Injuries due to cold weather are common among children and athletes who are involved in sports played in cold conditions. There are multiple cold-related injuries, with frostbite being the most common. Frostbite is a direct freezing injury to the peripheral tissues and occurs when the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions temperature drops below 0℃ (32°F). Common sites of frostbite include the nose Nose The nose is the human body's primary organ of smell and functions as part of the upper respiratory system. The nose may be best known for inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide, but it also contributes to other important functions, such as tasting. The anatomy of the nose can be divided into the external nose and the nasal cavity. Nose Anatomy (External & Internal), ears, fingers, and toes. Clinical signs include skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions pallor, anesthesia Anesthesia A state characterized by loss of feeling or sensation. This depression of nerve function is usually the result of pharmacologic action and is induced to allow performance of surgery or other painful procedures. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts, blistering, and tissue necrosis Necrosis The death of cells in an organ or tissue due to disease, injury or failure of the blood supply. Ischemic Cell Damage. The main treatment is rapid rewarming.
Last updated: Mar 25, 2025
Frostbite is injury to tissue resulting from cold exposure at temperatures below 0°C (32°F). Frostbite exists on the severe end of a spectrum, with frostnip and pernio at the milder end.
| Phase | Symptoms | Signs |
|---|---|---|
| Early | Cold, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, paresthesia | Deceptively few: discoloration, waxy/stiff tissue texture Texture Dermatologic Examination |
| Middle | Numbness, complete sensory Sensory Neurons which conduct nerve impulses to the central nervous system. Nervous System: Histology loss, loss of dexterity | Formation of blisters or bullae Bullae Erythema Multiforme, desquamation Desquamation Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS) |
| Late | Throbbing pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways that may persist for months or weeks | Tissue loss, demarcation, dry gangrene Gangrene Death and putrefaction of tissue usually due to a loss of blood supply. Small Bowel Obstruction |
Frostbite injury results from:
4 phases:
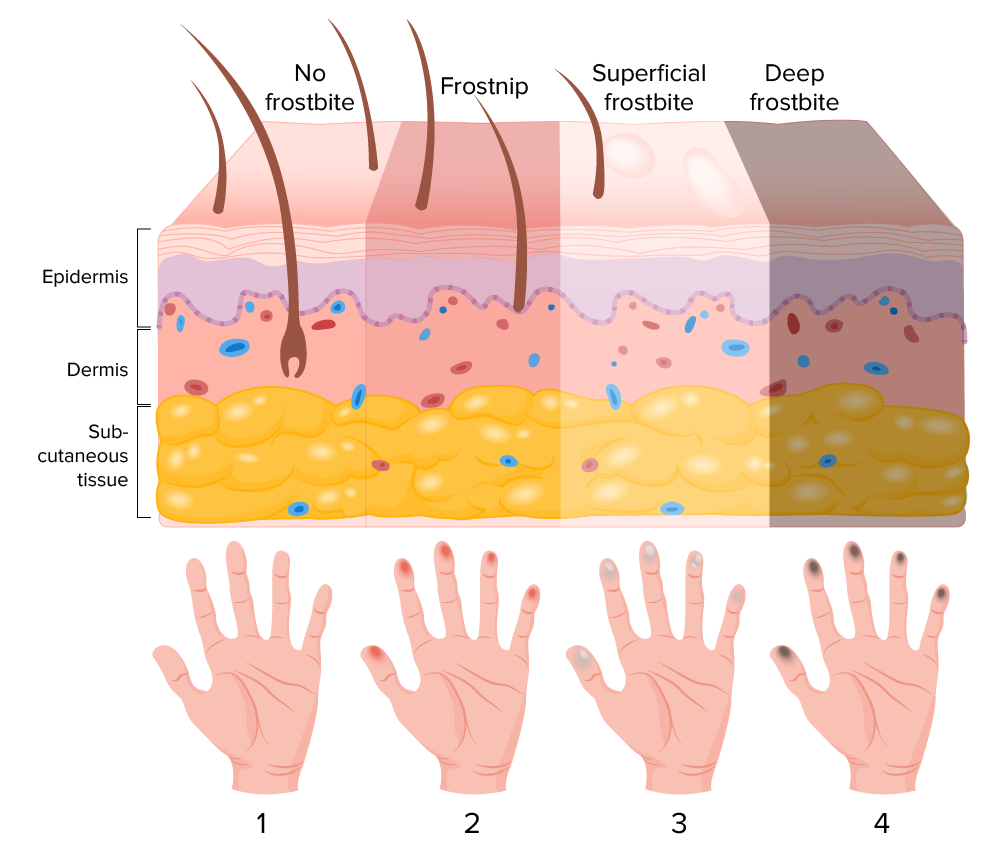
Stages of frostbite
Image by Lecturio.The diagnosis of frostbite is clinical and should be distinguished from less severe forms of cold injury (frostnip).
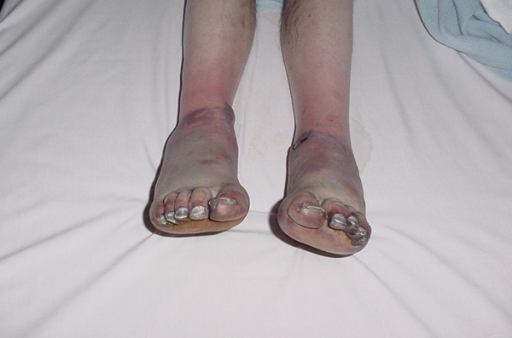
Initial presentation of frostbite on day 2
Image: “Grade IV frostbite requiring bilateral below knee amputations: a case report” by Ramdass MJ. License: CC BY 3.0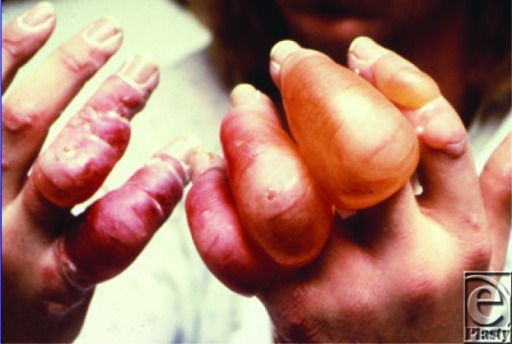
Frostbite in a 12-year-old girl who presented to the emergency department after waiting at a bus stop in winter
Image: “Urban blisters” by Chang N, Nunn R, Milner SM, Price LA. License: CC BY 2.0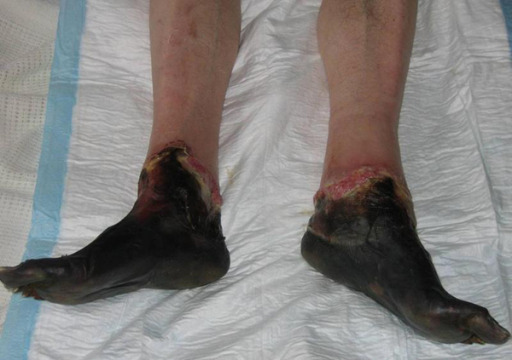
Appearance of grade IV frostbite with completely mummified feet 3 weeks post-injury
Image: “Grade IV frostbite requiring bilateral below knee amputations: a case report” by Ramdass MJ. License: CC BY 3.0