Focused assessment with sonography Sonography The visualization of deep structures of the body by recording the reflections or echoes of ultrasonic pulses directed into the tissues. Use of ultrasound for imaging or diagnostic purposes employs frequencies ranging from 1. 6 to 10 megahertz. Diagnostic Procedures in Gynecology for trauma is a point-of-care ultrasound examination protocol for the abdominal and thoracic cavities performed in the emergency room as part of the secondary survey Secondary Survey ABCDE Assessment in advanced trauma life support. The main goal of the FAST exam is to identify free intraperitoneal Intraperitoneal Peritoneum: Anatomy fluid (blood) and pericardial effusion Pericardial effusion Fluid accumulation within the pericardium. Serous effusions are associated with pericardial diseases. Hemopericardium is associated with trauma. Lipid-containing effusion (chylopericardium) results from leakage of thoracic duct. Severe cases can lead to cardiac tamponade. Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade from trauma. As FAST requires only an ultrasound machine at the bedside and an experienced sonographer, it is widely available, quicker, and less invasive than other image modalities. Focused assessment with sonography Sonography The visualization of deep structures of the body by recording the reflections or echoes of ultrasonic pulses directed into the tissues. Use of ultrasound for imaging or diagnostic purposes employs frequencies ranging from 1. 6 to 10 megahertz. Diagnostic Procedures in Gynecology for trauma has largely replaced diagnostic peritoneal lavage Diagnostic peritoneal lavage Washing out of the peritoneal cavity. The procedure is a diagnostic as well as a therapeutic technique following abdominal trauma or inflammation. Penetrating Abdominal Injury.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Focused assessment with sonography Sonography The visualization of deep structures of the body by recording the reflections or echoes of ultrasonic pulses directed into the tissues. Use of ultrasound for imaging or diagnostic purposes employs frequencies ranging from 1. 6 to 10 megahertz. Diagnostic Procedures in Gynecology for trauma (FAST) is a point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) examination protocol of the abdominal and thoracic cavities performed with the goal of identifying free intraperitoneal Intraperitoneal Peritoneum: Anatomy fluid and/or pericardial effusion Pericardial effusion Fluid accumulation within the pericardium. Serous effusions are associated with pericardial diseases. Hemopericardium is associated with trauma. Lipid-containing effusion (chylopericardium) results from leakage of thoracic duct. Severe cases can lead to cardiac tamponade. Pericardial Effusion and Cardiac Tamponade.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
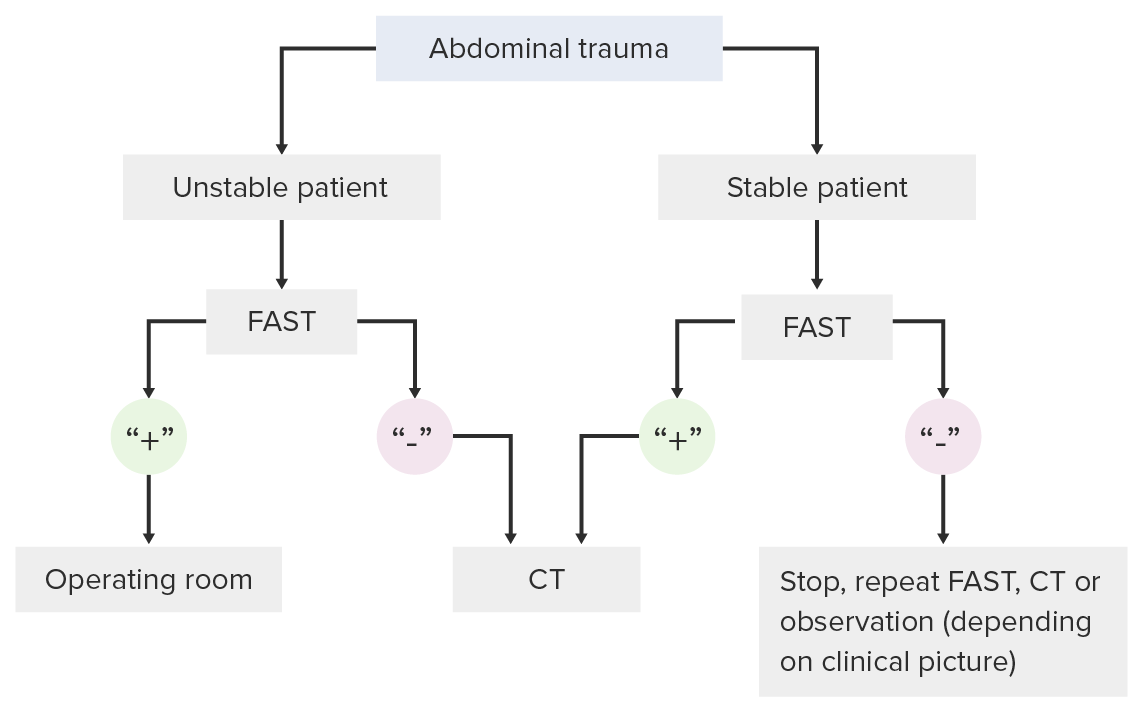
Decision-making pathway for use of the FAST exam in a trauma setting
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Imaging concepts of ultrasound
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0
Ultrasound machine
Image: “Aloka SSD 3500 ultrasound machine” by Kitmondo Marketplace. License: CC BY 2.0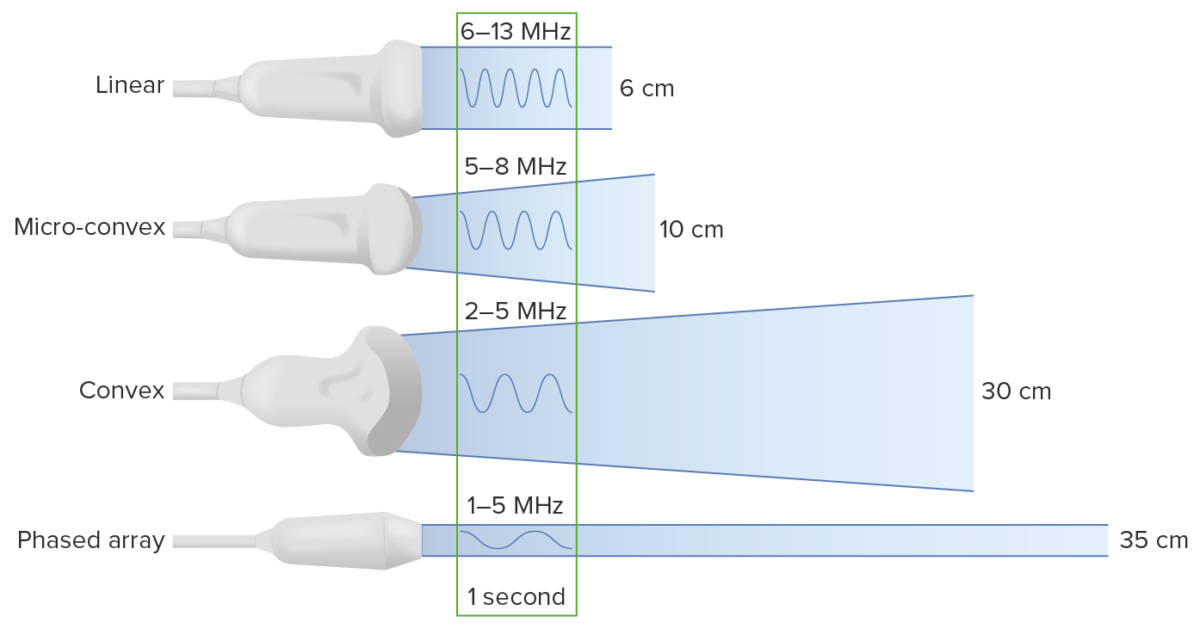
Types of transducers:
Note that decreasing the frequency increases the depth to which the ultrasound waves travel. However, this comes at the cost of image resolution.
Select probe Probe A device placed on the patient’s body to visualize a target Ultrasound (Sonography):
Location:
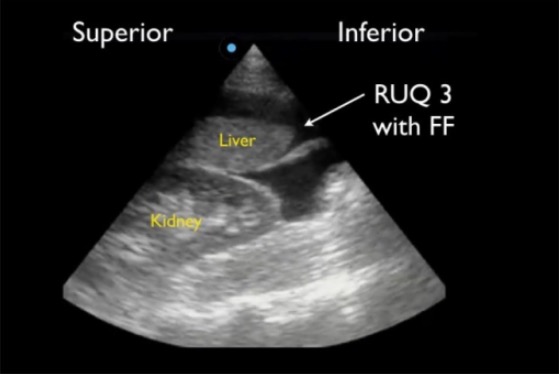
Positive RUQ FAST view showing superior paracolic gutter around caudal liver edge (RUQ3), the most sensitive region for detecting free fluid (FF)
Image: “Positive right upper quadrant (RUQ) FAST view” by Viveta Lobo, MD et al. License: CC BY 4.0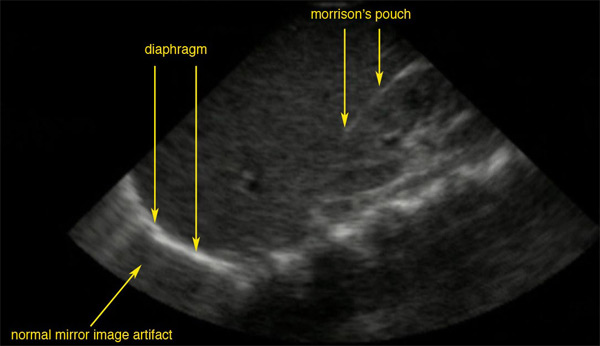
A normal ultrasonographic view of Morison’s pouch:
The bright line is the capsule of the kidney; there is no fluid present and hence there is no visible space.
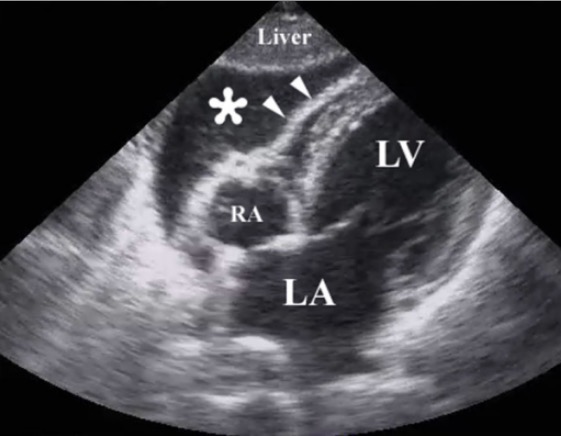
Resuscitative ultrasound image following a penetrating chest injury illustrating the presence of a pericardial tamponade from a hemopericardium (*):
Arrowheads illustrate the wall of the right ventricle.
RA: right atrium
LA: left atrium
LV: left ventricle
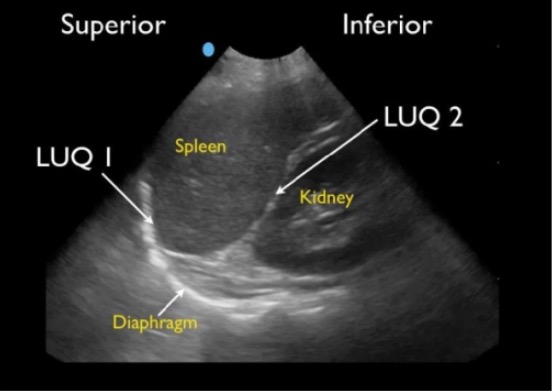
Normal splenorenal view:
Normal LUQ FAST view showing splenodiaphragmatic space (LUQ1) and splenorenal space (LUQ2)
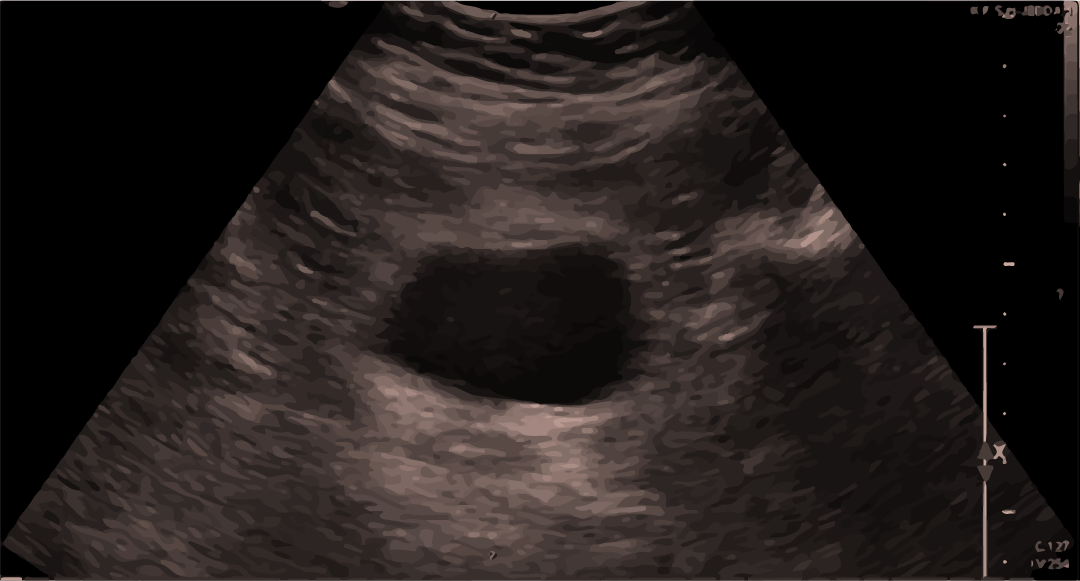
Normal ultrasound scan of the bladder:
Blood/fluid can be seen above or below the bladder.
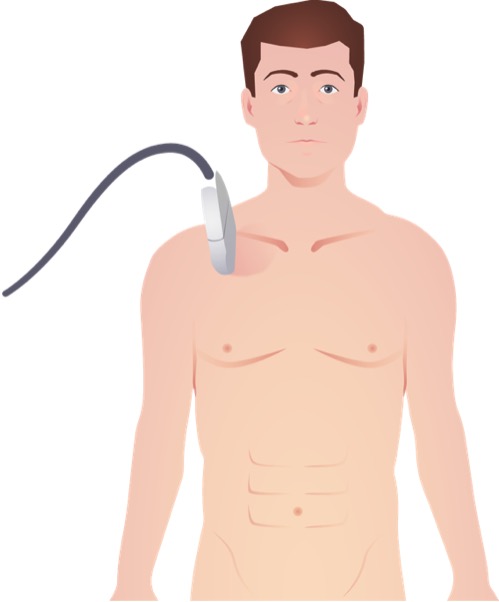
Placement of linear ultrasound probe for view of lung pleura and lung sliding in the evaluation for pneumothorax
Image by Lecturio.