Foreign body aspiration can lead to choking and death by obstructing airflow at the larynx Larynx The larynx, also commonly called the voice box, is a cylindrical space located in the neck at the level of the C3-C6 vertebrae. The major structures forming the framework of the larynx are the thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilage, and epiglottis. The larynx serves to produce sound (phonation), conducts air to the trachea, and prevents large molecules from reaching the lungs. Larynx: Anatomy or trachea Trachea The trachea is a tubular structure that forms part of the lower respiratory tract. The trachea is continuous superiorly with the larynx and inferiorly becomes the bronchial tree within the lungs. The trachea consists of a support frame of semicircular, or C-shaped, rings made out of hyaline cartilage and reinforced by collagenous connective tissue. Trachea: Anatomy. Foreign bodies may also become lodged deeper in the bronchi Bronchi The larger air passages of the lungs arising from the terminal bifurcation of the trachea. They include the largest two primary bronchi which branch out into secondary bronchi, and tertiary bronchi which extend into bronchioles and pulmonary alveoli. Bronchial Tree: Anatomy; this may not affect breathing but can cause infection or erosion Erosion Partial-thickness loss of the epidermis Generalized and Localized Rashes of bronchial walls. Foreign bodies (FBs) are more frequently aspirated by children, who may present with coughing or wheezing Wheezing Wheezing is an abnormal breath sound characterized by a whistling noise that can be relatively high-pitched and shrill (more common) or coarse. Wheezing is produced by the movement of air through narrowed or compressed small (intrathoracic) airways. Wheezing. As FBs are rarely visible on X-ray X-ray Penetrating electromagnetic radiation emitted when the inner orbital electrons of an atom are excited and release radiant energy. X-ray wavelengths range from 1 pm to 10 nm. Hard x-rays are the higher energy, shorter wavelength x-rays. Soft x-rays or grenz rays are less energetic and longer in wavelength. The short wavelength end of the x-ray spectrum overlaps the gamma rays wavelength range. The distinction between gamma rays and x-rays is based on their radiation source. Pulmonary Function Tests, other modalities of imaging, such as computed tomography or flexible bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy Endoscopic examination, therapy or surgery of the bronchi. Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia, must be employed when prompted by symptoms and clinical suspicion. The relative frequency Relative frequency Basics of Probability with which various objects are aspirated varies based on patient demographics. Prompt removal of the FB is the definitive treatment.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Foreign bodies (FBs) aspirated vary based on age.
Most cases involve materials not visible on radiographs (e.g., food, wood, and plastic). In these cases, characteristics of the lung appearance may suggest a foreign body. Computed tomography (CT) or bronchoscopy Bronchoscopy Endoscopic examination, therapy or surgery of the bronchi. Laryngomalacia and Tracheomalacia can confirm suspicion.
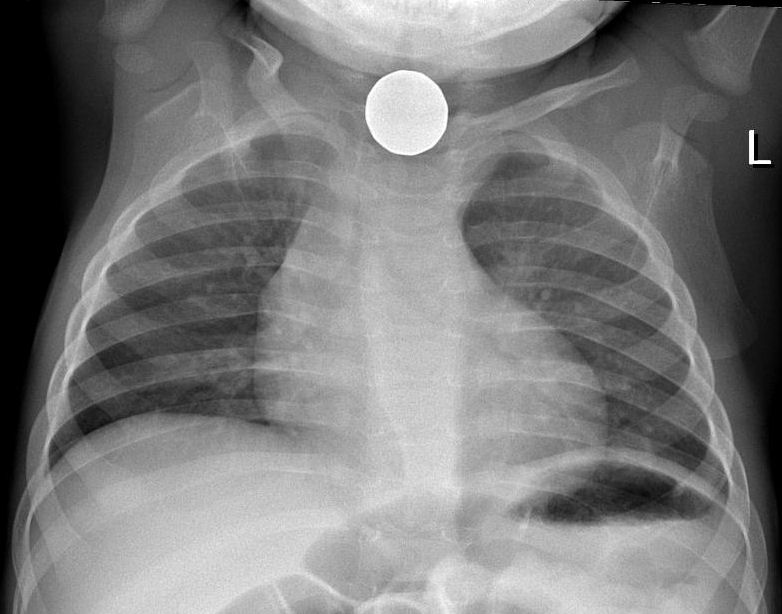
X-ray of coin on chest radiograph
Image: “Foreign body aspiration X-ray” by Samir. License: CC BY 3.0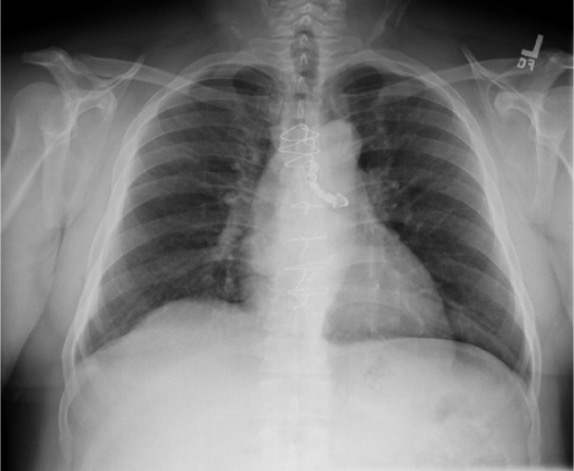
Chest radiograph shows a dental prosthesis lodged in the left mainstem bronchus.
Image: “Chest radiograph shows a dental prosthesis lodged in the left mainstem bronchus” by Department of Internal Medicine, Meharry Medical College, Nashville, TN 37208, USA. License: CC BY 3.0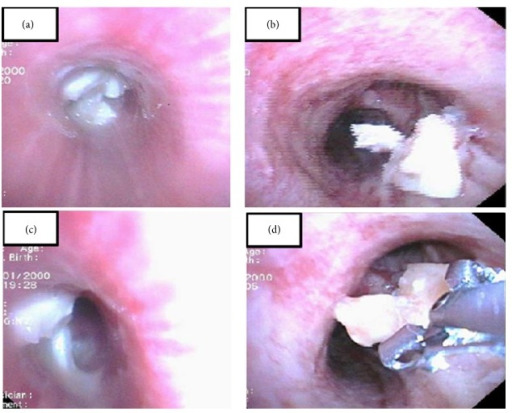
Bronchoscopy can be used for the diagnosis and retrieval of foreign bodies:
(a, c): A foreign body is noted in the left main bronchus.
(b): A foreign body is seen in the right bronchus.
(d): Retrieval of the foreign body via forceps
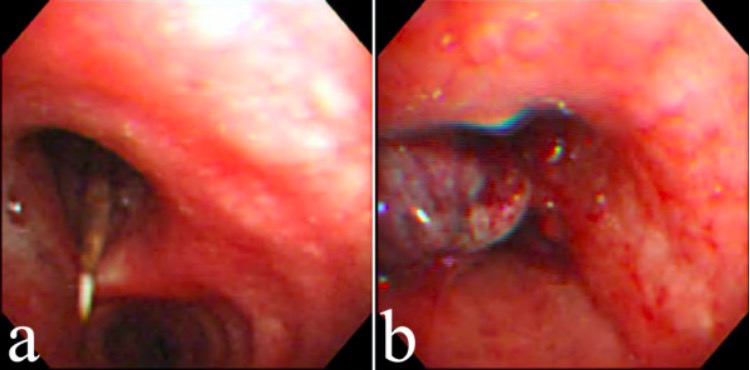
Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy reveals a dental floss pick in the left main bronchus (a) and granulation tissue formation after removal of the object with biopsy forceps (b).
Image: “Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy” by Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, Chung-Shan South Rd, Taipei, Taiwan. License: CC BY 2.0Airway Airway ABCDE Assessment obstruction requires immediate action given the high risk for asphyxia Asphyxia A pathological condition caused by lack of oxygen, manifested in impending or actual cessation of life. Drowning.
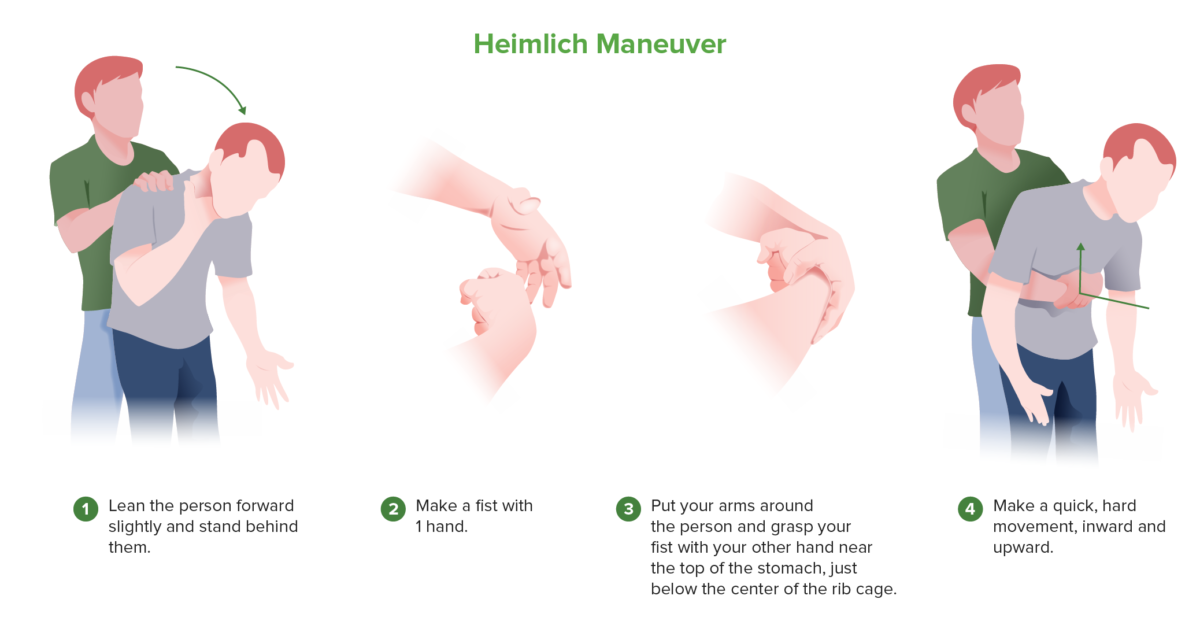
Heimlich maneuver
In a choking patient or an unconscious patient on whom rescue breaths are not providing adequate ventilation, airway obstruction with a foreign object should be considered. The Heimlich maneuver works by producing positive pressure in the lungs, forcefully expelling any foreign body in the upper airway.