A female genitourinary exam is performed either as a preventative screening Screening Preoperative Care exam or a problem-focused exam to evaluate complaints such as itching, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, lesions, or infection. The investigation includes inspection Inspection Dermatologic Examination, palpation Palpation Application of fingers with light pressure to the surface of the body to determine consistency of parts beneath in physical diagnosis; includes palpation for determining the outlines of organs. Dermatologic Examination, speculum exam, and bimanual exam. In combination with the subject’s history, the clinician Clinician A physician, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or another health professional who is directly involved in patient care and has a professional relationship with patients. Clinician–Patient Relationship uses exam findings to diagnose genital and pelvic conditions or to screen for cervical cancer Cervical cancer Cervical cancer, or invasive cervical carcinoma (ICC), is the 3rd most common cancer in women in the world, with > 50% of the cases being fatal. In the United States, ICC is the 13th most common cancer and the cause of < 3% of all cancer deaths due to the slow progression of precursor lesions and, more importantly, effective cancer screening. Cervical Cancer ( Pap smear Pap smear Cytological preparation of cells collected from a mucosal surface and stained with Papanicolaou stain. Cervical Cancer Screening).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Components of the external female genitalia include the mons pubis Mons pubis Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy, vulva Vulva The vulva is the external genitalia of the female and includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, vestibular bulb, and greater vestibular glands. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy ( labia minora Labia minora Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy and majora), clitoris Clitoris An erectile structure homologous with the penis, situated beneath the anterior labial commissure, partially hidden between the anterior ends of the labia minora. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy, urethral orifice, vestibule Vestibule An oval, bony chamber of the inner ear, part of the bony labyrinth. It is continuous with bony cochlea anteriorly, and semicircular canals posteriorly. The vestibule contains two communicating sacs (utricle and saccule) of the balancing apparatus. The oval window on its lateral wall is occupied by the base of the stapes of the middle ear. Ear: Anatomy, and external glands.
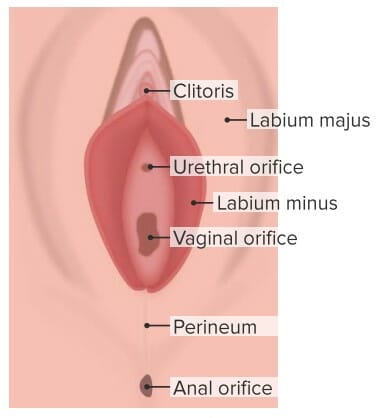
Anatomy of the external genitalia
Image by Lecturio.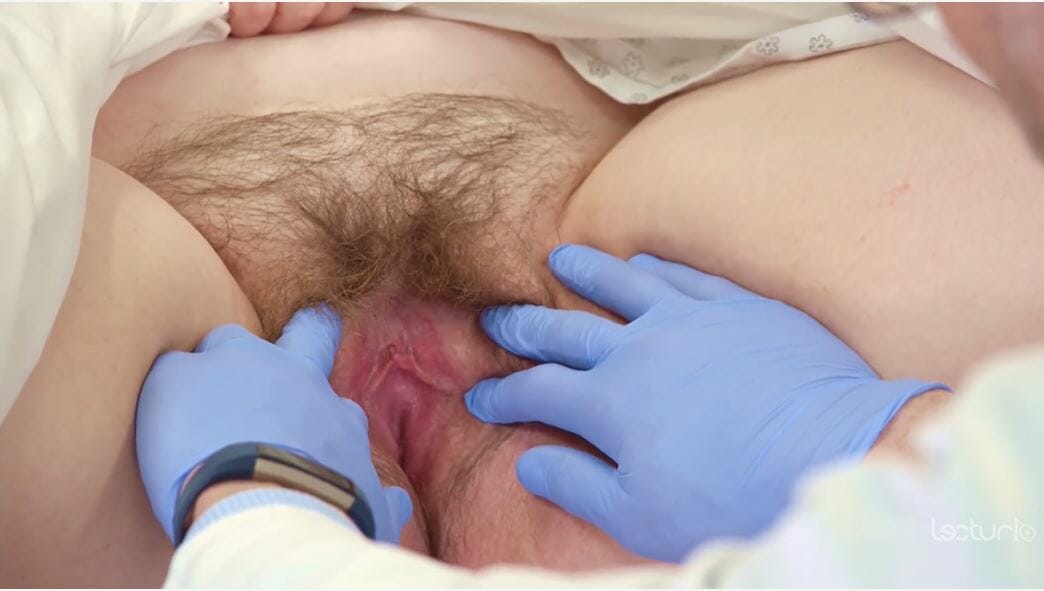
Inspection of the external female genitalia
Image by Lecturio.| Lesion | Description |
|---|---|
| Epidermoid cyst |
|
| Genital warts Genital Warts Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts) ( condyloma Condyloma Sexually transmitted form of anogenital warty growth caused by the human papillomaviruses. Male Genitourinary Examination acuminatum) | Warty lesions on the labia, within the vestibule Vestibule An oval, bony chamber of the inner ear, part of the bony labyrinth. It is continuous with bony cochlea anteriorly, and semicircular canals posteriorly. The vestibule contains two communicating sacs (utricle and saccule) of the balancing apparatus. The oval window on its lateral wall is occupied by the base of the stapes of the middle ear. Ear: Anatomy, or around the anus |
| Genital herpes Genital Herpes Genital herpes infections are common sexually transmitted infections caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2. Primary infection often presents with systemic, prodromal symptoms followed by clusters of painful, fluid-filled vesicles on an erythematous base, dysuria, and painful lymphadenopathy. Labial and Genital Herpes | Shallow, small, tender ulcers on an erythematous base |
| Lichen sclerosus Lichen Sclerosus Atrophy and shriveling of the skin of the vulva that is characterized by the whitish lichen sclerosus appearance, inflammation, and pruritus. Benign Vulvar Conditions |
|
| Vulvar squamous intraepithelial lesions (previously called vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia) |
|
| Syphilitic chancre Chancre The primary sore of syphilis, a painless indurated, eroded papule, occurring at the site of entry of the infection. Syphilis | A firm, nontender ulcer |
| Secondary syphilis Secondary Syphilis Syphilis ( condyloma Condyloma Sexually transmitted form of anogenital warty growth caused by the human papillomaviruses. Male Genitourinary Examination lata) | Slightly raised, flat, round, or oval papules covered by a gray exudate Exudate Exudates are fluids, cells, or other cellular substances that are slowly discharged from blood vessels usually from inflamed tissues. Pleural Effusion |
| Lichen planus Lichen planus Lichen planus (LP) is an idiopathic, cell-mediated inflammatory skin disease. It is characterized by pruritic, flat-topped, papular, purple skin lesions commonly found on the flexural surfaces of the extremities. Other areas affected include genitalia, nails, scalp, and mucous membranes. Lichen Planus |
|
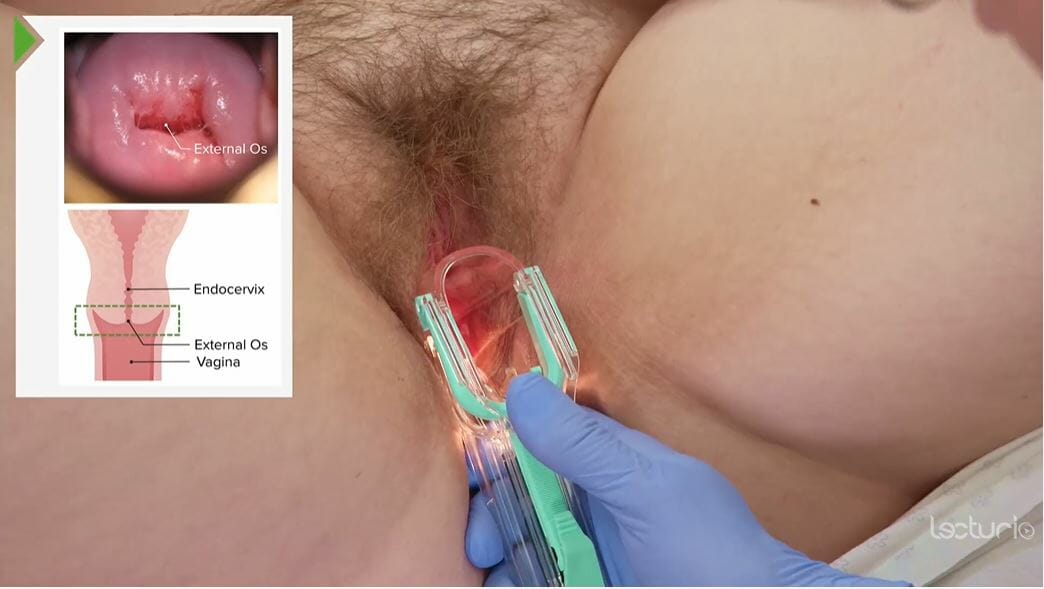
Speculum examination of the cervix
Image by Lecturio.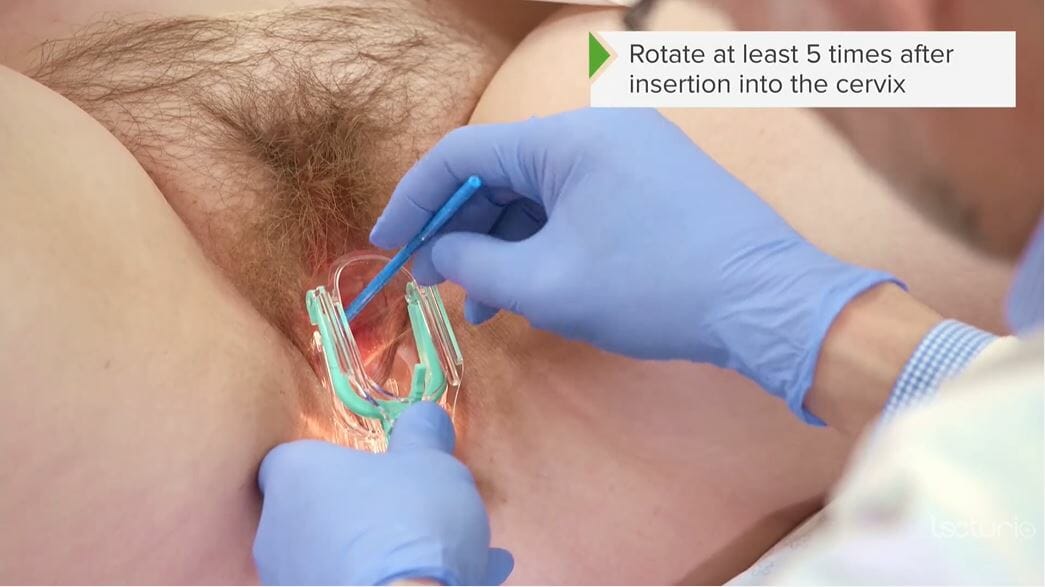
Use of a cervical/Pap brush to obtain a cervical specimen for cytology/Pap smear
Image by Lecturio.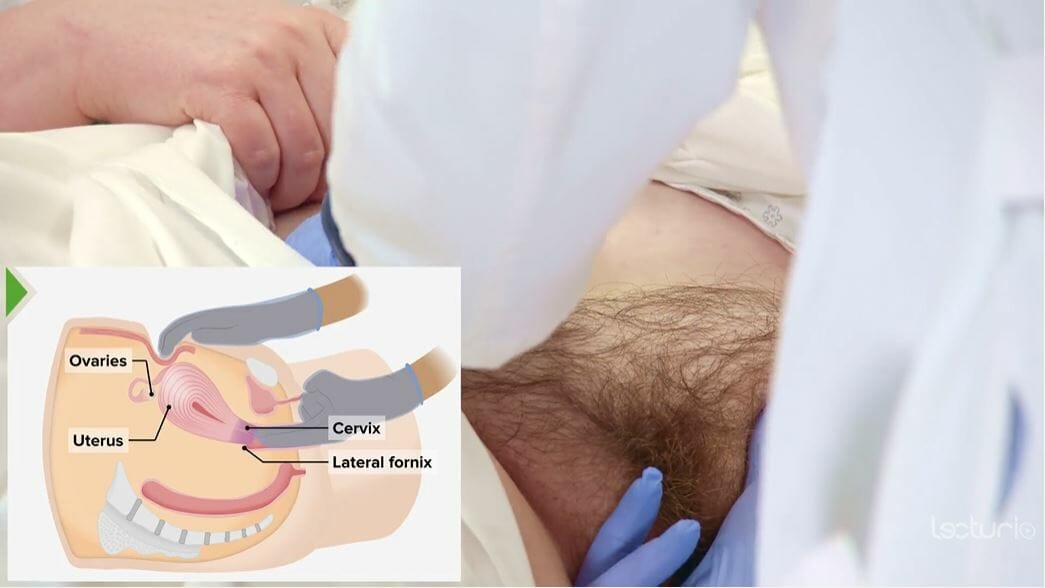
Bimanual examination: positioning of the hands during the exam, including the abdominal exam
Image by Lecturio.