Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) is a group of neonatal pediatric disorders caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. The term entails a range of physical and neurodevelopmental effects. Classification is based on severity and clinical presentation. Diagnosis is based on a history of prenatal alcohol exposure and the presence of characteristic physical and developmental abnormalities. Management involves surgical correction of structural anomalies and early initiation of support services to promote best outcomes.
Last updated: Jan 7, 2025
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) Consists of the postnatal physical, developmental, cognitive, and psychiatric deficits noted in a patient who has been exposed to alcohol while in utero.
Being an umbrella term, FASD has multiple conditions nested within it:
Alcohol is a teratogen that has irreversible effects:
Factors that contribute to pathogenesis:
Variation in susceptibility of fetus affected by:
Various combinations of features can be present.
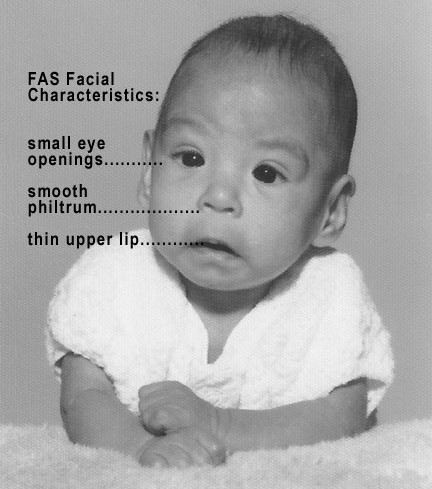
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder: infant with characteristic facial features
Image: “Male baby with FAS syndrome” by Teresa Kellerman. License: CC BY-SA 3.0Accurate and early diagnosis of FASD at < 6 years of age is important to enable interventions and improve outcomes.
There is currently no treatment for FASD; management focuses on early intervention and prevention.