Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome. Diagnosis is clinical with laboratory exams and imaging reserved to rule out other causes for the spectrum of symptoms. Management is centered around education and lifestyle modification, with both pharmacotherapy (e.g., antidepressants, anticonvulsants) and nonpharmacologic measures (e.g., low-impact exercise, sleep optimization, cognitive behavioral therapy) showing efficacy.
Last updated: Sep 11, 2025
While the cause is unknown, the following environmental triggers have been associated with the onset of fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome. Fibromyalgia.
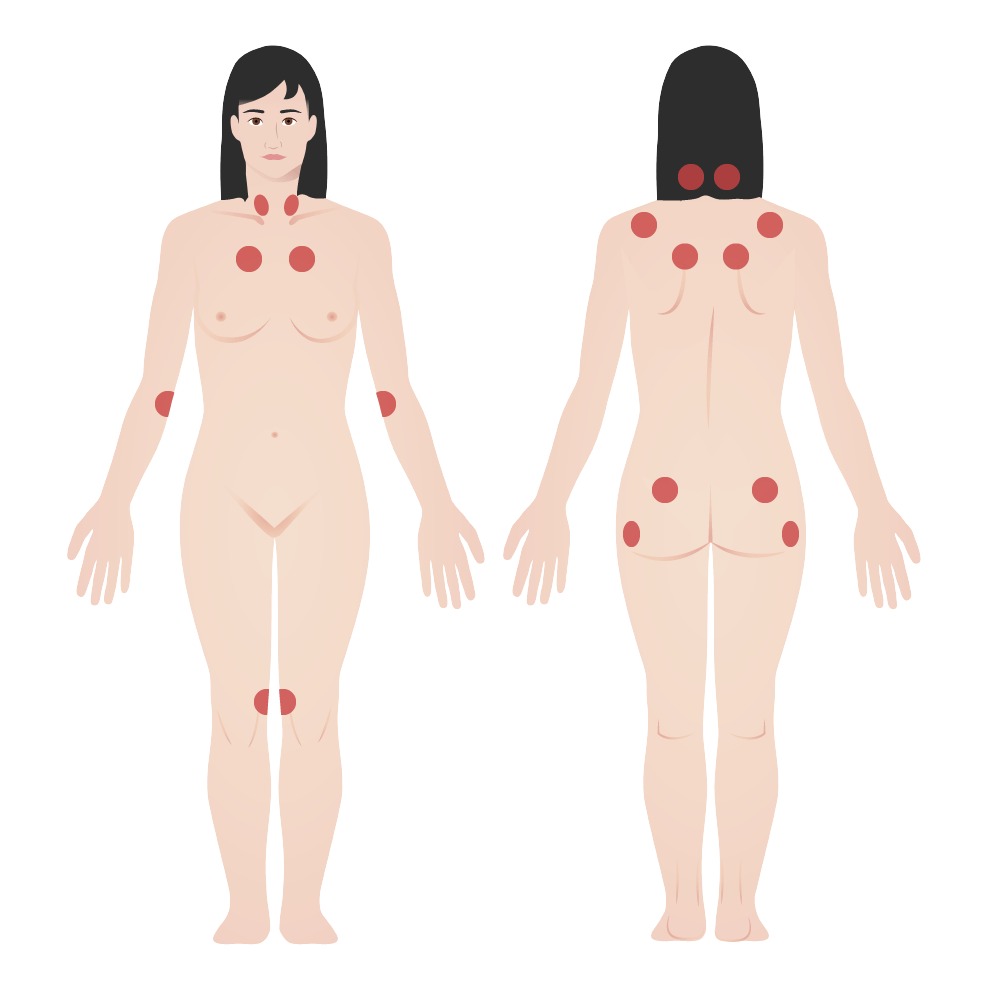
Fibromyalgia tender points:
The American College of Rheumatology diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia was historically based on the presence of tender points. The tender point exam was considered to be impractical, given the difficulty of performing it and the variability in results. The tender point exam was eliminated in the American College of Rheumatology 2010/2011/2016 criteria.[6]
Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome. Fibromyalgia is a chronic syndrome; therefore, diagnosis determination is recommended over multiple visits after sequential Sequential Computed Tomography (CT) observation and physical exams.
A history evaluation should include:[9]
A physical examination should include:[9]
An individual satisfies diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome. Fibromyalgia if the following 3 conditions are met MET Preoperative Care:
Widespread pain index Widespread Pain Index Fibromyalgia (note the distribution of pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways the patient has had in the past week; each area is worth 1 point): Score will be between 0 and 19.[3,9]
| Region 1 (left upper) | Region 2 (right upper) | Region 3 (left lower) |
|
|
|
|
| Region 4 (right lower) | Region 5 ( axial Axial Computed Tomography (CT)) | |
|
|
|
|
Symptom severity scale Scale Dermatologic Examination ( SSS SSS Sick sinus syndrome (SSS), also known as sinus node dysfunction, is characterized by degeneration of the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s primary pacemaker. Patients with SSS may be asymptomatic or may present with tachycardia or bradycardia. Sick Sinus Syndrome) score (0‒12):[3,9]
The SS SS Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) is an autoimmune condition characterized by diffuse collagen deposition and fibrosis. The clinical presentation varies from limited skin involvement to diffuse involvement of internal organs. Scleroderma scale Scale Dermatologic Examination score is the sum of the severity of the 3 symptoms ( fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia, waking unrefreshed, cognitive symptoms) plus the extent (severity) of somatic symptoms Somatic symptoms Major Depressive Disorder in general. The final score is between 0 and 12.
| A) Rate the following and add together (maximum score 9) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia | Waking unrefreshed | Cognitive symptoms |
| 0-3 | 0-3 | 0-3 |
|
|
||
| B) How many of the following symptoms have bothered the patient in the past 6 months? (maximum score 3) | ||
| Depression | Headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess | Pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways or cramps Cramps Ion Channel Myopathy in lower abdomen |
| 0-1 | 0-1 | 0-1 |
| SSS SSS Sick sinus syndrome (SSS), also known as sinus node dysfunction, is characterized by degeneration of the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart’s primary pacemaker. Patients with SSS may be asymptomatic or may present with tachycardia or bradycardia. Sick Sinus Syndrome score = A+B (maximum 12 points) | ||
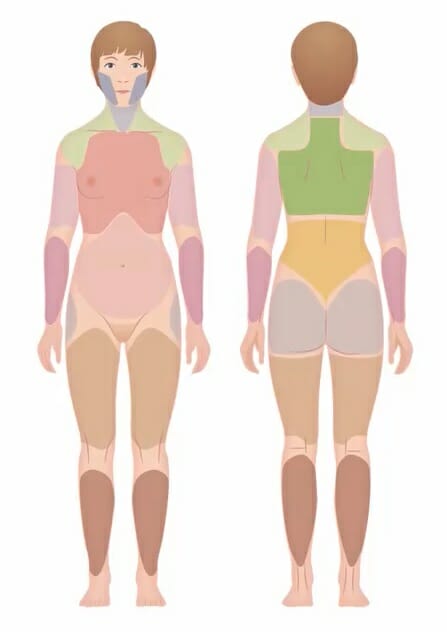
Widespread pain index:
A self-report assessment that identifies painful locations and the extent of symptoms, which has largely replaced the tender (trigger) point examination.
Management may vary based on location. The following recommendations are based on current US and European guidelines.
| Drug class | Drug | Dose | Advantaged | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCAs TCAs Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications used in the management of mood disorders, primarily depression. These agents, named after their 3-ring chemical structure, act via reuptake inhibition of neurotransmitters (particularly norepinephrine and serotonin) in the brain. Tricyclic Antidepressants | Amitriptyline Amitriptyline Tricyclic antidepressant with anticholinergic and sedative properties. It appears to prevent the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin at nerve terminals, thus potentiating the action of these neurotransmitters. Amitriptyline also appears to antagonize cholinergic and alpha-1 adrenergic responses to bioactive amines. Tricyclic Antidepressants | |||
| Cyclobenzaprine Cyclobenzaprine Spasmolytics (pharmacologically similar to TCAs TCAs Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications used in the management of mood disorders, primarily depression. These agents, named after their 3-ring chemical structure, act via reuptake inhibition of neurotransmitters (particularly norepinephrine and serotonin) in the brain. Tricyclic Antidepressants) | 5–20 mg orally at bedtime | |||
| SNRIs SNRIs Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants | Duloxetine Duloxetine A thiophene derivative and selective neurotransmitter uptake inhibitor for serotonin and noradrenaline (SNRI). It is an antidepressant agent and anxiolytic, and is also used for the treatment of pain in patients with diabetes mellitus and fibromyalgia. Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants | Dry mouth, headaches, nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics, diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea ( duloxetine Duloxetine A thiophene derivative and selective neurotransmitter uptake inhibitor for serotonin and noradrenaline (SNRI). It is an antidepressant agent and anxiolytic, and is also used for the treatment of pain in patients with diabetes mellitus and fibromyalgia. Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants), and constipation Constipation Constipation is common and may be due to a variety of causes. Constipation is generally defined as bowel movement frequency < 3 times per week. Patients who are constipated often strain to pass hard stools. The condition is classified as primary (also known as idiopathic or functional constipation) or secondary, and as acute or chronic. Constipation ( milnacipran Milnacipran A cyclopropanecarboxamide serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) that is used in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants) are common. | ||
| Milnacipran Milnacipran A cyclopropanecarboxamide serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) that is used in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants | ||||
| Gabapentinoids | Pregabalin Pregabalin A gamma-aminobutyric acid (gaba) derivative that functions as a calcium channel blocker and is used as an anticonvulsant as well as an anti-anxiety agent. It is also used as an analgesic in the treatment of neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. Second-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs | May improve pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways and sleep Sleep A readily reversible suspension of sensorimotor interaction with the environment, usually associated with recumbency and immobility. Physiology of Sleep | Dizziness Dizziness An imprecise term which may refer to a sense of spatial disorientation, motion of the environment, or lightheadedness. Lateral Medullary Syndrome (Wallenberg Syndrome), weight gain, somnolence, dry mouth, peripheral edema Peripheral edema Peripheral edema is the swelling of the lower extremities, namely, legs, feet, and ankles. Edema, and cognitive problems ( pregabalin Pregabalin A gamma-aminobutyric acid (gaba) derivative that functions as a calcium channel blocker and is used as an anticonvulsant as well as an anti-anxiety agent. It is also used as an analgesic in the treatment of neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. Second-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs) | |
| Gabapentin Gabapentin A cyclohexane-gamma-aminobutyric acid derivative that is used for the treatment of partial seizures; neuralgia; and restless legs syndrome. Second-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs | ||||
| Low-dose opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics | Tramadol Tramadol A narcotic analgesic proposed for severe pain. It may be habituating. Opioid Analgesics | 25–50 mg every 6 hours as needed |
|
|
Diagnosis Codes:
This code is used to diagnose
fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Fibromyalgia, a chronic disorder characterized by widespread musculoskeletal
pain
Pain
An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons.
Pain: Types and Pathways accompanied by
fatigue
Fatigue
The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli.
Fibromyalgia,
sleep
Sleep
A readily reversible suspension of sensorimotor interaction with the environment, usually associated with recumbency and immobility.
Physiology of Sleep,
memory
Memory
Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory.
Psychiatric Assessment, and mood issues.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ICD-10-CM | M79.7 | Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome. Fibromyalgia |
| SNOMED CT | 203039002 | Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome. Fibromyalgia (disorder) |
Medications:
These codes are for medications approved to manage the symptoms of
fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread body pain, chronic fatigue, mood disturbance, and cognitive disturbance. It also presents with other comorbid symptoms such as migraine headaches, depression, sleep disturbance, and irritable bowel syndrome.
Fibromyalgia. They include
serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants (
SNRIs
SNRIs
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants) like
duloxetine
Duloxetine
A thiophene derivative and selective neurotransmitter uptake inhibitor for serotonin and noradrenaline (SNRI). It is an antidepressant agent and anxiolytic, and is also used for the treatment of pain in patients with diabetes mellitus and fibromyalgia.
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants and anticonvulsants like
pregabalin
Pregabalin
A gamma-aminobutyric acid (gaba) derivative that functions as a calcium channel blocker and is used as an anticonvulsant as well as an anti-anxiety agent. It is also used as an analgesic in the treatment of neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia.
Second-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs.
| Coding System | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| RxNorm | 70343 | Duloxetine Duloxetine A thiophene derivative and selective neurotransmitter uptake inhibitor for serotonin and noradrenaline (SNRI). It is an antidepressant agent and anxiolytic, and is also used for the treatment of pain in patients with diabetes mellitus and fibromyalgia. Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants (ingredient) |
| RxNorm | 91361 | Pregabalin Pregabalin A gamma-aminobutyric acid (gaba) derivative that functions as a calcium channel blocker and is used as an anticonvulsant as well as an anti-anxiety agent. It is also used as an analgesic in the treatment of neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia. Second-Generation Anticonvulsant Drugs (ingredient) |
| RxNorm | 723 | Amitriptyline Amitriptyline Tricyclic antidepressant with anticholinergic and sedative properties. It appears to prevent the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin at nerve terminals, thus potentiating the action of these neurotransmitters. Amitriptyline also appears to antagonize cholinergic and alpha-1 adrenergic responses to bioactive amines. Tricyclic Antidepressants (ingredient) |