Gastric acid Gastric acid Hydrochloric acid present in gastric juice. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) medications include proton pump Pump ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols inhibitors (PPIs) and H₂ receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors antagonists (also known as H₂ blockers). The drugs work through different mechanisms to suppress acid secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies by parietal cells Parietal cells Rounded or pyramidal cells of the gastric glands. They secrete hydrochloric acid and produce gastric intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein that binds vitamin B12. Stomach: Anatomy in the stomach Stomach The stomach is a muscular sac in the upper left portion of the abdomen that plays a critical role in digestion. The stomach develops from the foregut and connects the esophagus with the duodenum. Structurally, the stomach is C-shaped and forms a greater and lesser curvature and is divided grossly into regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. Stomach: Anatomy. The most common indications include peptic ulcer Peptic ulcer Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) refers to the full-thickness ulcerations of duodenal or gastric mucosa. The ulcerations form when exposure to acid and digestive enzymes overcomes mucosal defense mechanisms. The most common etiologies include Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and prolonged use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Peptic Ulcer Disease disease, GERD GERD Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) occurs when the stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus. This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of the esophagus, causing symptoms such as retrosternal burning pain (heartburn). Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD), and dyspepsia Dyspepsia Impaired digestion, especially after eating. Lactose Intolerance. Adverse effects of PPIs include malabsorption Malabsorption General term for a group of malnutrition syndromes caused by failure of normal intestinal absorption of nutrients. Malabsorption and Maldigestion, acute interstitial nephritis Acute interstitial nephritis Inflammation of the interstitial tissue of the kidney. This term is generally used for primary inflammation of kidney tubules and/or surrounding interstitium. For primary inflammation of glomerular interstitium, see glomerulonephritis. Infiltration of the inflammatory cells into the interstitial compartment results in edema, increased spaces between the tubules, and tubular renal dysfunction. Acute Kidney Injury, and an increased risk of Clostridioides difficile infection. Adverse effects of H₂ blockers include CNS effects, bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias/ hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension, gynecomastia Gynecomastia Gynecomastia is a benign proliferation of male breast glandular ductal tissue, usually bilateral, caused by increased estrogen activity, decreased testosterone activity, or medications. The condition is common and physiological in neonates, adolescent boys, and elderly men. Gynecomastia, and galactorrhea Galactorrhea Excessive or inappropriate lactation in females or males, and not necessarily related to pregnancy. Galactorrhea can occur either unilaterally or bilaterally, and be profuse or sparse. Its most common cause is hyperprolactinemia. Hyperprolactinemia. Both classes are associated with drug interactions related to the cytochrome P450 Cytochrome P450 A superfamily of hundreds of closely related hemeproteins found throughout the phylogenetic spectrum, from animals, plants, fungi, to bacteria. They include numerous complex monooxygenases (mixed function oxygenases). In animals, these p450 enzymes serve two major functions: (1) biosynthesis of steroids, fatty acids, and bile acids; (2) metabolism of endogenous and a wide variety of exogenous substrates, such as toxins and drugs (biotransformation). They are classified, according to their sequence similarities rather than functions, into cyp gene families (>40% homology) and subfamilies (>59% homology). For example, enzymes from the cyp1, cyp2, and cyp3 gene families are responsible for most drug metabolism. Drug-Induced Liver Injury system.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Parietal cells Parietal cells Rounded or pyramidal cells of the gastric glands. They secrete hydrochloric acid and produce gastric intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein that binds vitamin B12. Stomach: Anatomy are located in the body of the stomach Stomach The stomach is a muscular sac in the upper left portion of the abdomen that plays a critical role in digestion. The stomach develops from the foregut and connects the esophagus with the duodenum. Structurally, the stomach is C-shaped and forms a greater and lesser curvature and is divided grossly into regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. Stomach: Anatomy and secrete hydrochloric acid Hydrochloric acid A strong corrosive acid that is commonly used as a laboratory reagent. It is formed by dissolving hydrogen chloride in water. Gastric acid is the hydrochloric acid component of gastric juice. Caustic Ingestion (Cleaning Products) ( HCl HCL Hairy cell leukemia (HCL) is a rare, chronic, B-cell leukemia characterized by the accumulation of small mature B lymphocytes that have “hair-like projections” visible on microscopy. The abnormal cells accumulate in the peripheral blood, bone marrow (causing fibrosis), and red pulp of the spleen, leading to cytopenias. Hairy Cell Leukemia) into the lumen.
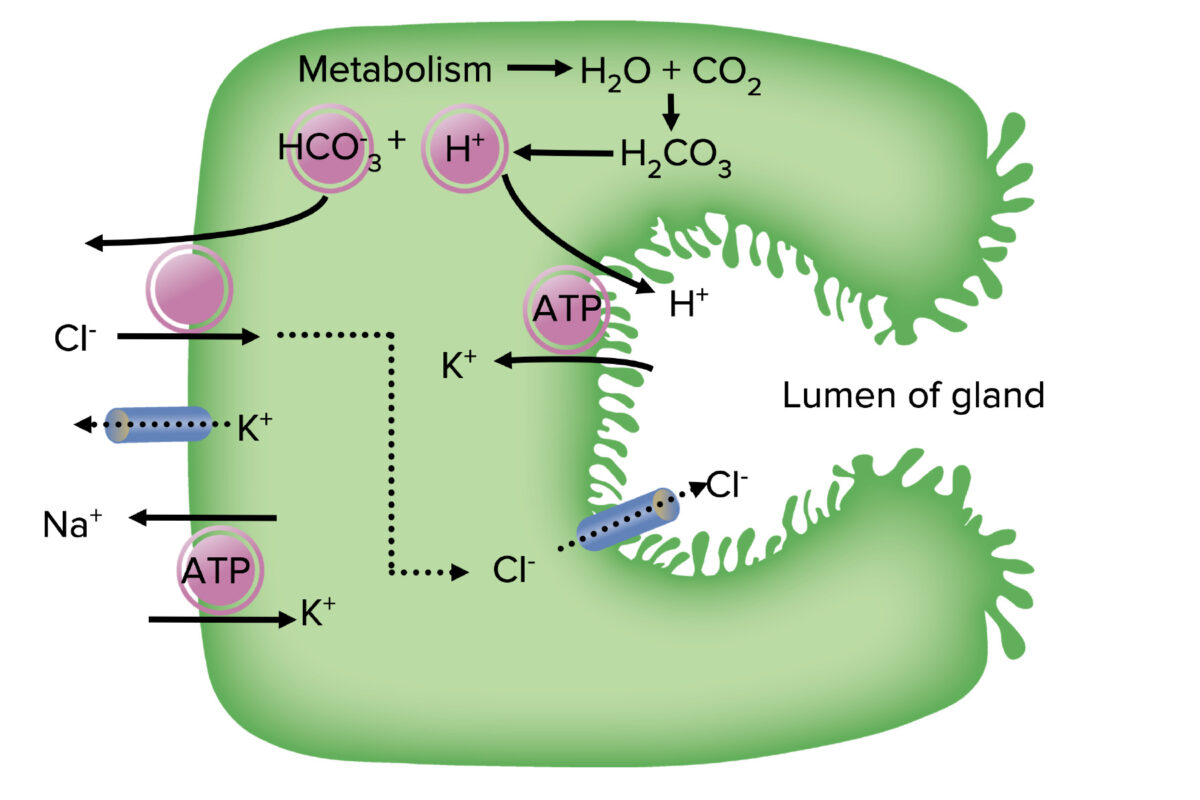
Ion transport in parietal cells:
Carbonic acid disassociates into a hydrogen (H+) ion and bicarbonate (HCO3–). The H+ is exchanged for potassium (K+) in the apical membrane by the H+/K+ ATPase. Bicarbonate is exchanged for chloride (Cl–) in the basolateral membrane, which then moves into the lumen. The Na+/K+ ATPase pump in the basolateral membrane creates the cell’s electrochemical gradient.
Acid production is stimulated by:
Common medication classes used to control gastric acid Gastric acid Hydrochloric acid present in gastric juice. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies include:
Proton pump Pump ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols inhibitors are a group of drugs irreversibly inhibiting the H+/K+ ATPase pump Pump ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols in gastric parietal cells Parietal cells Rounded or pyramidal cells of the gastric glands. They secrete hydrochloric acid and produce gastric intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein that binds vitamin B12. Stomach: Anatomy.
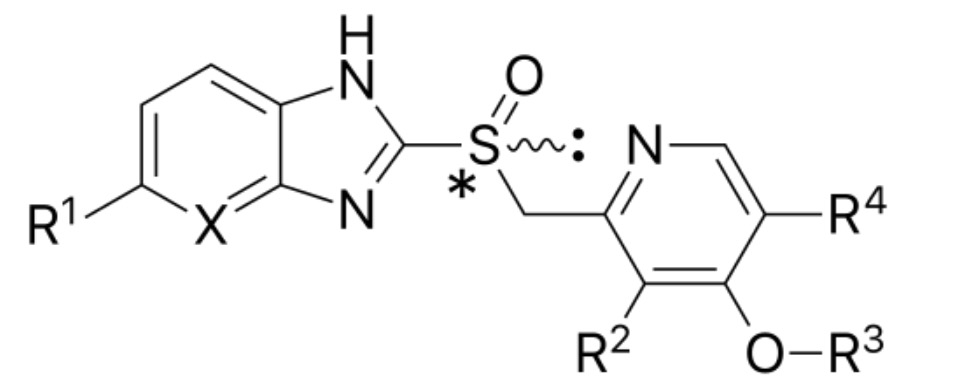
The basic chemical structure for proton pump inhibitors (PPIs):
Notice the benzimidazole structure on the left and the pyridine ring on the right.
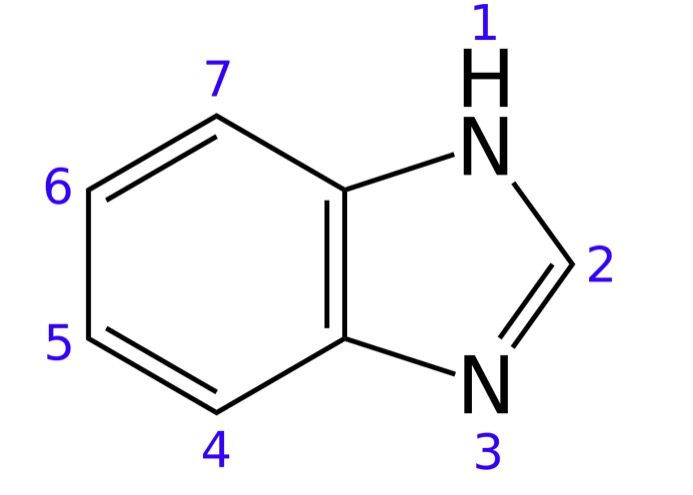
The chemical structure of benzimidazole (the base of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs))
Image: “Skeletal formula of benzimidazole with numbering convention” by Jynto. License: CC0 1.0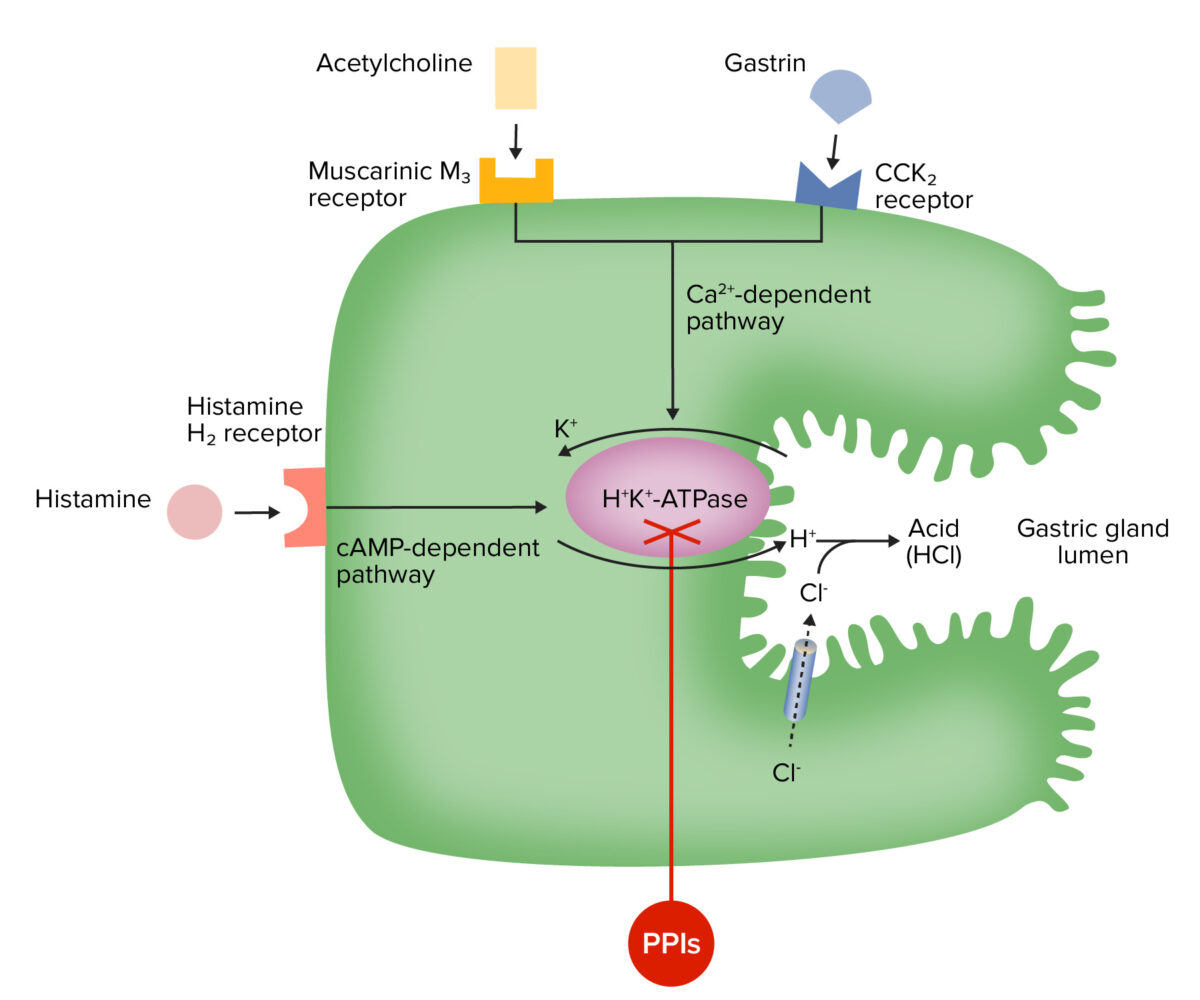
Mechanism of action of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs):
The drugs accumulate in the gland lumen, convert to the active form, and covalently bond to the H+/K+ ATPase, which results in irreversible pump inactivation and reduced acid secretion.
Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption:
Distribution:
Metabolism:
Excretion:
H₂ receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors antagonists (also known as H₂ blockers) are competitive inhibitors of H₂ receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors in parietal cells Parietal cells Rounded or pyramidal cells of the gastric glands. They secrete hydrochloric acid and produce gastric intrinsic factor, a glycoprotein that binds vitamin B12. Stomach: Anatomy, which aid in the reduction of acid secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies.
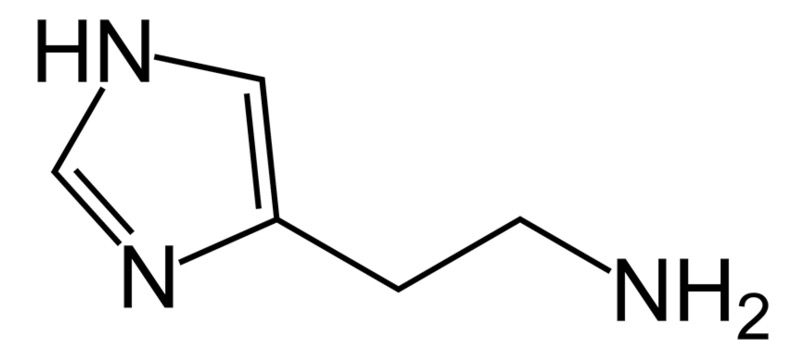
Chemical structure of histamine
Image: “Histamine” by Vaccinationist. License: Public Domain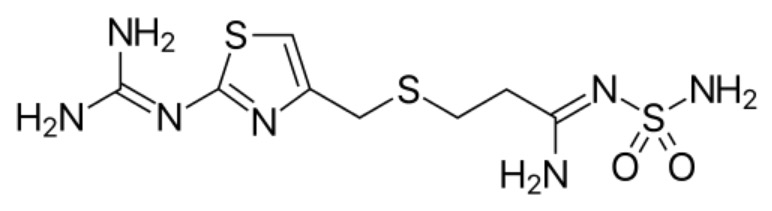
Chemical structure of famotidine:
Notice the similar base structure to histamine.
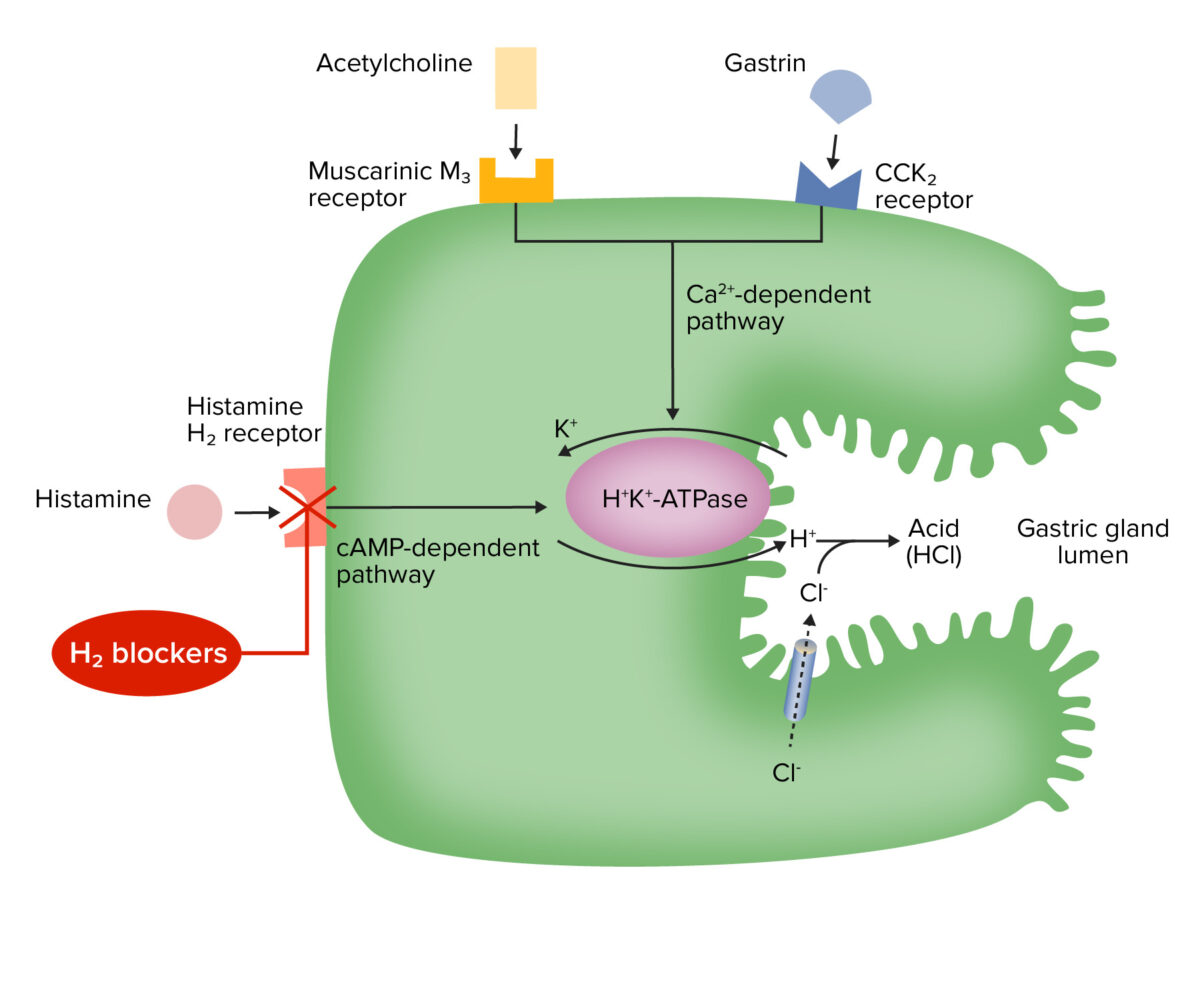
Mechanism of action for H2 receptor antagonists (H2 blockers):
The antihistamine effect blocks the activation of H+/K+ ATPase through the cAMP-dependent pathway, resulting in decreased acid secretion.
The medications can be potent inhibitors of cytochrome P450 Cytochrome P450 A superfamily of hundreds of closely related hemeproteins found throughout the phylogenetic spectrum, from animals, plants, fungi, to bacteria. They include numerous complex monooxygenases (mixed function oxygenases). In animals, these p450 enzymes serve two major functions: (1) biosynthesis of steroids, fatty acids, and bile acids; (2) metabolism of endogenous and a wide variety of exogenous substrates, such as toxins and drugs (biotransformation). They are classified, according to their sequence similarities rather than functions, into cyp gene families (>40% homology) and subfamilies (>59% homology). For example, enzymes from the cyp1, cyp2, and cyp3 gene families are responsible for most drug metabolism. Drug-Induced Liver Injury (particularly cimetidine Cimetidine A histamine congener, it competitively inhibits histamine binding to histamine h2 receptors. Cimetidine has a range of pharmacological actions. It inhibits gastric acid secretion, as well as pepsin and gastrin output. Antihistamines), resulting in ↑ plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products concentrations of: