Both gastrulation and neurulation are critical events that occur during the 3rd week of embryonic development. Gastrulation is the process by which the bilaminar disk differentiates into a trilaminar disc, made up of the 3 primary germ layers: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm. During this process, a structure called the notochord is formed in the midline in the mesodermal layer; the notochord is critical in inducing neurulation. Neurulation is the process by which some of the ectoderm in the trilaminar embryo Embryo The entity of a developing mammal, generally from the cleavage of a zygote to the end of embryonic differentiation of basic structures. For the human embryo, this represents the first two months of intrauterine development preceding the stages of the fetus. Fertilization and First Week develops into the neural tube and neural crest Neural crest The two longitudinal ridges along the primitive streak appearing near the end of gastrulation during development of nervous system (neurulation). The ridges are formed by folding of neural plate. Between the ridges is a neural groove which deepens as the fold become elevated. When the folds meet at midline, the groove becomes a closed tube, the neural tube. Hirschsprung Disease cells, which will go on to form all of the neural tissue in the body. This process is completed by the end of the 3rd week.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Progression of early human development from fertilization through the blastocyst stage:
During these stages, the embryo is surrounded by a layer of extracellular matrix known as the zona pellucida.

Development of the bilaminar dikc as the embryo is invading into the uterine wall:
As the cytotrophoblast cells divide, cells on the uterine side begin losing their membranes, releasing hydrolytic enzymes and allowing the embryo to “digest” some of the uterine lining to facilitate implantation. These “free nuclei” are the syncytiotrophoblast cells.
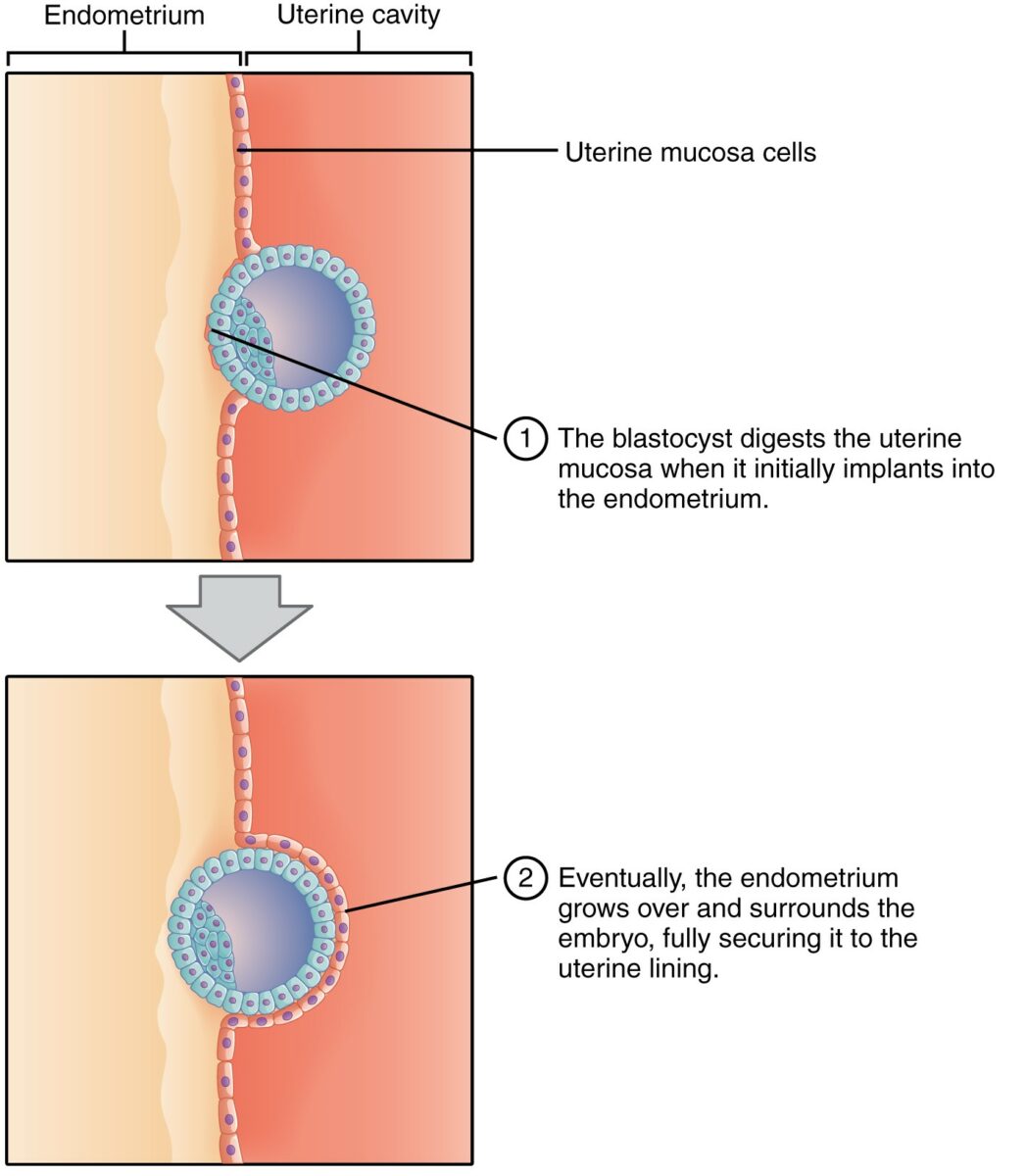
Implantation of the blastocyst:
At this stage, the embryo exists as an outer cell mass and an inner cell mass. Note how, as the blastocyst digests the uterine wall, a layer of endometrium (pink cells) grows over and surrounds the embryo, securing it to the uterine lining.
Image: “Implantation” by Phil Schatz. License: CC BY 4.0, cropped by Lecturio.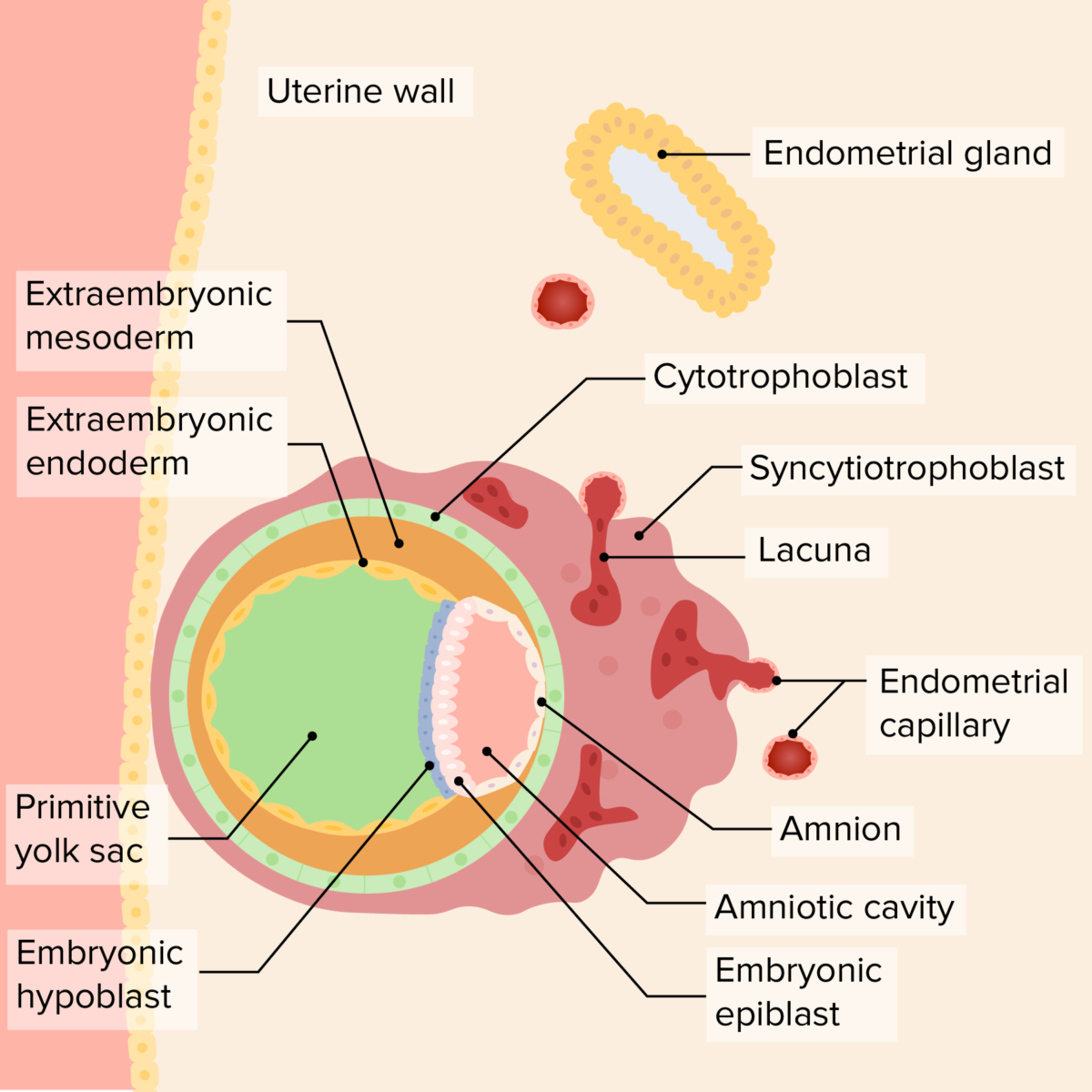
Relationship of the bilaminar disc, yolk sac, and amniotic cavity in the early embryo:
As the embryo invades further, the endometrial lining covers the embryo, securing it to the uterine wall. The primary yolk sac develops “beneath” the hypoblast, while the amniotic cavity begins growing “above” the epiblast. The syncytiotrophoblast surrounds endometrial capillaries, which rupture, forming lacuna, which will ultimately become the maternal component of the placenta. A layer of extraembryonic mesoderm grows outside both the yolk sac and the amniotic cavity; ultimately the chorionic cavity will develop in this area.
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Gastrulation is the process by which the bilaminar disk develops into the trilaminar disc.
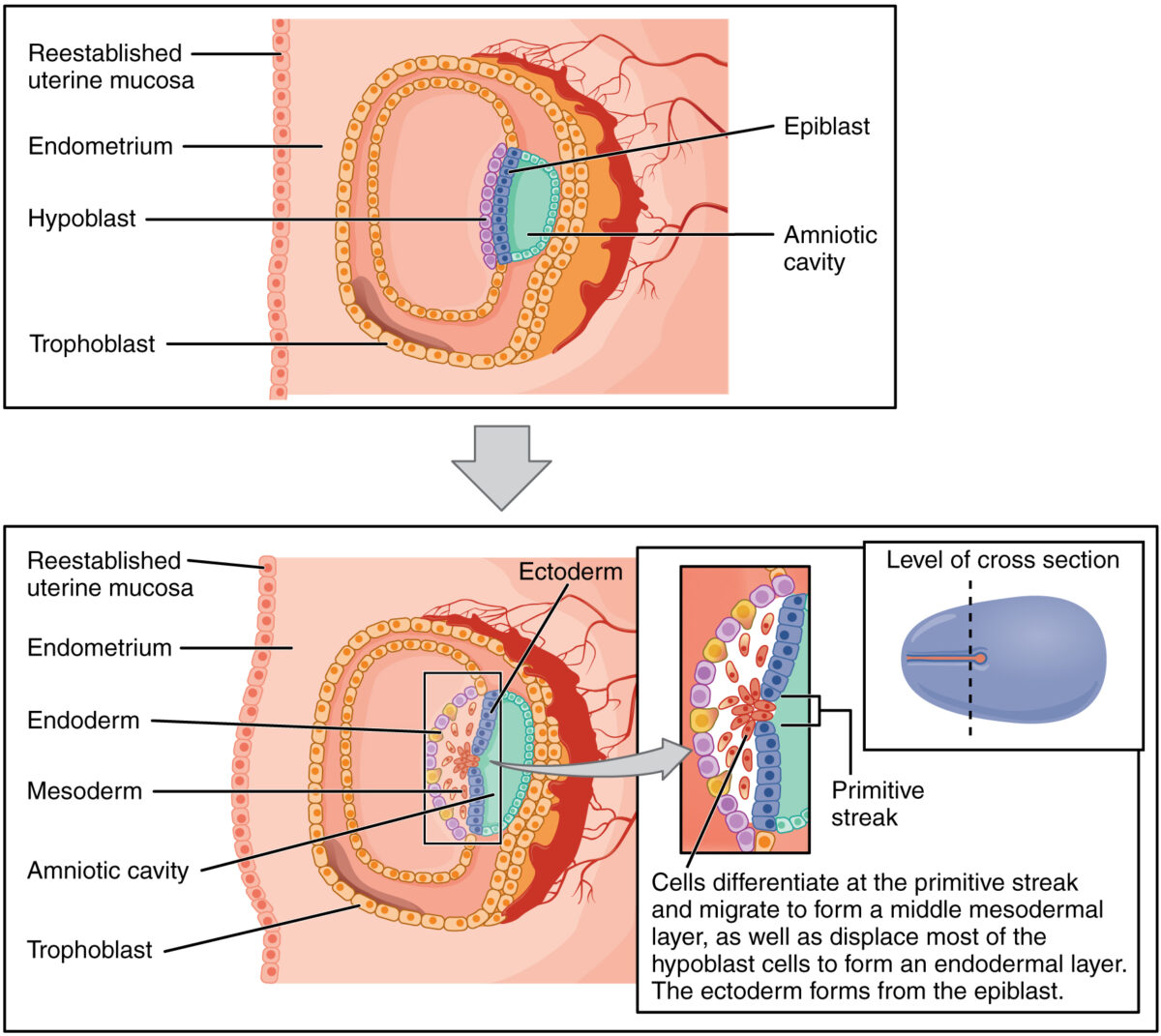
Process of gastrulation:
Cells from the epiblast migrate down through the primitive streak and displace most of the hypoblast cells, becoming the endoderm. Cells that remain in the middle become the mesoderm. Cells that remain in the epiblast layer become the ectoderm.
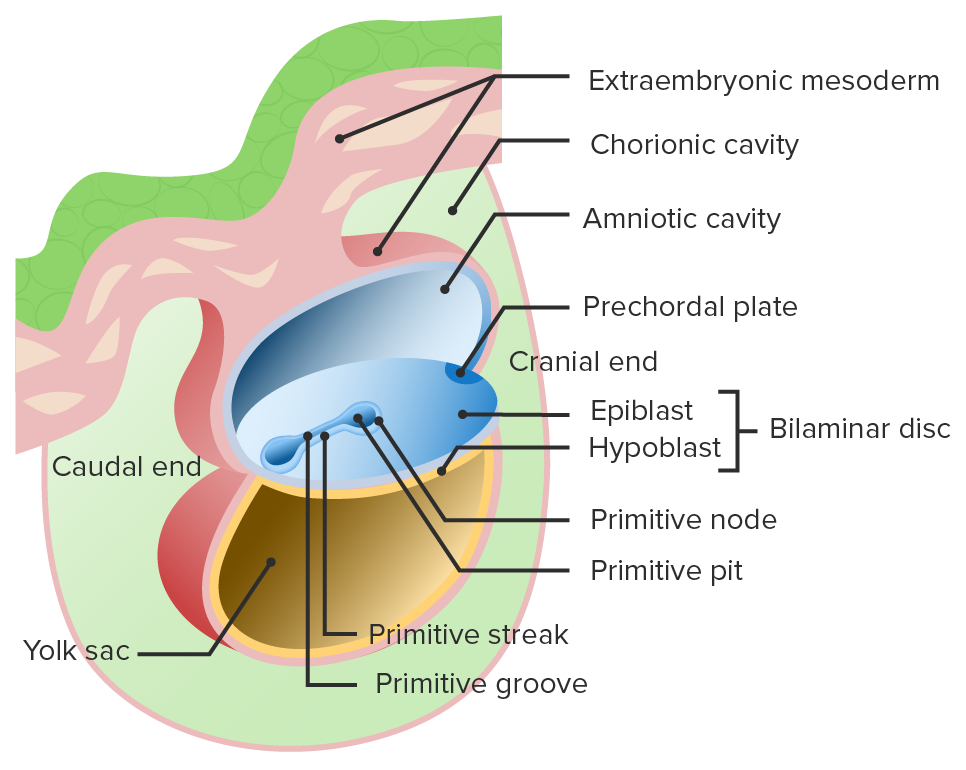
Beginning of gastrulation:
The primitive streak and primitive groove form in the bilaminar disc.
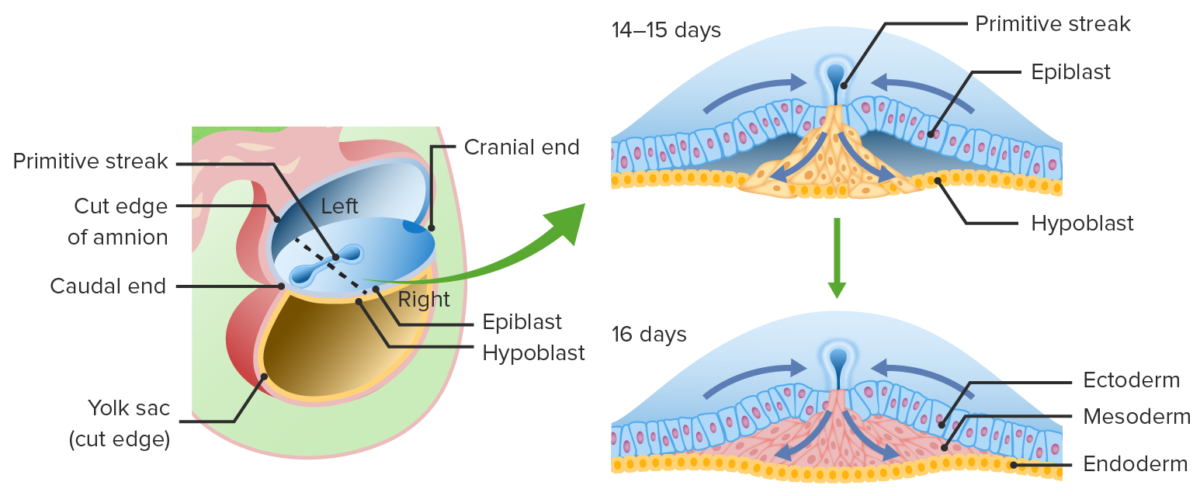
Migration of epiblast cells through the primitive groove:
These epiblast cells displace the hypoblast to become the endoderm and create a middle layer known as mesoderm. Epiblast cells that remain on the dorsal surface differentiate into ectoderm.
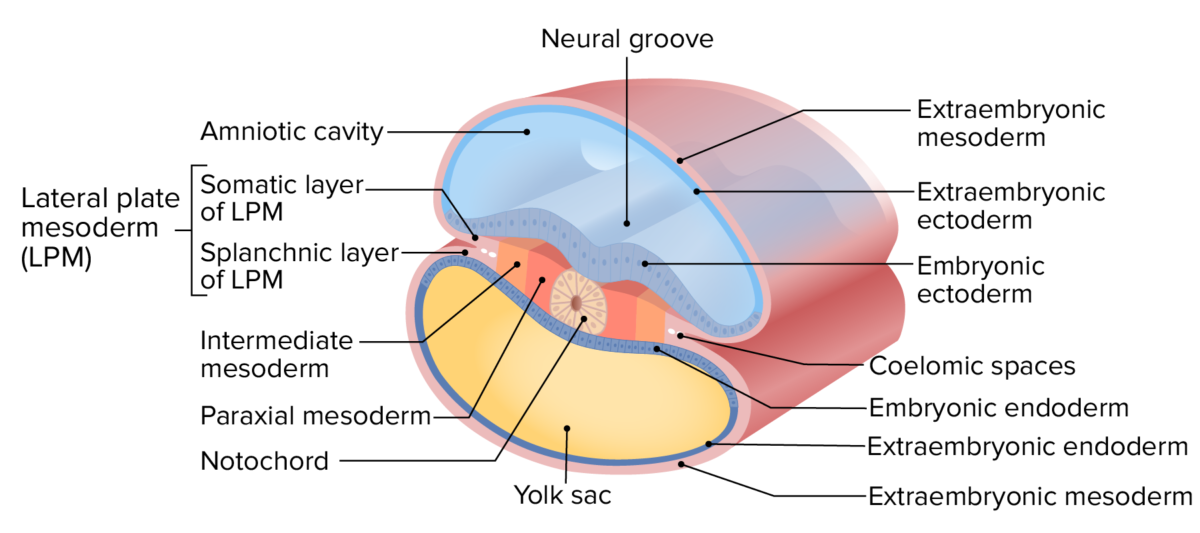
Layers of the trilaminar disc
Image by Lecturio.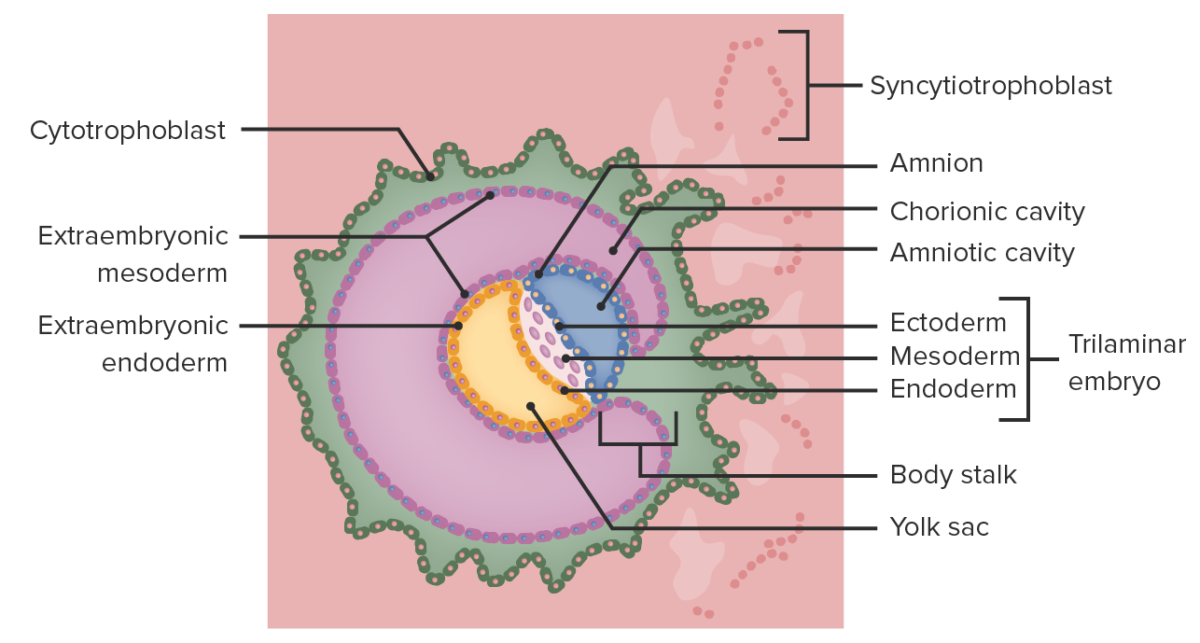
Formation of the chorionic cavity
Image by Lecturio.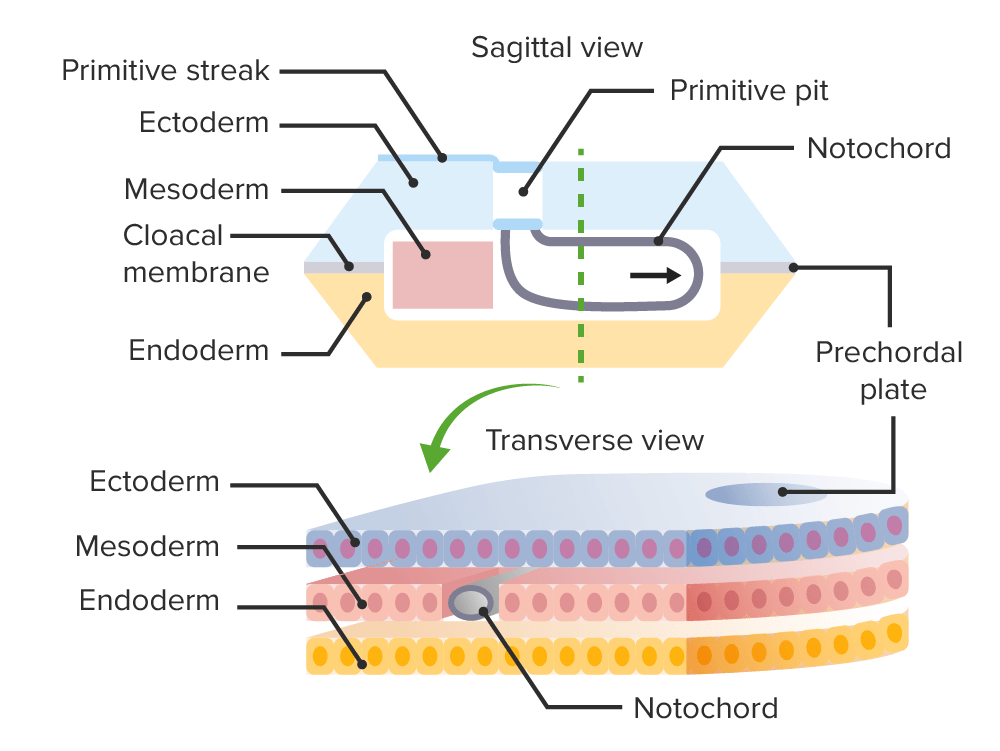
Formation of the notochord during gastrulation.
Image by Lecturio.Neurulation is the process by which ectoderm in the trilaminar embryo Embryo The entity of a developing mammal, generally from the cleavage of a zygote to the end of embryonic differentiation of basic structures. For the human embryo, this represents the first two months of intrauterine development preceding the stages of the fetus. Fertilization and First Week develops into the neural tube.
Beginning in the 3rd week, a group of ectodermal cells progresses through the following structures:
Development requires folate Folate Folate and vitamin B12 are 2 of the most clinically important water-soluble vitamins. Deficiencies can present with megaloblastic anemia, GI symptoms, neuropsychiatric symptoms, and adverse pregnancy complications, including neural tube defects. Folate and Vitamin B12; folate deficiency Folate deficiency A nutritional condition produced by a deficiency of folic acid in the diet. Many plant and animal tissues contain folic acid, abundant in green leafy vegetables, yeast, liver, and mushrooms but destroyed by long-term cooking. Alcohol interferes with its intermediate metabolism and absorption. Folic acid deficiency may develop in long-term anticonvulsant therapy or with use of oral contraceptives. This deficiency causes anemia, macrocytic anemia, and megaloblastic anemia. It is indistinguishable from vitamin B12 deficiency in peripheral blood and bone marrow findings, but the neurologic lesions seen in B12 deficiency do not occur. Megaloblastic Anemia → neural tube defects Neural tube defects Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed NTD) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open NTD). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects
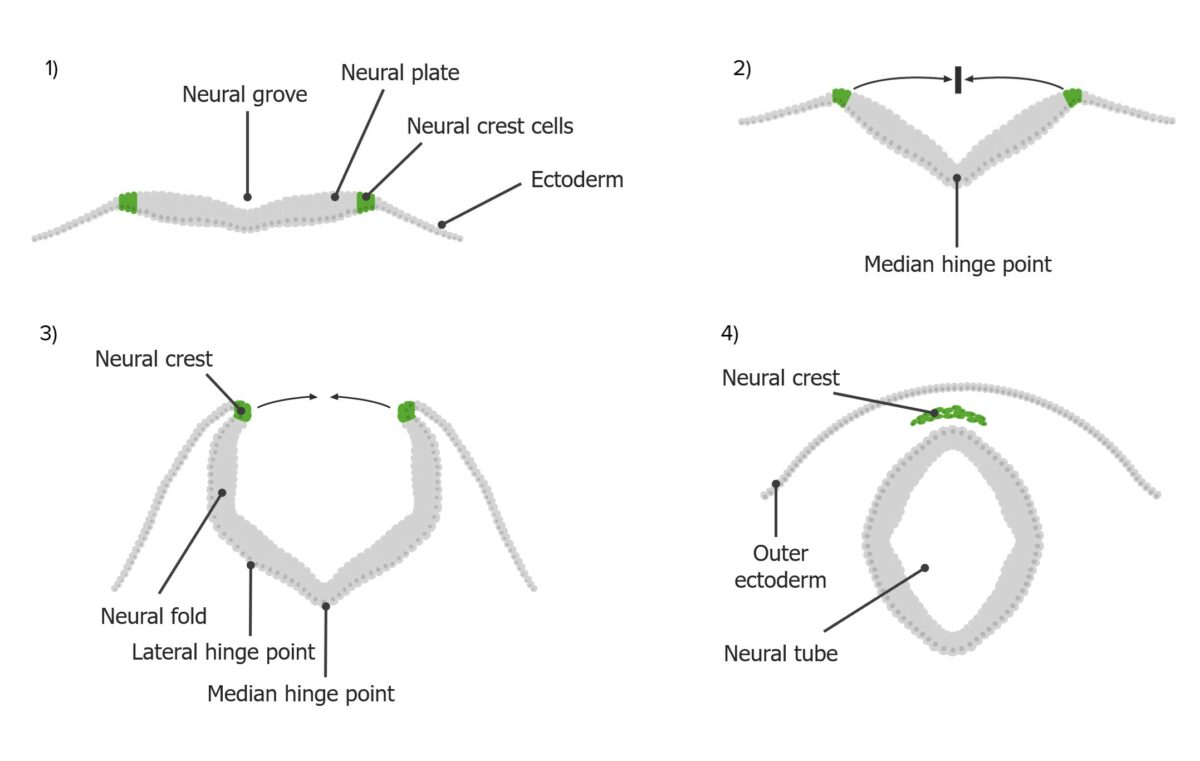
The process of neurulation:
Neural crest cells (green) are derived from the neural plate (gray), which folds upwards and inwards towards the midline to create the neural tube.
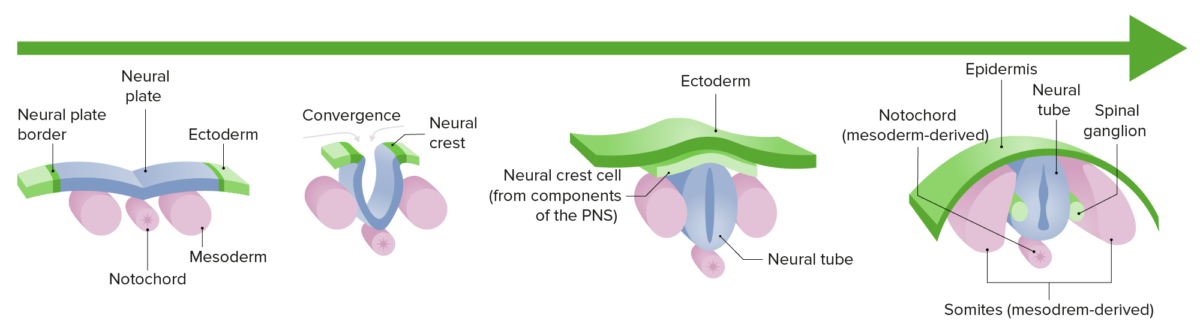
Neurulation:
Differentiation and growth of the neural plate into the neural tube during the 1st trimester of gestation
Spontaneous abortion Abortion Expulsion of the product of fertilization before completing the term of gestation and without deliberate interference. Spontaneous Abortion ( miscarriage Miscarriage Spontaneous abortion, also known as miscarriage, is the loss of a pregnancy before 20 weeks’ gestation. However, the layperson use of the term “abortion” is often intended to refer to induced termination of a pregnancy, whereas “miscarriage” is preferred for spontaneous loss. Spontaneous Abortion): abnormalities of gastrulation typically result in multiple congenital Congenital Chorioretinitis anomalies. These embryos are typically incompatible with life, and the result is a spontaneous loss of the pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care, usually in the 1st trimester.
Neural tube defects Neural tube defects Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed NTD) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open NTD). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects ( NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects): caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during embryologic development, potentially resulting in protrusion of neural tissue. Neural tube defects Neural tube defects Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed NTD) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open NTD). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects may involve the spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is the major conduction pathway connecting the brain to the body; it is part of the CNS. In cross section, the spinal cord is divided into an H-shaped area of gray matter (consisting of synapsing neuronal cell bodies) and a surrounding area of white matter (consisting of ascending and descending tracts of myelinated axons). Spinal Cord: Anatomy and/or cranium Cranium The skull (cranium) is the skeletal structure of the head supporting the face and forming a protective cavity for the brain. The skull consists of 22 bones divided into the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) and the neurocranium. Skull: Anatomy and may be open (involving the meninges Meninges The brain and the spinal cord are enveloped by 3 overlapping layers of connective tissue called the meninges. The layers are, from the most external layer to the most internal layer, the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Between these layers are 3 potential spaces called the epidural, subdural, and subarachnoid spaces. Meninges: Anatomy and/or neural tissue) or closed (involving the bony vertebral column Vertebral column The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull and caudally by the sacrum. Vertebral Column: Anatomy). Prenatal diagnosis by ultrasonography and maternal α-fetoprotein level is common. Management of open NTDs NTDs Neural tube defects (NTDs) are the 2nd-most common type of congenital birth defects. Neural tube defects can range from asymptomatic (closed ntd) to very severe malformations of the spine or brain (open ntd). Neural tube defects are caused by the failure of the neural tube to close properly during the 3rd and 4th week of embryological development. Neural Tube Defects is mainly surgical.