Anticonvulsant drugs are pharmacological agents used to achieve seizure control and/or prevent seizure episodes. Anticonvulsants encompass various drugs with different mechanisms of action including ion-channel (Na+ and Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+) blocking and GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS reuptake inhibition. Phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproic acid, and ethosuximide are the 1st-generation antiseizure drugs. Anticonvulsant drugs generally have complicated pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetics is the science that analyzes how the human body interacts with a drug. Pharmacokinetics examines how the drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics, multiple drug interactions, and narrow therapeutic ranges compared with new-generation drugs.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Anticonvulsant drugs are used to suppress abnormal electrical activity in the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification through various mechanisms.
The hyperexcitable state of neurons Neurons The basic cellular units of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. Nervous System: Histology results via the following 3 steps:
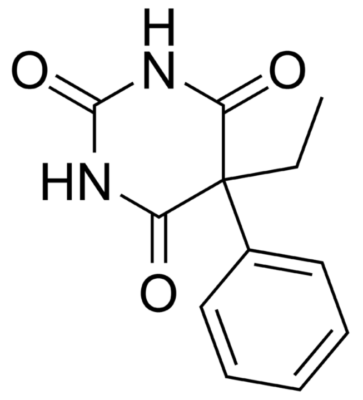
Chemical structure of phenobarbital
Image: “Phenobarbital” by Harbinary. License: Public Domain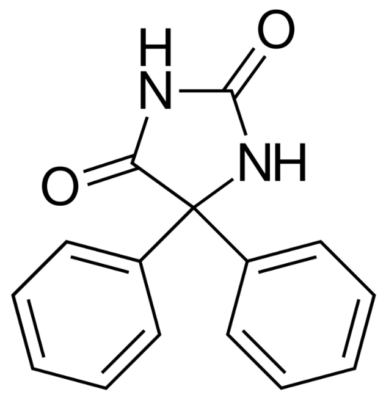
Chemical structure of phenytoin
Image: “Phenytoin structure” by Harbin. License: Public Domain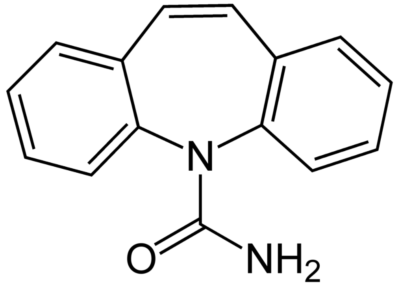
Chemical structure of carbamazepine
Image: “Carbamazepine structural formulae” by Jü. License: Public Domain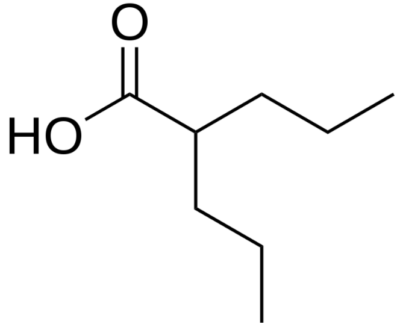
Chemical structure of valproic acid
Image: “Valproic acid” by Harbin. License: Public Domain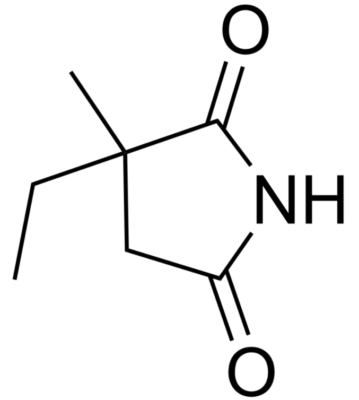
Chemical structure of ethosuximide
Image: “Ethosuximide” by Fvasconcellos. License: Public DomainTreatment of absence seizures Absence seizures Brief period of unresponsiveness thats lasts about 4–30 seconds and can occur multiple times per day Seizures in Children
| Medications | Mechanism of action | Major adverse effects | Interactions | Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barbiturates Barbiturates A class of chemicals derived from barbituric acid or thiobarbituric acid. Many of these are gaba modulators used as hypnotics and sedatives, as anesthetics, or as anticonvulsants. Intravenous Anesthetics (phenobarbital) | Binds to GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors subunits → ↑ GABA GABA The most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS inhibitory activity |
|
Induces CYP and UGT | Generalized and focal seizures Focal Seizures Seizures in Children |
| Phenytoin | Blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane |
|
Induces CYP and UGT |
|
| Carbamazepine | Blocks Na+ channels Channels The Cell: Cell Membrane |
|
Induces CYP and UGT |
|
| Valproic acid |
|
|
Inhibits CYP and UGT |
|
| Ethosuximide | ↓ T-type Ca CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)2+ channel currents | Drowsiness (CNS depression) | ↑ Phenytoin effects | Absence seizures Absence seizures Brief period of unresponsiveness thats lasts about 4–30 seconds and can occur multiple times per day Seizures in Children |