Fetal growth restriction (FGR), also known as intrauterine fetal growth restriction (IUGR), is an estimated fetal weight Estimated Fetal Weight Obstetric Imaging ( EFW EFW Obstetric Imaging) or abdominal circumference < 10th percentile for gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. The term small for gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care (SGA) is sometimes erroneously used interchangeably with FGR. However, SGA refers to babies born with a birth weight < 10th percentile for gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Defining FGR is challenging because each fetus has a different growth potential that may not be accounted for. The most commonly recognized classifications for FGR are symmetrical Symmetrical Dermatologic Examination or asymmetrical. Symmetrical Symmetrical Dermatologic Examination FGR occurs when all parts of the fetus are equally small and is typically the result of a complication early in pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Asymmetrical FGR occurs when there is disproportionately lagging growth in different body parts; most commonly, the fetus will have a normal size head and a small body. The causes of FGR can be broadly grouped into maternal, fetal, and placental. Fetal growth restriction is diagnosed by ultrasonography and confirmed by weight at birth. Management is often targeted to the underlying etiology, if known. Depending on the etiology, these fetuses may be at increased risk for complications such as preterm birth Preterm birth Preterm labor refers to regular uterine contractions leading to cervical change prior to 37 weeks of gestation; preterm birth refers to birth prior to 37 weeks of gestation. Preterm birth may be spontaneous due to preterm labor, preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (PPROM), or cervical insufficiency. Preterm Labor and Birth, intrauterine fetal death, and neurologic sequelae. Close surveillance Surveillance Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth and delivery planning by a skilled provider is crucial.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) is the term used to describe fetuses with an estimated fetal weight Estimated Fetal Weight Obstetric Imaging ( EFW EFW Obstetric Imaging) or abdominal circumference < 10th percentile for gestational age Gestational age The age of the conceptus, beginning from the time of fertilization. In clinical obstetrics, the gestational age is often estimated as the time from the last day of the last menstruation which is about 2 weeks before ovulation and fertilization. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care.
The most commonly recognized classifications of FGR are as follows:
Symmetrical Symmetrical Dermatologic Examination FGR:
Asymmetrical FGR:
Other less commonly used classifications include:
Many potential causes and risk factors contribute to FGR.
Dating:
History and physical:
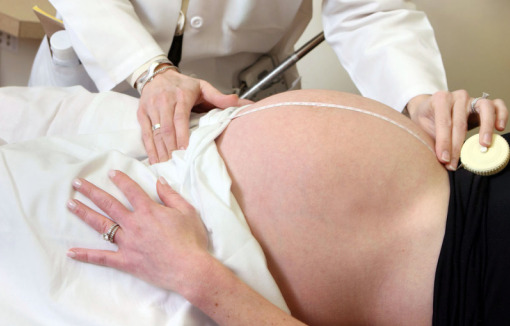
Fundal height measurement:
As shown, the measuring tape is placed between the pubic symphysis and the top of the uterine fundus. The height is reported in centimeters and should match the gestational age (in weeks) within 3 cm.
Ultrasonography:
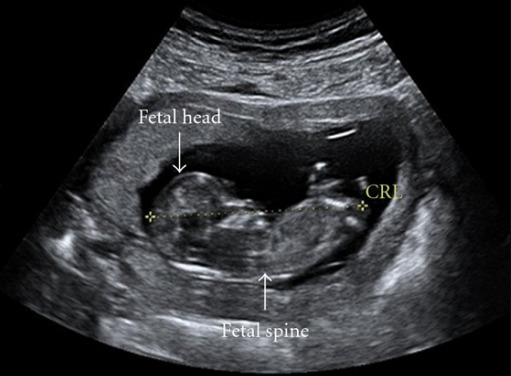
An ultrasound showing a crown-rump length (CRL) measurement, which is the most accurate way to date a pregnancy.
Image: “Ultrasound image of a 12-week fetus.” by hild Health, Royal Aberdeen Children’s Hospital, University of Aberdeen, Foresterhill, Aberdeen. License: CC BY 3.0Management starts with adequate treatment of the underlying cause, if identified, such as:
Fetal growth restriction is associated with several complications. These complications can be seen before or immediately after delivery but can also been seen months to years after.