Galactosemia is a disorder caused by defects in galactose Galactose An aldohexose that occurs naturally in the d-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins. Deficiency of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase causes an error in galactose metabolism called galactosemia, resulting in elevations of galactose in the blood. Lactose Intolerance metabolism. Galactosemia is an inherited, autosomal-recessive condition, which results in inadequate galactose Galactose An aldohexose that occurs naturally in the d-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins. Deficiency of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase causes an error in galactose metabolism called galactosemia, resulting in elevations of galactose in the blood. Lactose Intolerance processing and high blood levels of monosaccharide. The rare disorder often presents in infants with symptoms of lethargy Lethargy A general state of sluggishness, listless, or uninterested, with being tired, and having difficulty concentrating and doing simple tasks. It may be related to depression or drug addiction. Hyponatremia, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia, diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea, and jaundice Jaundice Jaundice is the abnormal yellowing of the skin and/or sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin. Hyperbilirubinemia is caused by either an increase in bilirubin production or a decrease in the hepatic uptake, conjugation, or excretion of bilirubin. Jaundice. Serious neurologic complications such as speech and motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology deficits (e.g., ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia) may occur. Diagnosis is made through blood testing, which detects an absence or low level of the enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body's constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes necessary to process galactose Galactose An aldohexose that occurs naturally in the d-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins. Deficiency of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase causes an error in galactose metabolism called galactosemia, resulting in elevations of galactose in the blood. Lactose Intolerance. Treatment is avoidance of lactose and galactose Galactose An aldohexose that occurs naturally in the d-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins. Deficiency of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase causes an error in galactose metabolism called galactosemia, resulting in elevations of galactose in the blood. Lactose Intolerance in the diet.
Last updated: Apr 17, 2025
Galactosemia is an autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance, inborn error Error Refers to any act of commission (doing something wrong) or omission (failing to do something right) that exposes patients to potentially hazardous situations. Disclosure of Information of carbohydrate metabolism resulting in the inability of the body to metabolize galactose Galactose An aldohexose that occurs naturally in the d-form in lactose, cerebrosides, gangliosides, and mucoproteins. Deficiency of galactosyl-1-phosphate uridyltransferase causes an error in galactose metabolism called galactosemia, resulting in elevations of galactose in the blood. Lactose Intolerance into glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance.
Galactosemia is an inherited disorder caused by a genetic mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations, which leads to enzyme deficiency.
The condition is autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance: Each child has a 25% chance of inheriting the disease if both parents are affected.
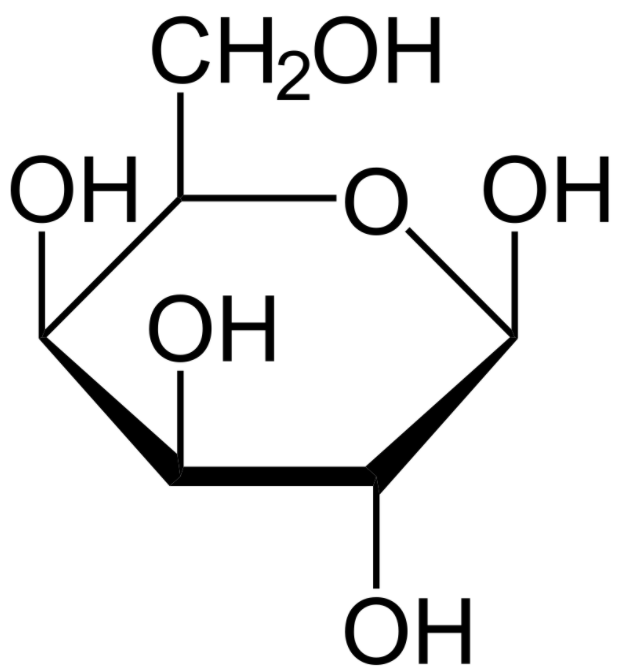
A structure of the monosaccharide galactose (Haworth projection):
Patients with galactosemia are unable to degrade galactose. Glucose and galactose have the same chemical formula but differ in the location of the 1 hydroxyl group.
Symptoms may appear days to weeks after birth.
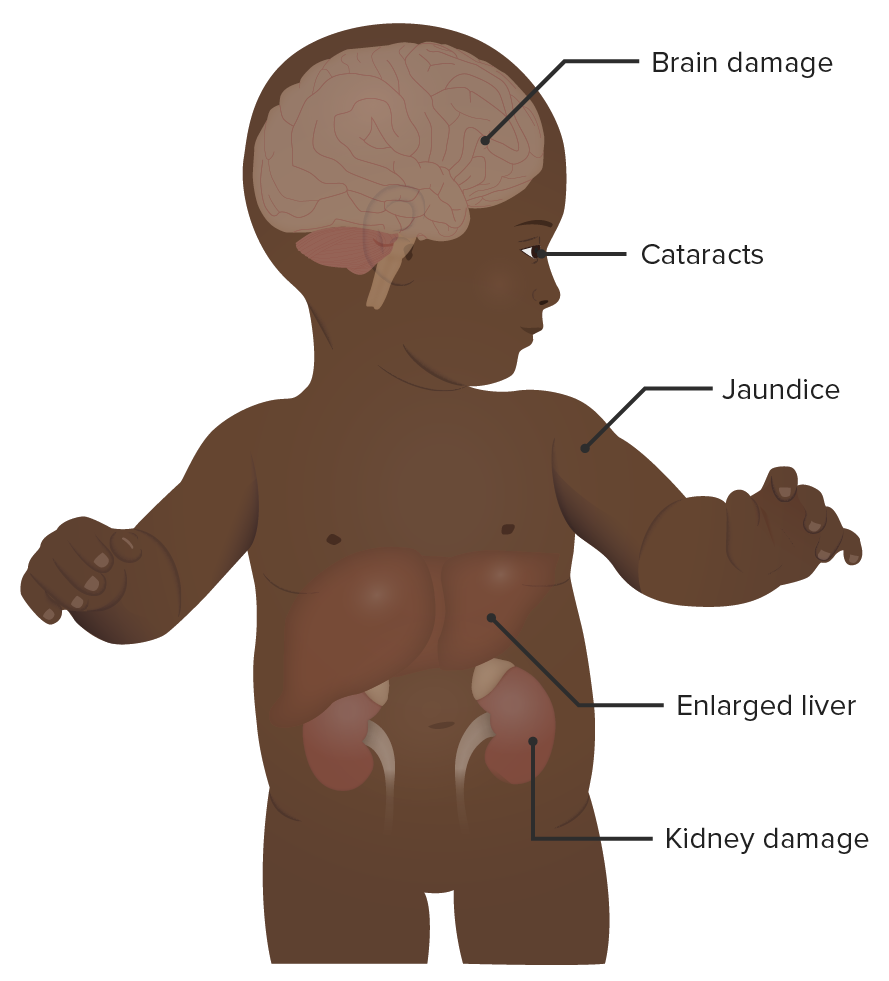
A baby with galactosemia:
As noted in the image, galactosemia has numerous clinical signs and symptoms. Neurologic, renal, hepatic, and ocular side effects may occur. The symptoms appear early and are often apparent within the 1st month of life.
The test should be performed on all infants who exhibit symptoms.