Fragile X syndrome (FXS), also known as Martin-Bell syndrome, is a genetic condition with X-linked inheritance X-linked inheritance Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Alport Syndrome. Both boys and girls may be affected, but the severity is much worse in boys. Characteristic features include a long face, prominent forehead Forehead The part of the face above the eyes. Melasma and chin Chin The anatomical frontal portion of the mandible, also known as the mentum, that contains the line of fusion of the two separate halves of the mandible (symphysis menti). This line of fusion divides inferiorly to enclose a triangular area called the mental protuberance. On each side, inferior to the second premolar tooth, is the mental foramen for the passage of blood vessels and a nerve. Melasma, large ears, flat feet, and large testes Testes Gonadal Hormones post-puberty for boys. Fragile X syndrome is the most common cause of inherited intellectual disability Disability Determination of the degree of a physical, mental, or emotional handicap. The diagnosis is applied to legal qualification for benefits and income under disability insurance and to eligibility for social security and workman's compensation benefits. ABCDE Assessment and is also associated with autism. Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies confirms the diagnosis. Treatment is aimed at improving associated symptoms.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) occurs due to a loss of function Loss of Function Inflammation mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in the fragile X mental retardation 1 (FMR1) gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics on the X chromosome X chromosome The female sex chromosome, being the differential sex chromosome carried by half the male gametes and all female gametes in human and other male-heterogametic species. Basic Terms of Genetics. FMR1 codes for fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), which is important in brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and gonadal ( testes Testes Gonadal Hormones and ovaries Ovaries Ovaries are the paired gonads of the female reproductive system that contain haploid gametes known as oocytes. The ovaries are located intraperitoneally in the pelvis, just posterior to the broad ligament, and are connected to the pelvic sidewall and to the uterus by ligaments. These organs function to secrete hormones (estrogen and progesterone) and to produce the female germ cells (oocytes). Ovaries: Anatomy) development.
More than 99% of cases are due to unstable trinucleotide (CGG) repeat expansion in the promoter region of the FMR1 gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics:
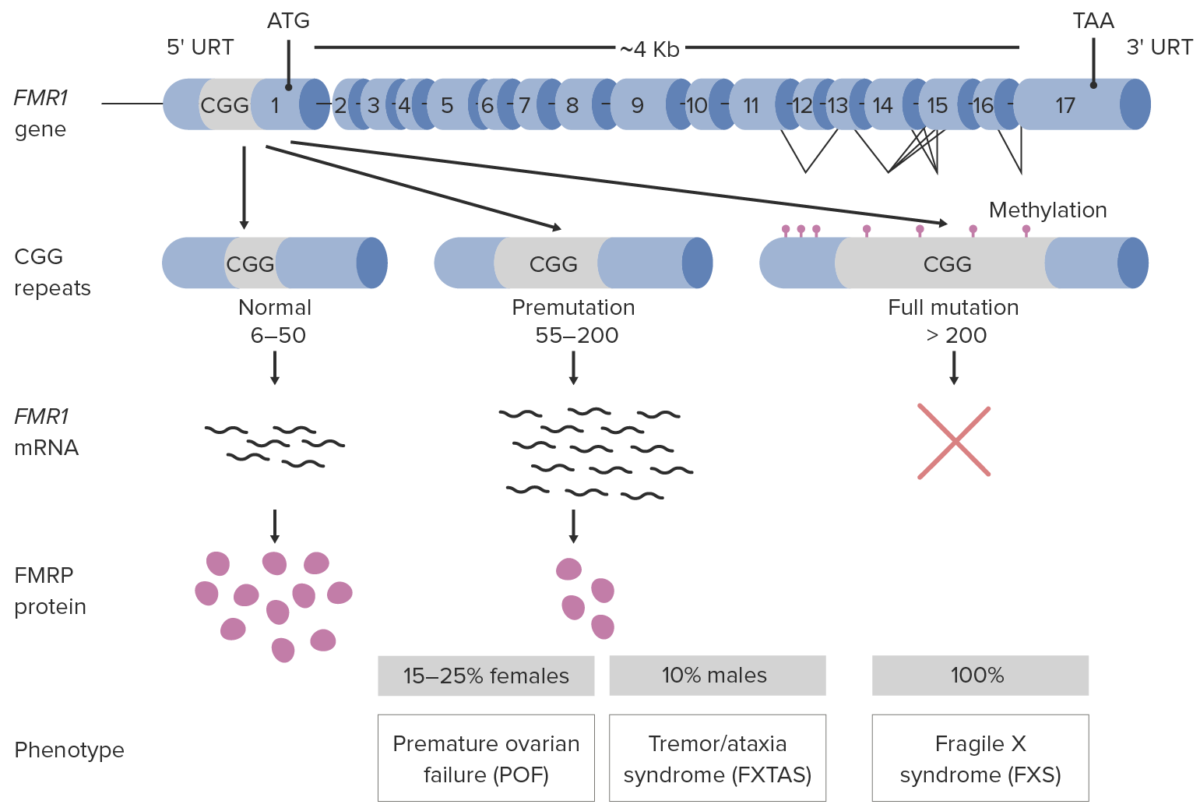
Pathophysiology of fragile X syndrome
FXTAS: Fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome
The inheritance pattern is X-linked X-linked Genetic diseases that are linked to gene mutations on the X chromosome in humans or the X chromosome in other species. Included here are animal models of human X-linked diseases. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) dominant:
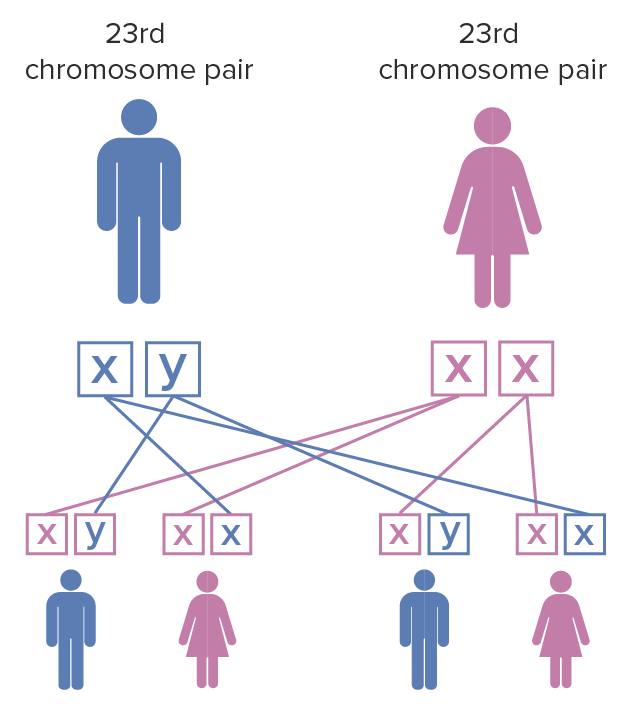
Fragile X syndrome inheritance pattern:
The mother has a pair of X chromosomes that have undergone mutation; the father has unaffected X and Y chromosomes. When the female with fragile X mutation on both of the X chromosomes has children, each child has a 100% chance of inheriting the disease. Females are less severely affected by fragile X syndrome than males due to X chromosome inactivation.
Girls and those with premutations have variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables and often less severe clinical manifestations. The following are the clinical features of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with classic FXS (full mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations).
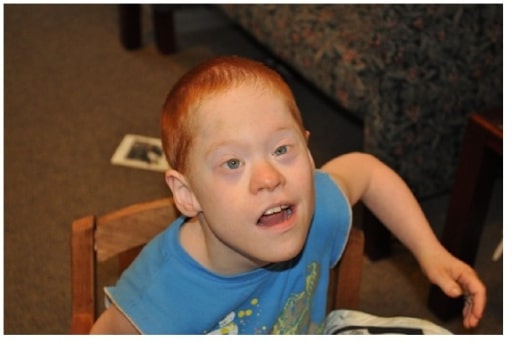
Boy with co-occurrence of Down’s syndrome and full mutation FXS
Image: “Boy with cooccurrence DS and full mutation FXS” by Emory University, Department of Human Genetics, 2165 N. Decatur Road, Decatur, GA 30033, USA. License: CC BY 3.0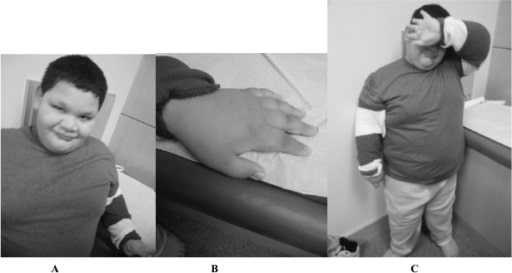
A 9-year-old boy with full mutation FXS: Notice the round face and prominent ears (A), short fingers (B), and truncal obesity (C).
Image: “Fragile X boy with the Prader-Willi phenotype” by Medical Investigation of Neurodevelopmental Disorders (M.I.N.D.) Institute, University of California Davis Health System, Sacramento, California, USA. License: CC BY 2.5There is no curative treatment for FXS. Treatment is tailored to the symptoms present. Supportive therapy includes the following:
The following conditions are differential diagnoses of FXS:
The following are conditions of concern for those with premutations for FXS.