Fever is defined as a measured body temperature Body Temperature The measure of the level of heat of a human or animal. Heatstroke of at least 38℃ (100.4℉). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E Prostaglandin E Three of the six naturally occurring prostaglandins. They are considered primary in that no one is derived from another in living organisms. Originally isolated from sheep seminal fluid and vesicles, they are found in many organs and tissues and play a major role in mediating various physiological activities. Eicosanoids2 in the hypothalamus Hypothalamus The hypothalamus is a collection of various nuclei within the diencephalon in the center of the brain. The hypothalamus plays a vital role in endocrine regulation as the primary regulator of the pituitary gland, and it is the major point of integration between the central nervous and endocrine systems. Hypothalamus. This process increases the physiologic “set-point” of body temperature Body Temperature The measure of the level of heat of a human or animal. Heatstroke. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions. Fever is a symptom of a wide array of diseases; therefore, an accurate history and review of other symptoms are crucial in finding the cause. The major etiologies of fever include infectious (most common), non-infectious, neurogenic, and drug-induced. High fever can have systemic effects that put the individual at risk of both short- and long-term dysfunction. In severe cases, fever may lead to death if untreated.
Last updated: May 19, 2025
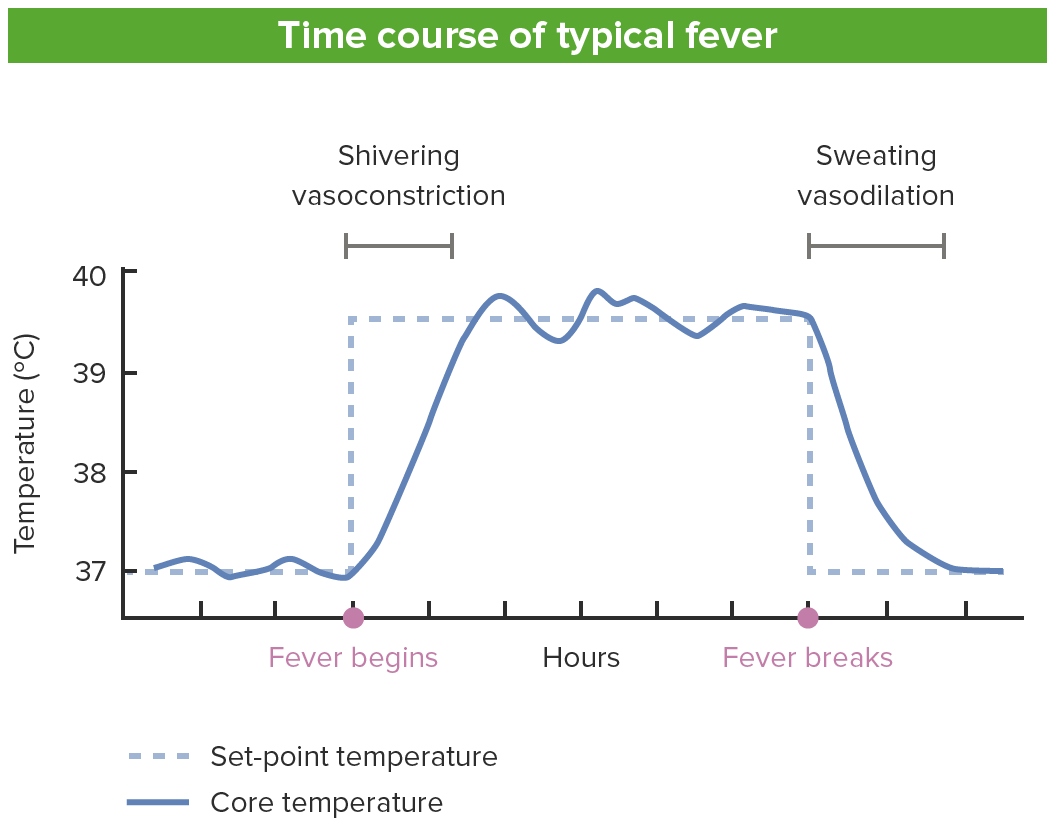
Time course of a typical fever
Image by Lecturio.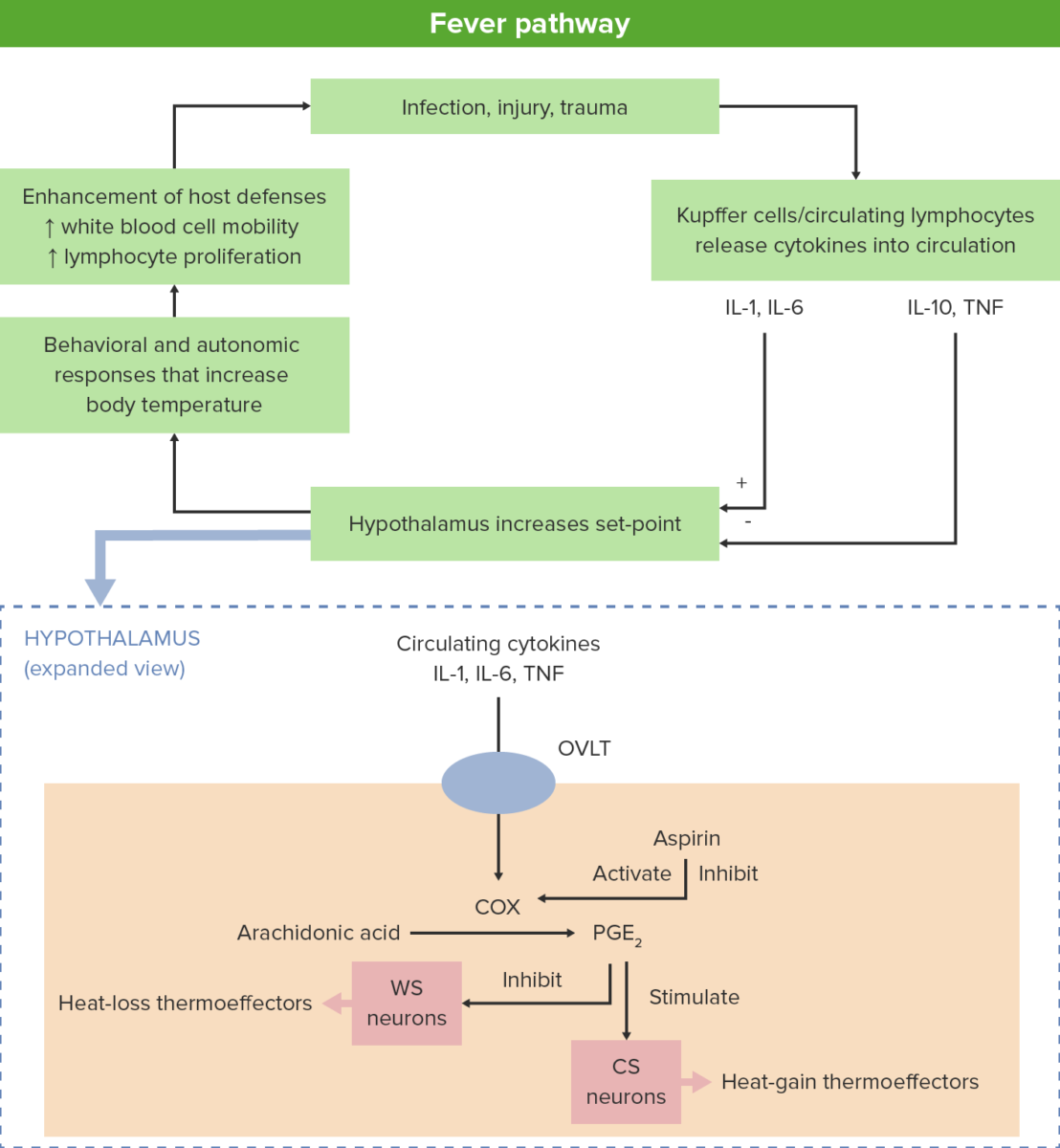
Mechanisms of fever generation
A stressor of the body (e.g., infection, injury, trauma) incites lymphocytes to release cytokines which, in turn, stimulate the hypothalamus.
Within the hypothalamus, the vascular organ of lamina terminalis, or supraoptic crest (OVLT) activates cyclooxygenases (COX), which catalyzes the formation of prostaglandins (PGE2).
These hormone-like substances produce fever by activating cold-sensitive (CS) neurons and inhibiting warm-sensitive (WS) neurons.
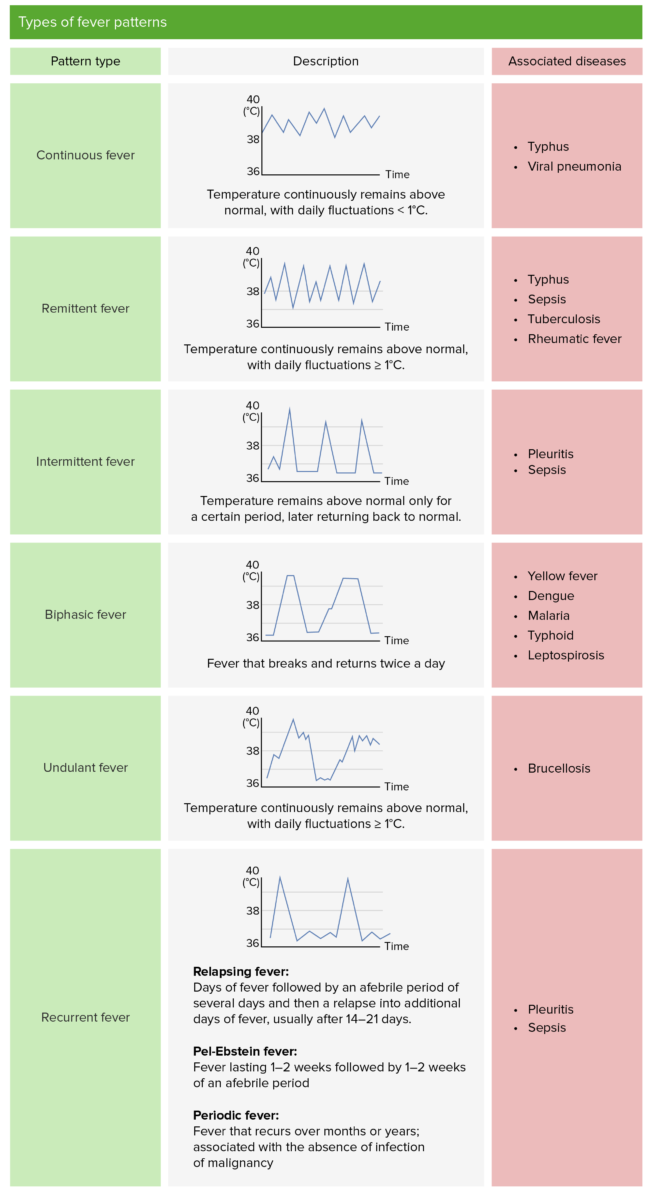
Types of fever patterns
Image by Lecturio.| Cellular | Local | Systemic |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The following conditions are associated with elevated body temperature Body Temperature The measure of the level of heat of a human or animal. Heatstroke: