Friedreich ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia is an autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance disorder characterized by progressive spinocerebellar degeneration. It presents in the 1st to 2nd decades of life with progressive gait Gait Manner or style of walking. Neurological Examination ataxia Ataxia Impairment of the ability to perform smoothly coordinated voluntary movements. This condition may affect the limbs, trunk, eyes, pharynx, larynx, and other structures. Ataxia may result from impaired sensory or motor function. Sensory ataxia may result from posterior column injury or peripheral nerve diseases. Motor ataxia may be associated with cerebellar diseases; cerebral cortex diseases; thalamic diseases; basal ganglia diseases; injury to the red nucleus; and other conditions. Ataxia-telangiectasia, weakness, tremor Tremor Cyclical movement of a body part that can represent either a physiologic process or a manifestation of disease. Intention or action tremor, a common manifestation of cerebellar diseases, is aggravated by movement. In contrast, resting tremor is maximal when there is no attempt at voluntary movement, and occurs as a relatively frequent manifestation of parkinson disease. Myotonic Dystrophies, dysarthria Dysarthria Disorders of speech articulation caused by imperfect coordination of pharynx, larynx, tongue, or face muscles. This may result from cranial nerve diseases; neuromuscular diseases; cerebellar diseases; basal ganglia diseases; brain stem diseases; or diseases of the corticobulbar tracts. The cortical language centers are intact in this condition. Wilson Disease, dysphagia Dysphagia Dysphagia is the subjective sensation of difficulty swallowing. Symptoms can range from a complete inability to swallow, to the sensation of solids or liquids becoming "stuck." Dysphagia is classified as either oropharyngeal or esophageal, with esophageal dysphagia having 2 sub-types: functional and mechanical. Dysphagia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most commonly inherited cardiomyopathy, which is characterized by an asymmetric increase in thickness (hypertrophy) of the left ventricular wall, diastolic dysfunction, and often left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, and/or diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship eventually become bedridden. Diagnosis is confirmed by genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies showing trinucleotide repeat expansion in the FXN gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics. Treatment is supportive and most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship die of heart disease in the 4th or 5th decade of life.
Last updated: Jan 24, 2025
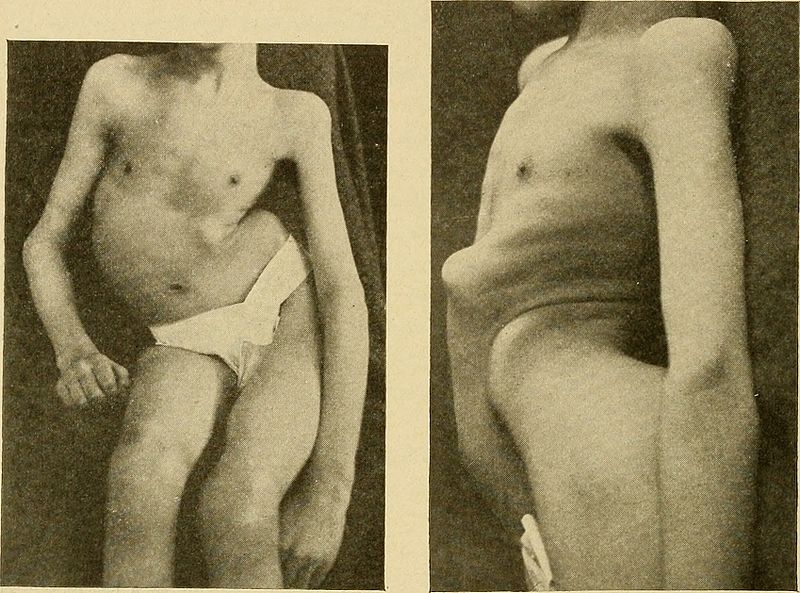
Example of severe kyphoscoliosis, a common finding in Friedreich ataxia
Image: “Lateral curvature of the spine and round shoulders ” by Lovett, Robert W. License: Public Domain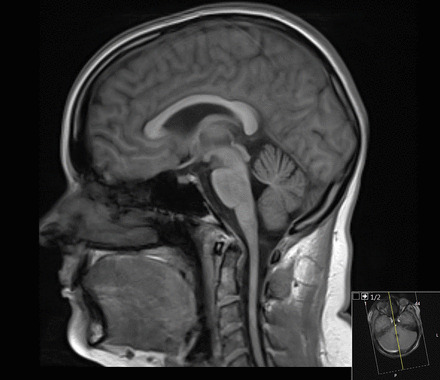
MRI of a patient with Friedreich ataxia: notice the thinning of the cervical spinal cord
Image: “Figure 6” by Rajith Nilantha de Silva et al. License: CC BY 4.0The differential diagnosis for FA FA Inhaled Anesthetics includes the following conditions: