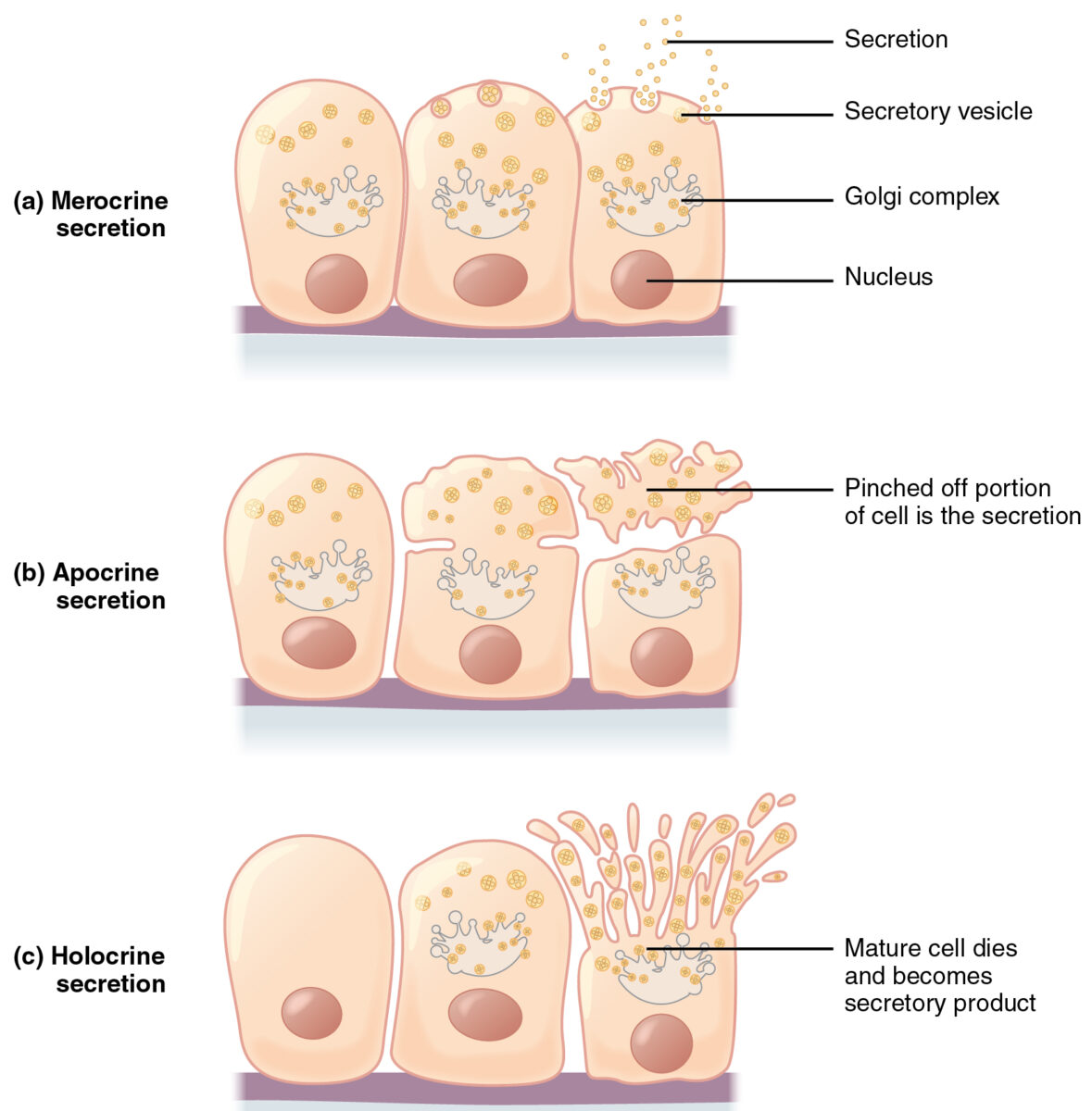
Merocrine secretion is the most common. Cells synthesize their products and store them in granules. Upon stimulation, granules move to the apical surface, granule membranes fuse with cell membranes, and the product is exocytosed. During apocrine secretion, the product is stored at the apical surface and breaks off with the cytoplasm. Holocrine secretion involves cell apoptosis and release of the secretory product.
Image: “Modes of Glandular Secretion” by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0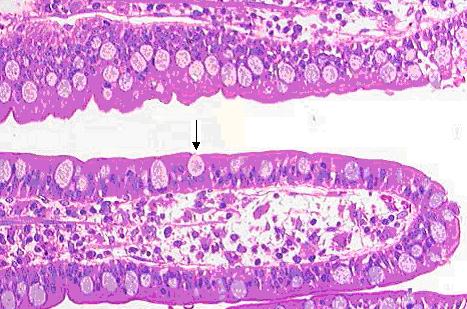
Goblet cell
Image: “Gobletcell” by Arcadian. License: Public Domain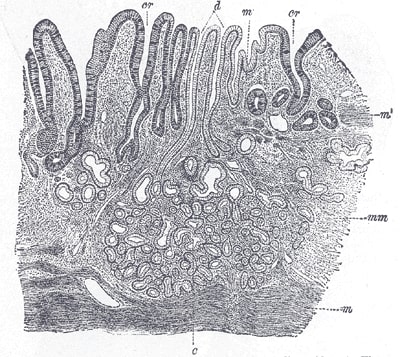
Section of the mucous membrane of the human stomach, near the cardiac orifice. (v. Ebner, after J. Schaffer.) x45.
c: cardiac glands
d: ducts of the cardiac glands
cr: gland similar to the intestinal glands and with goblet cells
mm: mucous membrane
m: muscularis mucoae
m’: muscular tissue within the mucous membrane
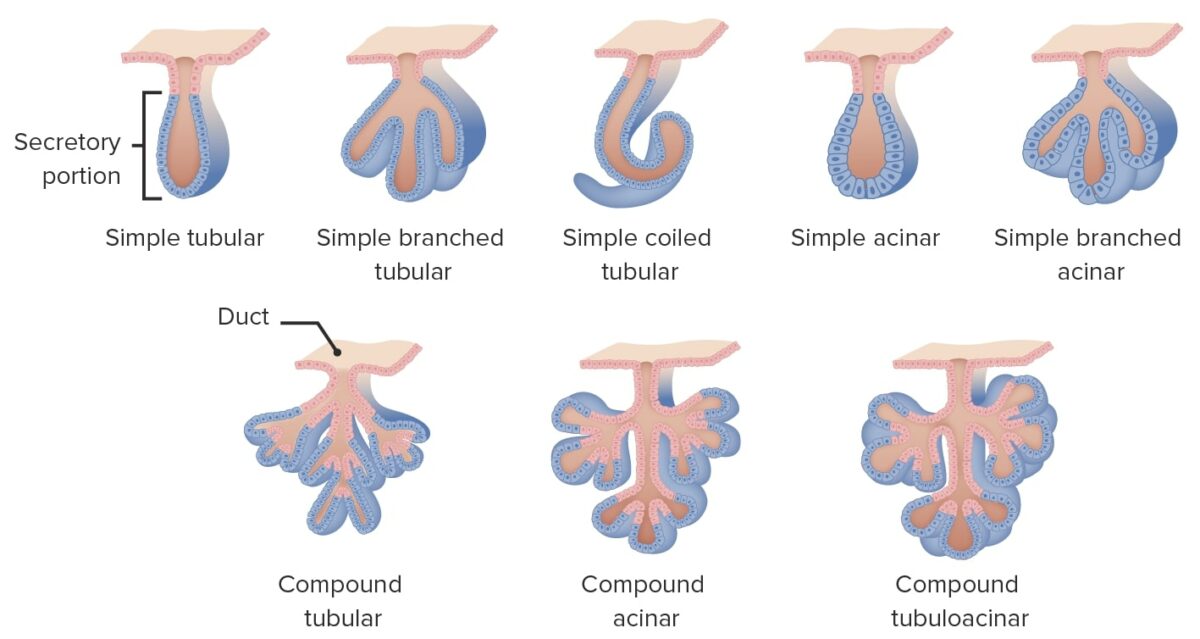
Multicellular glands can get more complex by acquiring a duct. If the ducts don’t branch, the gland is called simple. Branched glands are called compound glands. Compound glands are further subdivided into tubular, acinar, and tubuloacinar glands.
Image by Lecturio.