Children are particularly vulnerable to developing dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration because they have higher insensible water loss and more elevated metabolic rates than adults. In addition, children's inability to communicate their needs compounds with large losses of fluids (e.g., diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea, vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia), putting them at even higher risk. Dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration is defined as a decrease in total body water Total body water Body Fluid Compartments, and can be characterized as mild, moderate, or severe. Fluid replacement treatment is based on severity. Clinicians must be prepared to administer optimal rehydration Rehydration Dengue Virus therapy in addition to the other required measures for the causal illness. When treated promptly, dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration starts to resolve clinically within the first few hours.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration is a decrease in total body water Total body water Body Fluid Compartments, both intracellular and extracellular.
Dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration in children worldwide is primarily caused by diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea:
In most cases, a good history and physical exam are sufficient to diagnose dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration and its etiology. Laboratory testing is reserved for severe cases and to monitor rehydration Rehydration Dengue Virus.
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery | < 5% in infants, < 3% in older children | 5%–10% in infants, 3%–9% in older children | > 10% in infants, > 9% in older children |
| Dry mucosas (first sign) | – | +/-, looks dry | +, looks parched |
| Skin turgor Skin turgor Malnutrition in children in resource-limited countries (last sign) | + | +/- | -, tenting |
| Anterior fontanelle depression Anterior fontanelle depression Malnutrition in children in resource-limited countries | – | + | +/++ |
| Mental status | Normal | Fatigued/irritable | Apathy Apathy Lack of emotion or emotional expression; a disorder of motivation that persists over time. Wernicke Encephalopathy and Korsakoff Syndrome/ lethargy Lethargy A general state of sluggishness, listless, or uninterested, with being tired, and having difficulty concentrating and doing simple tasks. It may be related to depression or drug addiction. Hyponatremia |
| Enophthalmos Enophthalmos Recession of the eyeball into the orbit. Marfan Syndrome | – | + | + |
| Breathing | Normal | Deep, may be tachypneic | Deep and tachypneic |
| Heart rate Heart rate The number of times the heart ventricles contract per unit of time, usually per minute. Cardiac Physiology | Normal | Increased | Very high |
| Hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension | – | + | + |
| Distal perfusion | Normal | Feels cold, 3–4 seconds | Acrocyanotic, > 4 seconds |
| Urinary output | Decreased | Oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation | Oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation/ anuria Anuria Absence of urine formation. It is usually associated with complete bilateral ureteral (ureter) obstruction, complete lower urinary tract obstruction, or unilateral ureteral obstruction when a solitary kidney is present. Acute Kidney Injury |

Components of the CHEM-7:
Na: sodium
Cl: chloride
BUN: blood urea nitrogen
K: potassium
HCO3: bicarbonate
Cr: creatinine
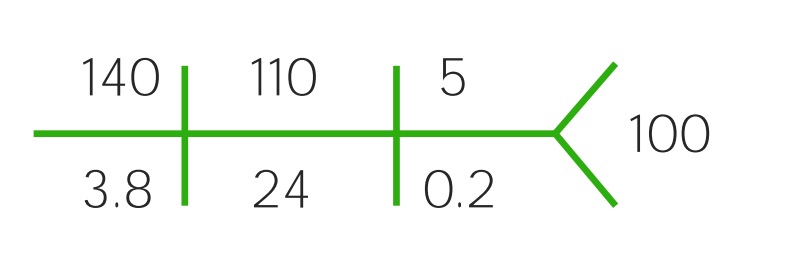
CHEM-7 with normal values
Image by Lecturio.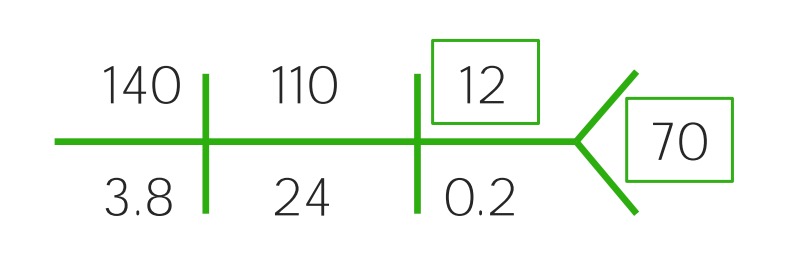
Example of a CHEM-7 for a child with mild dehydration: Notice the slight rise of the BUN and the decreased glucose.
Image by Lecturio.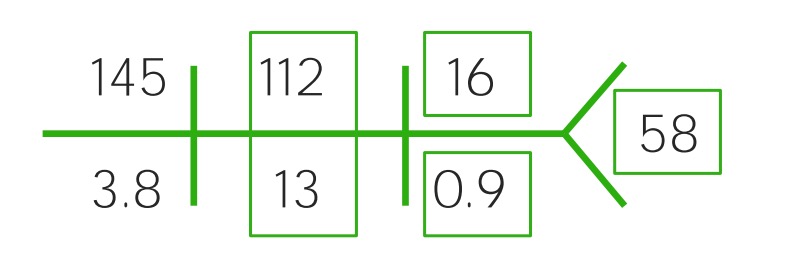
Example of a CHEM-7 for a child with moderate dehydration: Notice the increased sodium (145), chloride (112) and BUN (16), while bicarbonate (13) and glucose (58) have decreased sharply. It’s becoming acidotic.
Image by Lecturio.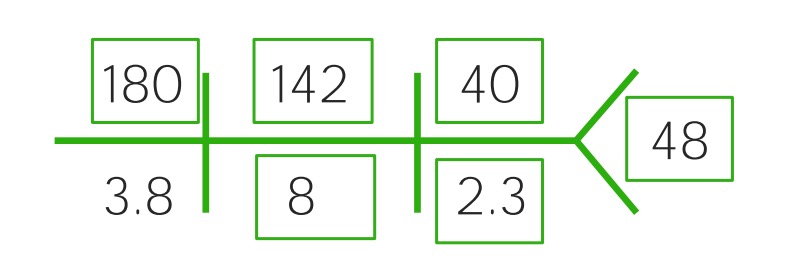
Example of a CHEM-7 for a child with severe dehydration: Notice the increased sodium (180), chloride (142), BUN (40), and creatinine (2.3), while bicarbonate (8) and glucose (48) have decreased sharply. It’s becoming acidotic.
Image by Lecturio.Severe dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration can cause hypoperfusion of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and vital organs and is considered a medical emergency to be addressed rapidly.
A child who weighs 25 kg with severe dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration:
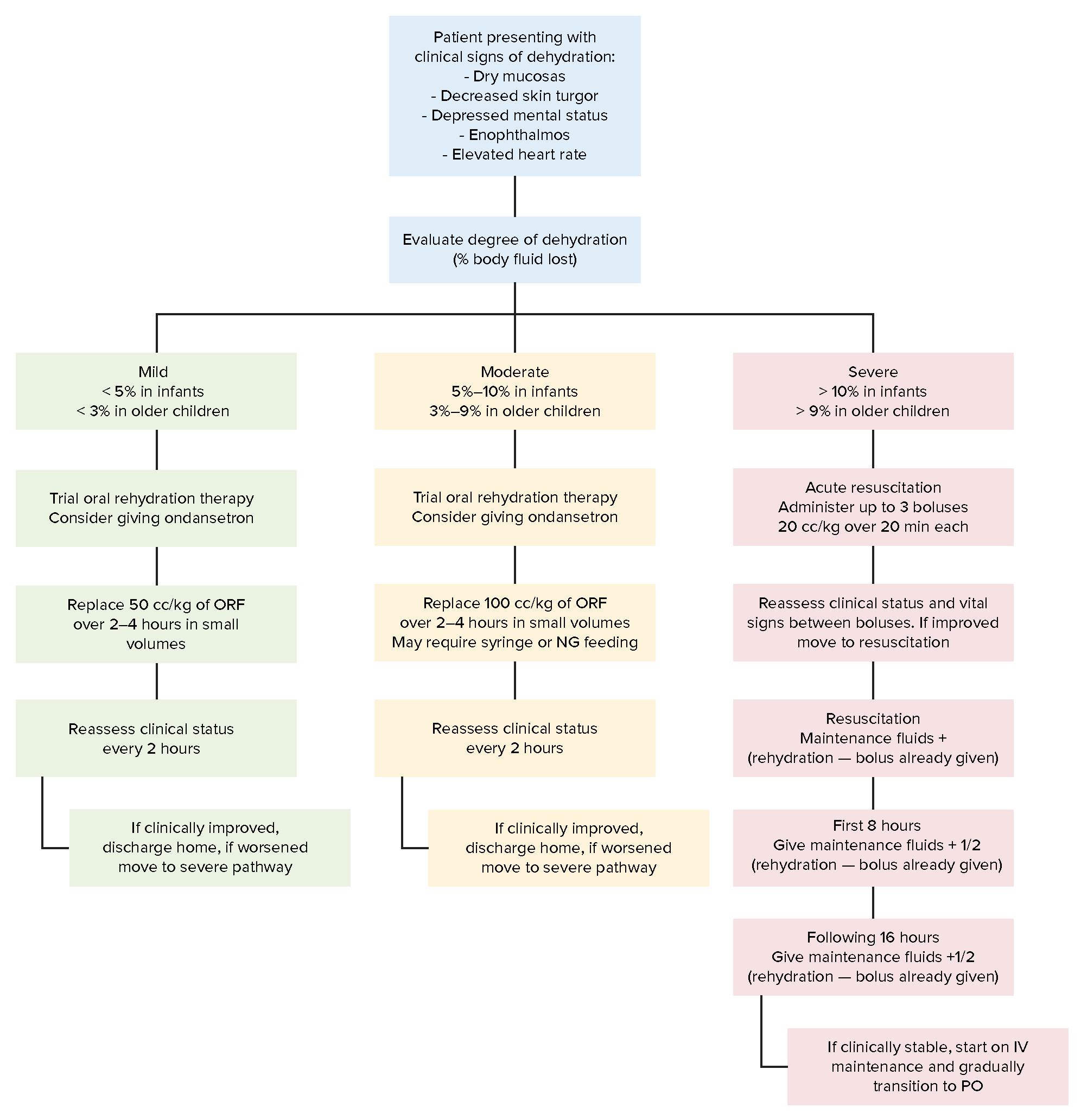
Approach to evaluation and treatment with oral replacement fluid (ORF) or intravenous (IV) fluids of children with dehydration based on severity of symptoms
Image by Lecturio.Daily requirements = maintenance fluids + growth fluids: