Traumatic injuries to the genitourinary (GU) tract include injuries to the kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy, ureter, bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess, urethra Urethra A tube that transports urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body in both the sexes. It also has a reproductive function in the male by providing a passage for sperm. Urinary Tract: Anatomy, or genitals. Typically, injuries to the GU tract alone are not life threatening, but can be associated with other potentially more significant injuries. The GU system is divided into the upper GU tract ( kidneys Kidneys The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located retroperitoneally against the posterior wall of the abdomen on either side of the spine. As part of the urinary tract, the kidneys are responsible for blood filtration and excretion of water-soluble waste in the urine. Kidneys: Anatomy and ureters Ureters One of a pair of thick-walled tubes that transports urine from the kidney pelvis to the urinary bladder. Urinary Tract: Anatomy) and the lower GU tract ( bladder Bladder A musculomembranous sac along the urinary tract. Urine flows from the kidneys into the bladder via the ureters, and is held there until urination. Pyelonephritis and Perinephric Abscess, urethra Urethra A tube that transports urine from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body in both the sexes. It also has a reproductive function in the male by providing a passage for sperm. Urinary Tract: Anatomy, and external genitalia). Mechanisms include blunt and penetrating injuries. Diagnosis relies on thorough physical exam and imaging. Management depends on the severity of injury and ranges from simple observation and supportive measures to major surgical interventions. Timely diagnosis and intervention are crucial for preventing complications and ensuring optimal outcomes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Upper genitourinary (GU) tract:
Lower GU tract:
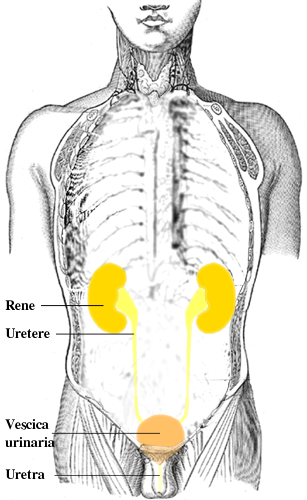
Organs of the urinary tract
Image: “Urinary tract it” by Lennert B. License: CC BY 2.5Blunt injuries:
Penetrating injuries:
Pathophysiology:
Clinical presentation:
Diagnosis:
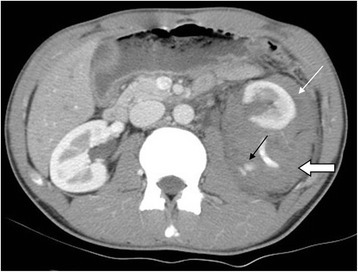
Grade IV left renal injury from a motor vehicle accident
Contrast-enhanced CT in arterial phase in axial section showed contrast medium extravasation (black arrow), perirenal hematoma (open arrow), and pararenal hematoma (white arrow).
Management:
Mechanisms:
Symptoms:
Diagnosis:
Management:
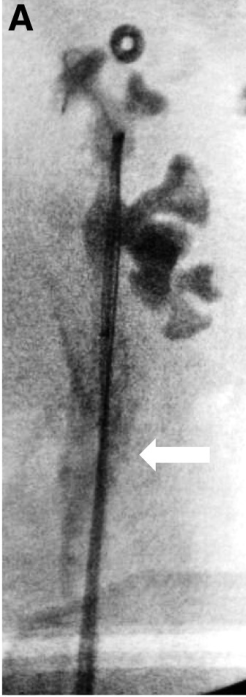
Iatrogenic ureteral trauma sustained during ureter instrumentation
Intra-operative pyelogram shows contrast extravasation (arrow) from left ureter.
Extraperitoneal:
Intraperitoneal Intraperitoneal Peritoneum: Anatomy:
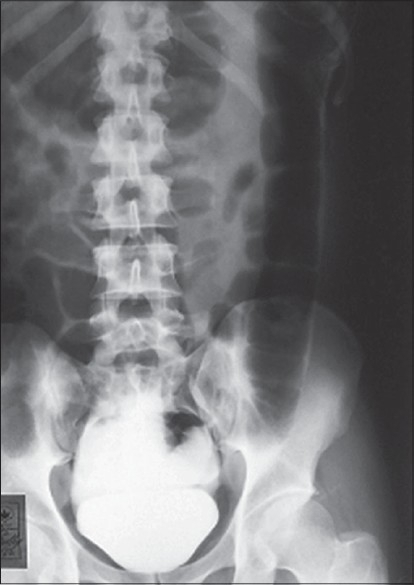
Intraperitoneal bladder rupture: cystogram showing leakage of the contrast into the peritoneal cavity
Image: “Intraperitoneal bladder rupture mimicking acute renal failure” by Arun KG. License: CC BY 2.0Symptoms:
Anterior urethral injuries:
Posterior urethral injuries:
Diagnosis: retrograde urethrogram (RUG)
Management:
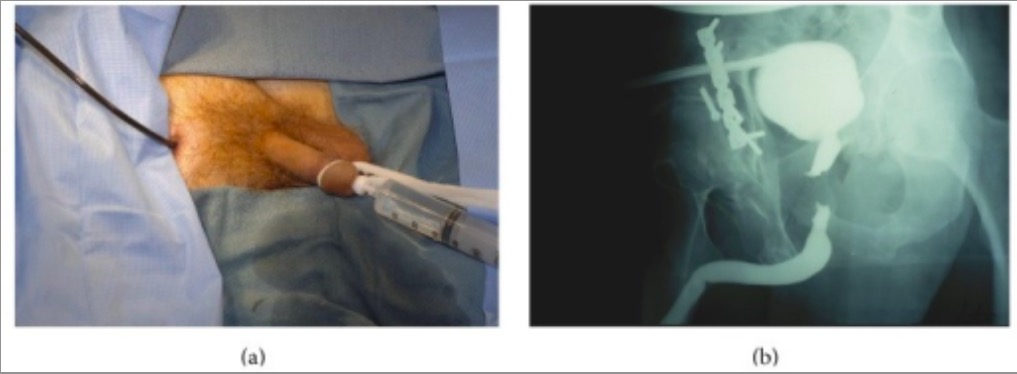
Individual with a history of pelvic trauma:
(a): A retrograde urethrogram is performed as contrast is simultaneously injected into the posterior urethra through the flexible cystoscope with the tip in the distal prostatic urethra.
(b): Imaging accurately demonstrates the length and location of the defect.

Penile fracture: clinical photograph showing a swollen penis with ‘egg plant’ deformity and deviation to the right side
Image: “Synergism of clinical evaluation and penile sonographic imaging in diagnosis of penile fracture: a case report” by Bello JO. License: CC BY 2.0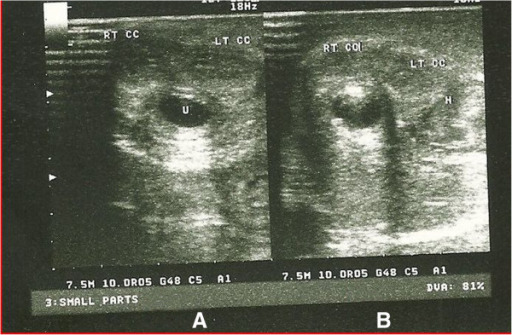
Sonourethrogram of penile fracture
A: Sonourethrogram at the distal aspect of the penile shaft, showing a normal right (RT CC) and left corpus cavernosa (LT CC) and normal urethra (U)
B: Sonourethrogram at the proximal 1/3 of the penile shaft showing a normal right corpus cavernosum, and a ruptured left corpus cavernosum with associated hematoma (H)