Gestational trophoblastic diseases are a spectrum of placental disorders resulting from abnormal placental trophoblastic growth. These disorders range from benign Benign Fibroadenoma molar pregnancies (complete and partial moles Moles Primary Skin Lesions) to neoplastic conditions such as invasive moles Moles Primary Skin Lesions and choriocarcinoma. Diagnosis is confirmed by elevated serum beta human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and ultrasound findings, which are dependent on the disorder. Treatment is primarily through dilation and curettage Curettage A scraping, usually of the interior of a cavity or tract, for removal of new growth or other abnormal tissue, or to obtain material for tissue diagnosis. It is performed with a curet (curette), a spoon-shaped instrument designed for that purpose. Benign Bone Tumors and/or methotrexate Methotrexate An antineoplastic antimetabolite with immunosuppressant properties. It is an inhibitor of tetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase and prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolate, necessary for synthesis of thymidylate, an essential component of DNA. Antimetabolite Chemotherapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hydatidiform moles Moles Primary Skin Lesions are characterized by cystic Cystic Fibrocystic Change swelling Swelling Inflammation of the chorionic villi Chorionic villi Threadlike vascular projections of the chorion. Chorionic villi may be free or embedded within the decidua forming the site for exchange of substances between fetal and maternal blood (placenta). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity and proliferation of the chorionic epithelium Epithelium The epithelium is a complex of specialized cellular organizations arranged into sheets and lining cavities and covering the surfaces of the body. The cells exhibit polarity, having an apical and a basal pole. Structures important for the epithelial integrity and function involve the basement membrane, the semipermeable sheet on which the cells rest, and interdigitations, as well as cellular junctions. Surface Epithelium: Histology. There are 2 types: complete mole Mole Nevi (singular nevus), also known as “moles,” are benign neoplasms of the skin. Nevus is a non-specific medical term because it encompasses both congenital and acquired lesions, hyper- and hypopigmented lesions, and raised or flat lesions. Nevus/Nevi and partial mole Mole Nevi (singular nevus), also known as “moles,” are benign neoplasms of the skin. Nevus is a non-specific medical term because it encompasses both congenital and acquired lesions, hyper- and hypopigmented lesions, and raised or flat lesions. Nevus/Nevi.
| Complete mole Mole Nevi (singular nevus), also known as “moles,” are benign neoplasms of the skin. Nevus is a non-specific medical term because it encompasses both congenital and acquired lesions, hyper- and hypopigmented lesions, and raised or flat lesions. Nevus/Nevi | Partial mole Mole Nevi (singular nevus), also known as “moles,” are benign neoplasms of the skin. Nevus is a non-specific medical term because it encompasses both congenital and acquired lesions, hyper- and hypopigmented lesions, and raised or flat lesions. Nevus/Nevi | |
|---|---|---|
| Karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System | 46,XX or 46,XY | Triploid (69,XXX, 69, XXY XXY Klinefelter syndrome is a chromosomal aneuploidy characterized by the presence of 1 or more extra X chromosomes in a male karyotype, most commonly leading to karyotype 47,XXY. Klinefelter syndrome is associated with decreased levels of testosterone and is the most common cause of congenital hypogonadism. Klinefelter Syndrome, or 69,XYY) |
| Formed from | Enucleated egg and a single sperm | 2 sperm and 1 egg |
| Fetal parts | Absent | Present |
| Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) level | ↑↑↑ | ↑ |
| Ultrasound findings |
|
Reveals fetal parts |
| Malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax risk | Higher risk for choriocarcinoma | Rare |
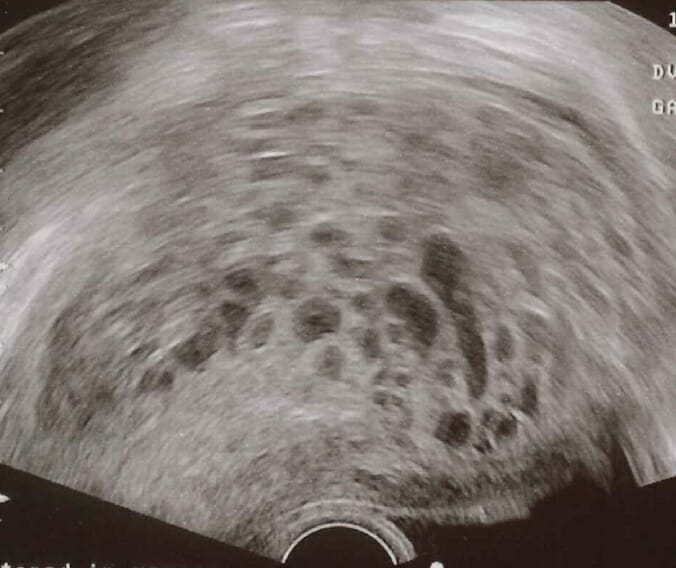
Transvaginal ultrasound of a hydatidiform mole: A characteristic “snowstorm pattern” is observed in ultrasound scan.
Image: “Transvaginal ultrasonography showing a molar pregnancy” by Mikael Häggström. License: CC0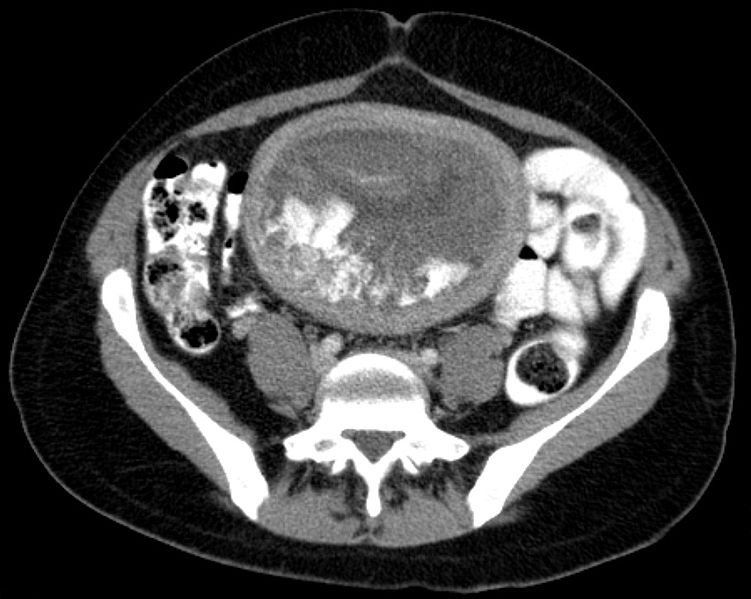
Hydatid in axial computed tomography (CT) image
Image: “Blasenmole Computertomographie axial” by Hellerhoff. License: CC BY-SA 3.0Choriocarcinoma is a highly aggressive malignant neoplasm of trophoblastic cells that can develop during or after pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care in the mother or baby.
Can be preceded by:
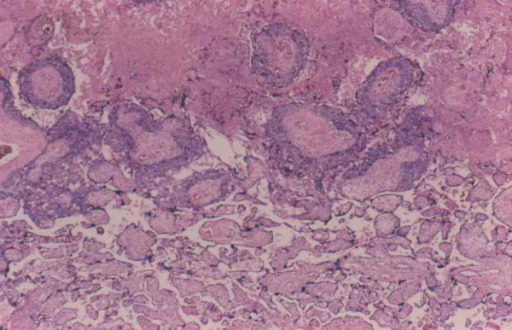
Choriocarcinoma with central necrosis
Image: “Interface between choriocarcinoma with central necrosis and normal placenta” by Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, St. Louis University, Missouri, USA. License: CC BY 2.0The following conditions are differential diagnoses of gestational trophoblastic disease: