Giardiasis is caused by Giardia duodenalis (also known as G. lamblia or G. intestinalis), a flagellated protozoan that can infect the intestinal tract. Transmission most commonly occurs through the ingestion of cysts in contaminated water, food, or via person-to-person fecal–oral spread. Excystation occurs in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, and trophozoites attach to the intestinal mucosa via a ventral adhesive disc, leading to malabsorption. The hallmark symptom of giardiasis is foul-smelling steatorrhea. Patients who develop chronic infections may experience weight loss, failure to thrive, and vitamin deficiencies as a result of malabsorption. The diagnosis is made through detection of Giardia organisms, antigens, or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in the stool. Management includes supportive treatment and antimicrobial therapy with tinidazole, metronidazole, nitazoxanide, or albendazole. Prevention measures include proper handwashing and water treatment.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Giardiasis is caused by the flagellated protozoan, Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles duodenalis (synonyms: G. lamblia, G. intestinalis).
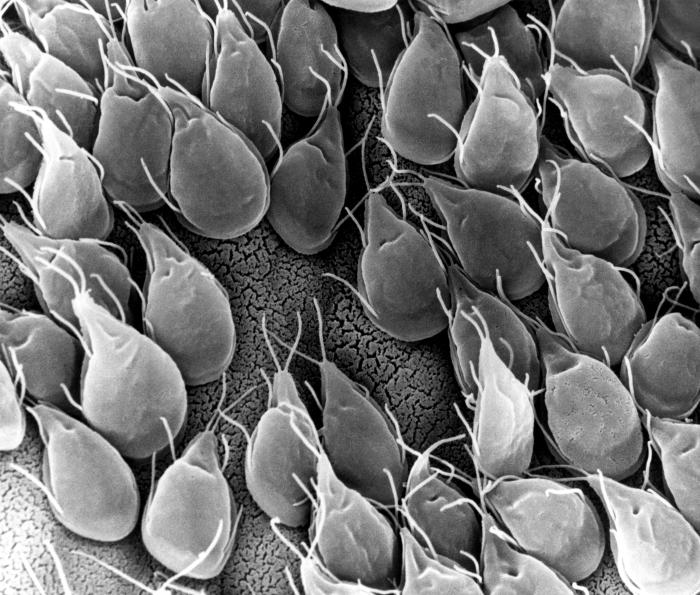
Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) image of G. lamblia trophozoites
Image: “SEM” by CDC/Dr. Stan Erlandsen. License: Public Domain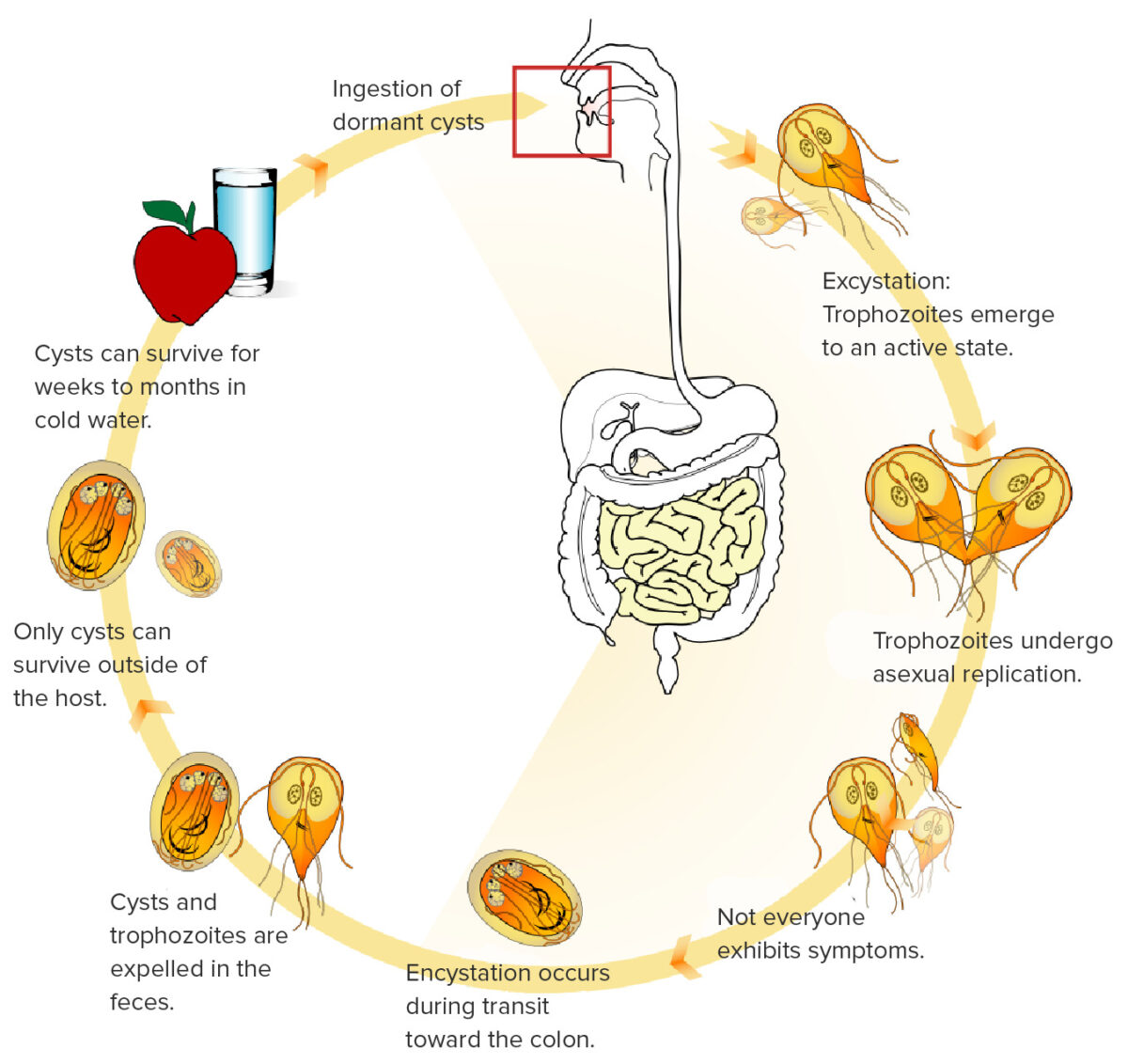
This image shows the life cycle of G. lamblia. Cysts can survive for long periods of time in cold water and then be inadvertently consumed. Once consumed, the cysts transform into trophozoite form, replicate, and infect the intestines. The trophozoites attach to the intestinal villi, resulting in symptoms.
Image: “Giardia life cycle” by LadyofHats. License: Public Domain, edited by Lecturio.While some patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship may be asymptomatic, the hallmark clinical feature of giardiasis is malabsorptive diarrhea Malabsorptive diarrhea Norovirus.
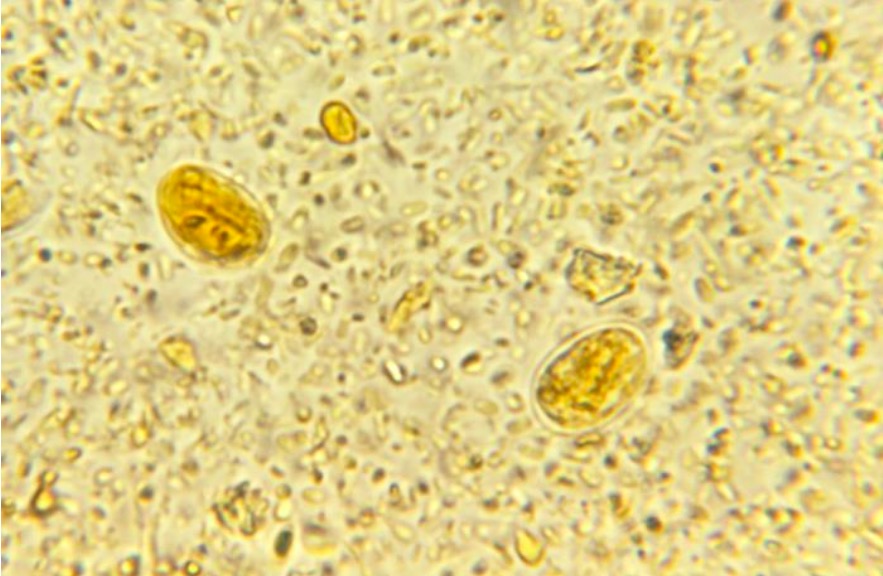
Stool microscopy revealing the presence of 2 G. lamblia cysts
Image: “ 21085” by CDC. License: Public Domain| Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles | Leishmania Leishmania Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The disease is endemic to Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Mediterranean, and South and Central America. Clinical presentation varies, dependent on the pathogenicity of the species and the host’s immune response. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis | Trypanosoma | Trichomonas Trichomonas A genus of parasitic flagellate eukaryotes distinguished by the presence of four anterior flagella, an undulating membrane, and a trailing flagellum. Nitroimidazoles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics |
|
|
|
|
| Forms |
|
|
|
|
| Transmission |
|
|
|
Sexually transmitted |
| Clinical | Giardiasis | Leishmaniasis Leishmaniasis Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The mildest form is cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), characterized by painless skin ulcers. The mucocutaneous type involves more tissue destruction, causing deformities. Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), the most severe form, presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fever. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis |
|
Trichomoniasis |
| Diagnosis |
|
|
|
|
| Treatment |
|
Depends on the clinical syndrome:
|
Depends on the clinical disease:
|
|
| Prevention |
|
|
|
|
ELISA: enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
DFA: direct immunofluorescence assay
NAAT: nucleic acid amplification assay
PCR: polymerase chain reaction
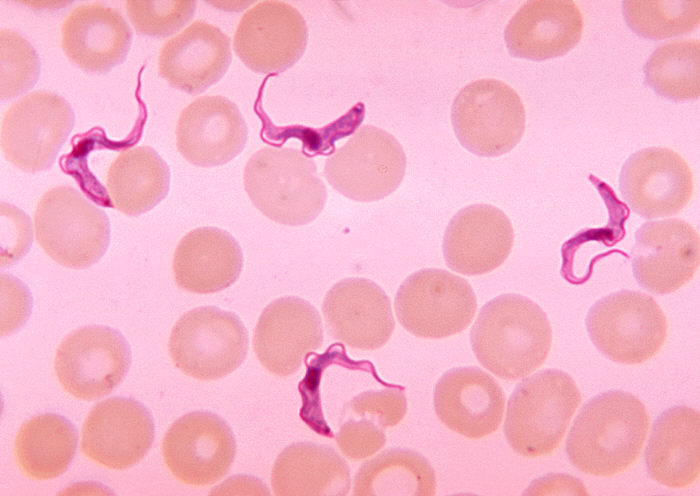
Blood smear demonstrating Trypanosoma trypomastigotes
Image: “Ms. Michaels forms” by CDC/Dr. Myron G. Schultz. License: Public Domain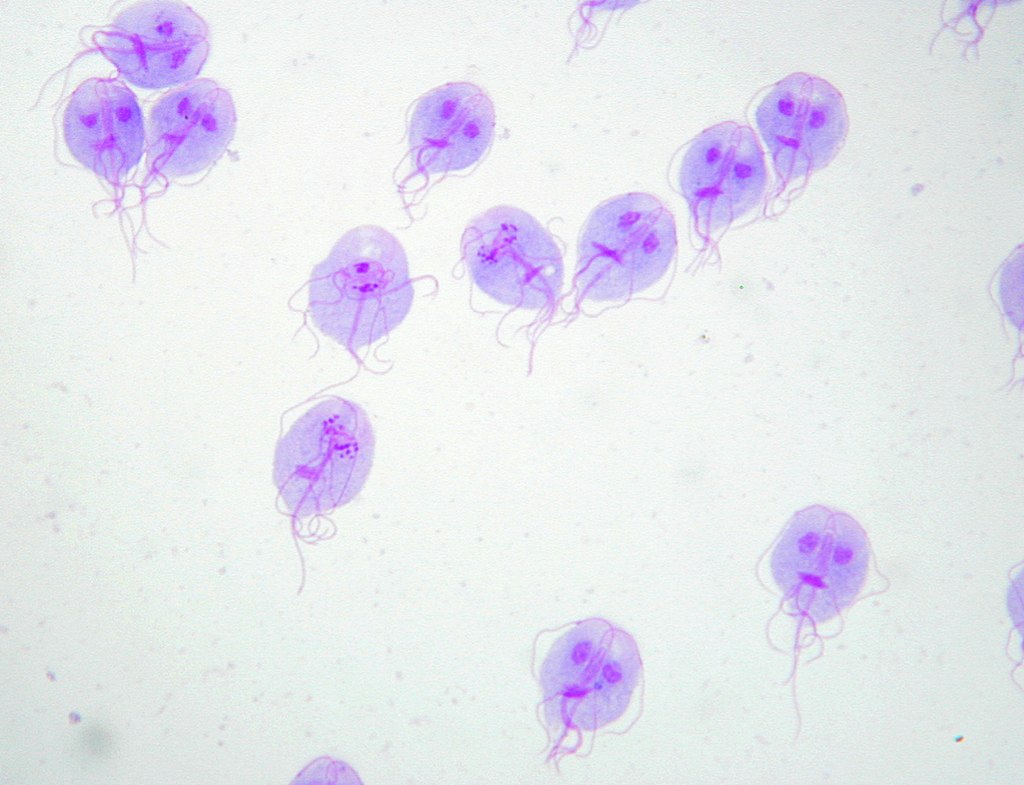
Giemsa’s stain of G. lamblia trophozoites
Image: “Trophozoites of Giardia lamblia” by Eva Nohýnková, Department of Tropical Medicine, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Hospital Bulovka, Czech Republic. License: CC BY 4.0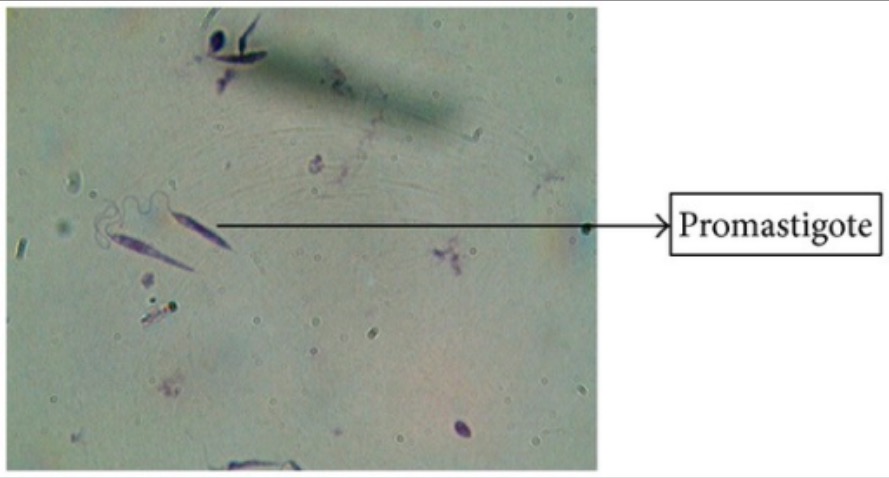
Giemsa’s stain of Leishmania promastigotes
Image: “Giemsa stain” by Arriyadh Community College, King Saud University, P.O. Box 28095, Riyadh 11437, Saudi Arabia. License: CC BY 3.0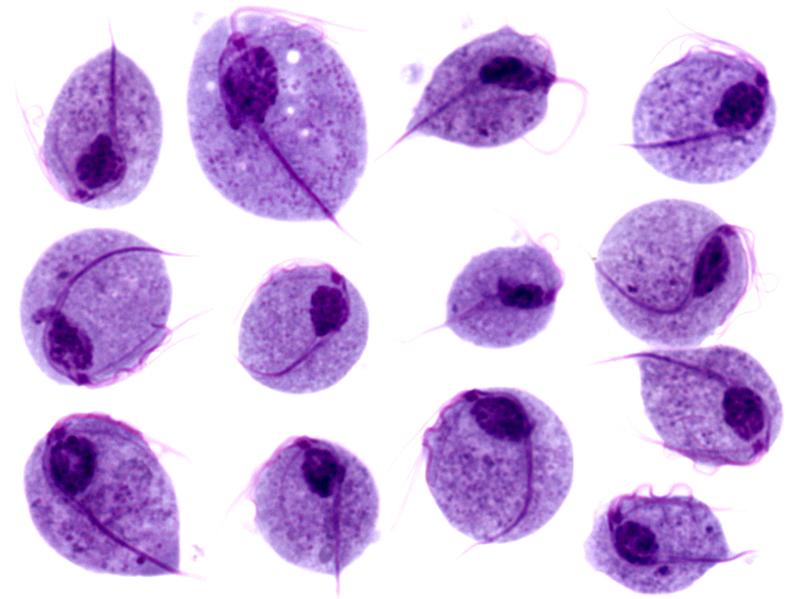
Microscopic images of Trichomonas vaginalis trophozoites
Image: “Trichomonas protozoa” by isis325. License: CC BY 2.0.