Foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Foot: Anatomy deformities in children include congenital or acquired malformations of the feet. Two common examples are talipes equinovarus, commonly known as clubfoot, and metatarsus adductus, also called metatarsus varus. Depending on their etiology, foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Foot: Anatomy deformities can be self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children or may require surgical correction. Early detection and recognition are crucial for proper treatment.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Clubfoot, also called talipes equinovarus, is a complex condition with a plantar flexed foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Foot: Anatomy (equinus), adductus of the forefoot, and an inversion deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs of the heel (varus).
Etiology is debated, as the majority of infants with clubfoot have no identifiable syndromic, genetic, or extrinsic cause.
There are multiple classification systems for talipes equinovarus:
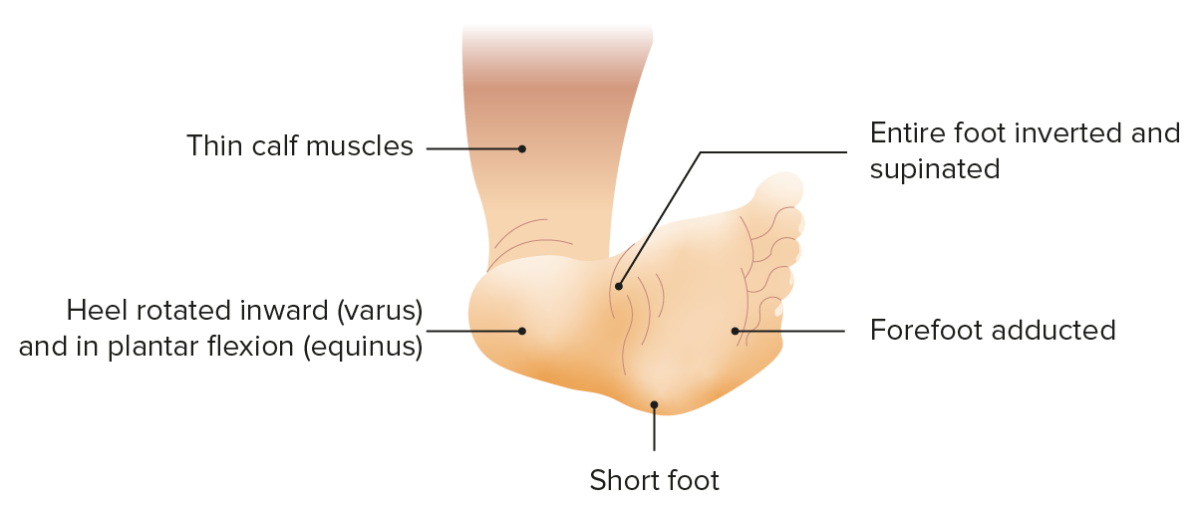
Talipes equinovarus (clubfoot)
Foot deformity featuring plantar flexion, medial rotation of the forefoot and inward facing sole
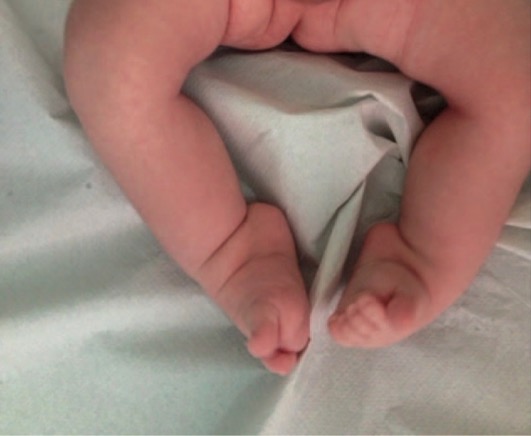
Bilateral talipes equinovarus (clubfoot) in newborn patient
Image: “Uncommon III grade clubfoot” by Universitary Department of Anatomic, Histologic, Forensic and Locomotor Apparatus Sciences-Section of Locomotor Apparatus Sciences, Sapienza University of Rome. License: CC BY 4.0Refer to a pediatric orthopedic surgeon soon after birth for prompt initiation of treatment.
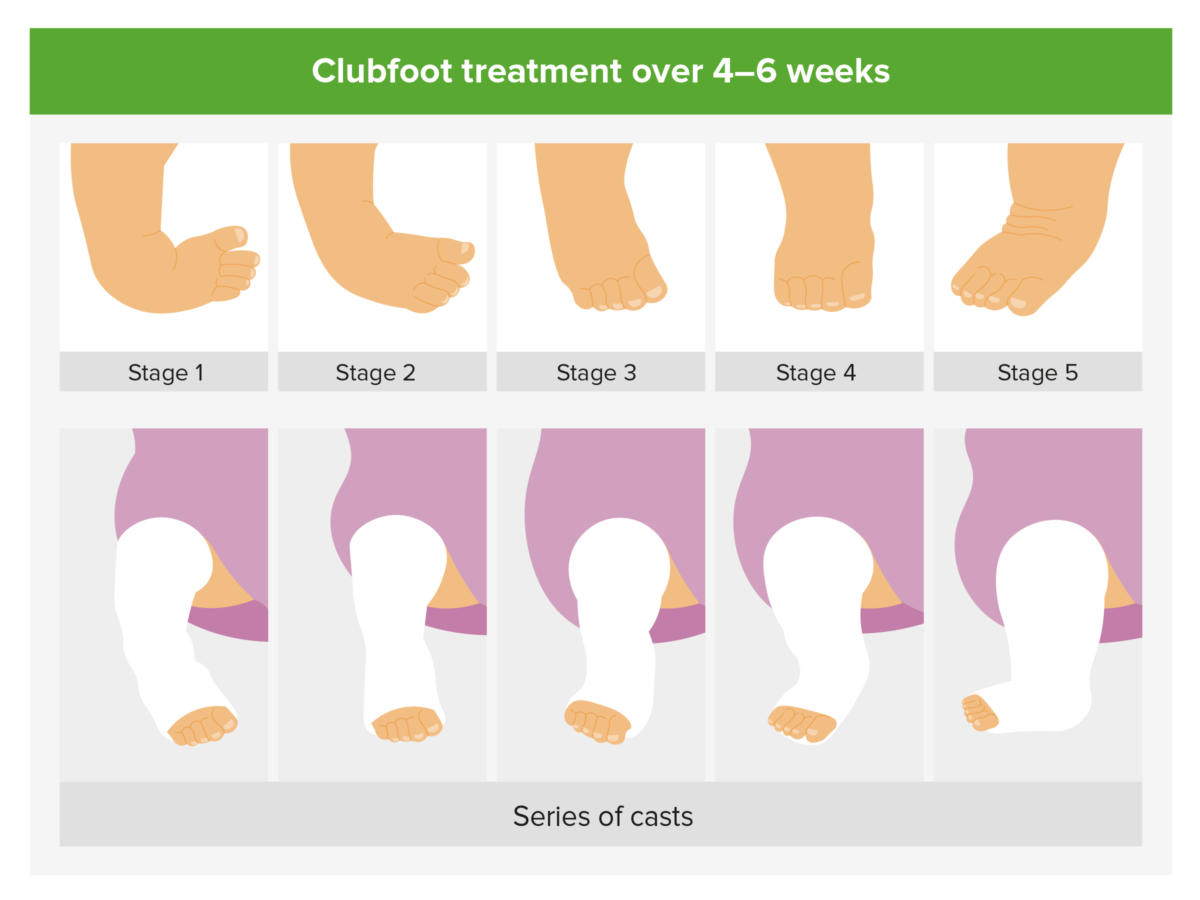
Ponseti method
Consecutive splinting with casts made following the Ponseti method allow for gradual correction of talipes equinovarus (clubfoot).
CAVE:
Metatarsus adductus is a common congenital foot Foot The foot is the terminal portion of the lower limb, whose primary function is to bear weight and facilitate locomotion. The foot comprises 26 bones, including the tarsal bones, metatarsal bones, and phalanges. The bones of the foot form longitudinal and transverse arches and are supported by various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Foot: Anatomy deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs that presents with adduction Adduction Examination of the Upper Limbs, or inward deviation of the forefoot (at the tarsometatarsal joint Tarsometatarsal Joint Foot: Anatomy), with normal hindfoot alignment.
The exact cause is unknown, although 1 proposed etiology is the mechanical effect of a small uterine space.
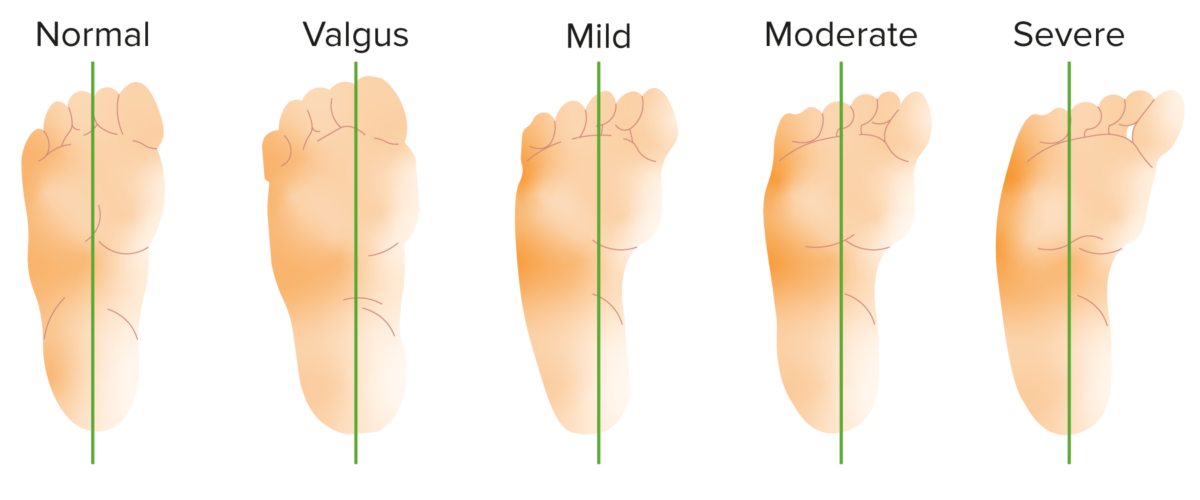
Bleck classification of metatarsus adductus by heel bisector method
This method is used for classifying the severity of metatarsus adductus deformity. Normal heel bisector line through the 2nd and 3rd toe web space, mild heel bisector line through the 3rd toe, moderate heel bisector through 3rd and 4th toe web space, and severe heel bisector through the 4th and 5th toe web space.
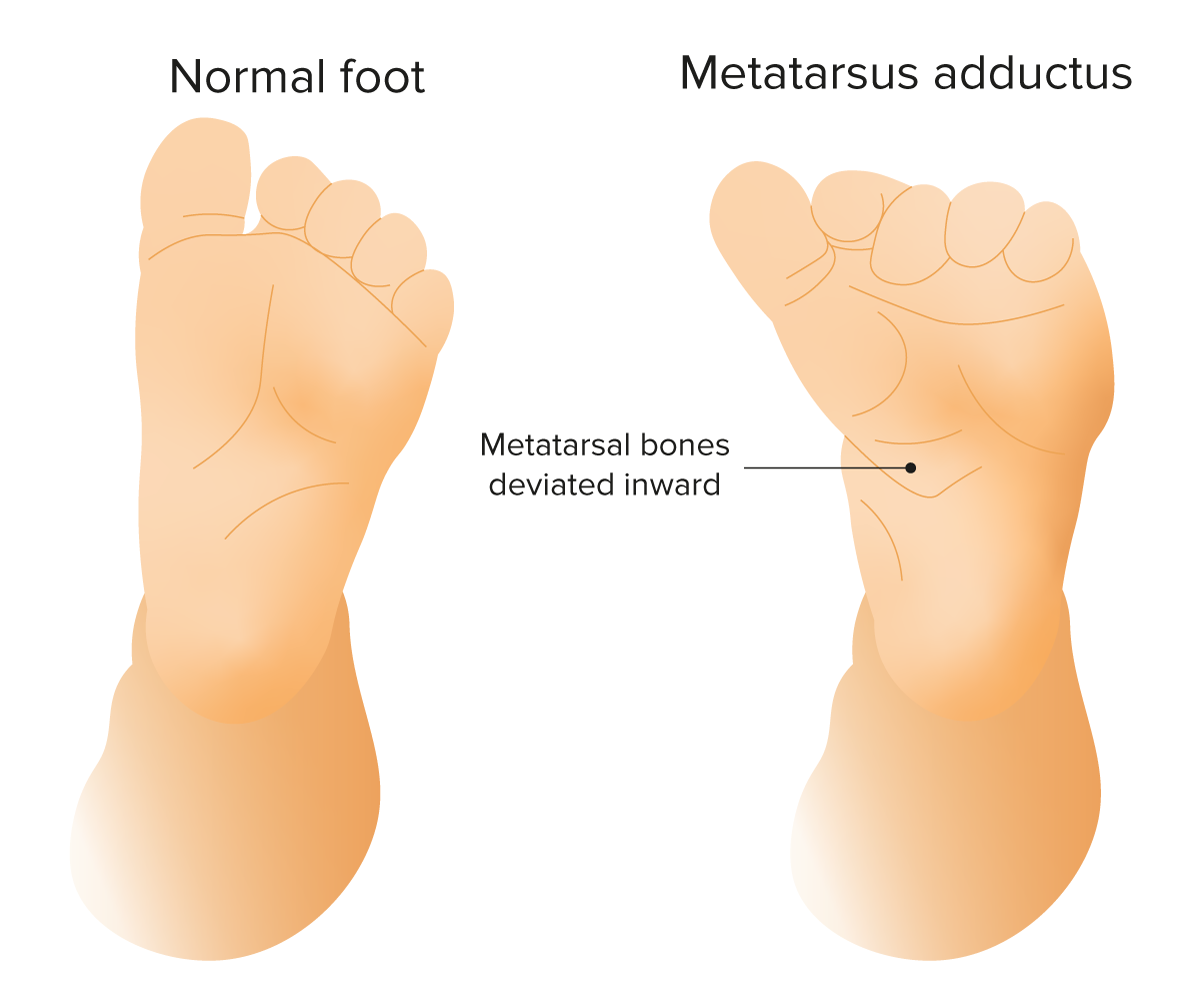
Metatarsus adductus: common congenital foot deformity featuring medial deviation of the forefoot at the tarsometatarsal joint
Image by Lecturio.Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is excellent, if treatment is started early.
The following conditions may accompany talipes equinovarus and metatarsus adductus: