Fatty acid metabolism includes the processes of either breaking down fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance to generate energy (catabolic) or creating fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance for storage or use (anabolic). Besides being a source of energy, fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance can also be utilized for cellular membranes or signaling molecules Signaling molecules Second Messengers. Synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and beta oxidation are almost the reverse of each other, and special reactions are required for variations ( unsaturated fatty acids Unsaturated fatty acids Fatty acids in which the carbon chain contains one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bonds. Fatty Acids and Lipids, very-long-chain fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance (VLCFAs)). Synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) occurs in the cell cytoplasm, while oxidation occurs in mitochondria Mitochondria Semiautonomous, self-reproducing organelles that occur in the cytoplasm of all cells of most, but not all, eukaryotes. Each mitochondrion is surrounded by a double limiting membrane. The inner membrane is highly invaginated, and its projections are called cristae. Mitochondria are the sites of the reactions of oxidative phosphorylation, which result in the formation of ATP. They contain distinctive ribosomes, transfer RNAs; amino Acyl tRNA synthetases; and elongation and termination factors. Mitochondria depend upon genes within the nucleus of the cells in which they reside for many essential messenger RNAs. Mitochondria are believed to have arisen from aerobic bacteria that established a symbiotic relationship with primitive protoeukaryotes. The Cell: Organelles. Shuttling across membranes within a cell requires additional processes, such as the citrate and carnitine shuttles. In certain physiologic states, an increase in fatty acid oxidation can lead to the production of ketone bodies Ketone bodies The metabolic substances acetone; 3-hydroxybutyric acid; and acetoacetic acid (acetoacetates). They are produced in the liver and kidney during fatty acids oxidation and used as a source of energy by the heart, muscle and brain. Ketone Body Metabolism, which can also be utilized as an energy source, particularly in the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and muscles.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance (FAs) are classified based on their carbon chain saturation and length.
Saturation:
Length:
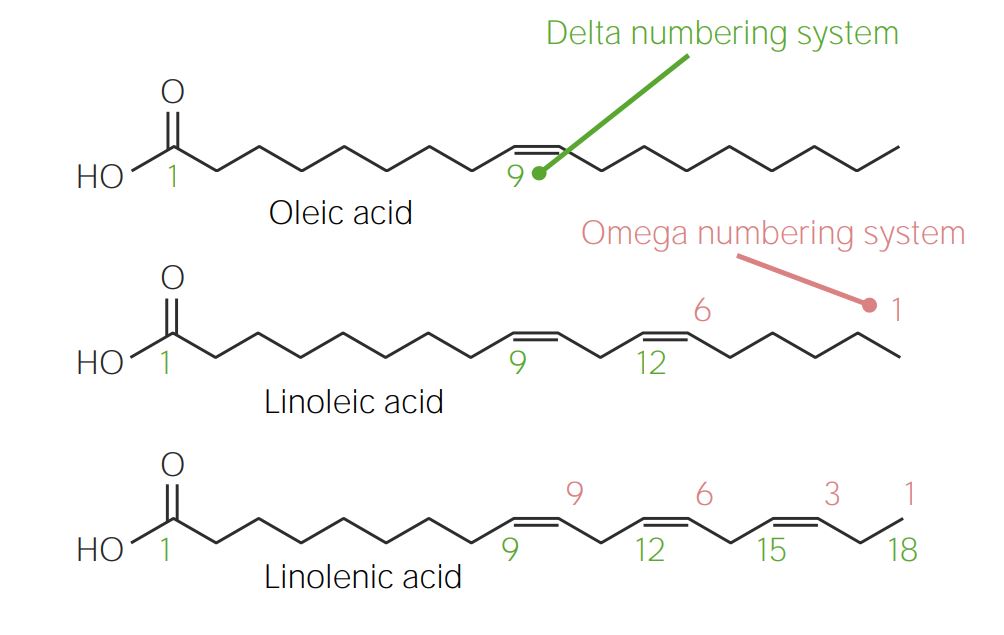
Comparison of the delta and omega numbering systems for fatty acids:
In the delta numbering system (green), carbons are numbered from the carboxyl (COOH) group (left) to the methyl (CH3) group (right). The opposite occurs in the omega numbering system (red).
FAs are utilized for:
Glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance is needed to produce acetyl CoA, which is required for FA FA Inhaled Anesthetics synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
The process of FA FA Inhaled Anesthetics synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) continues in the cytoplasm:
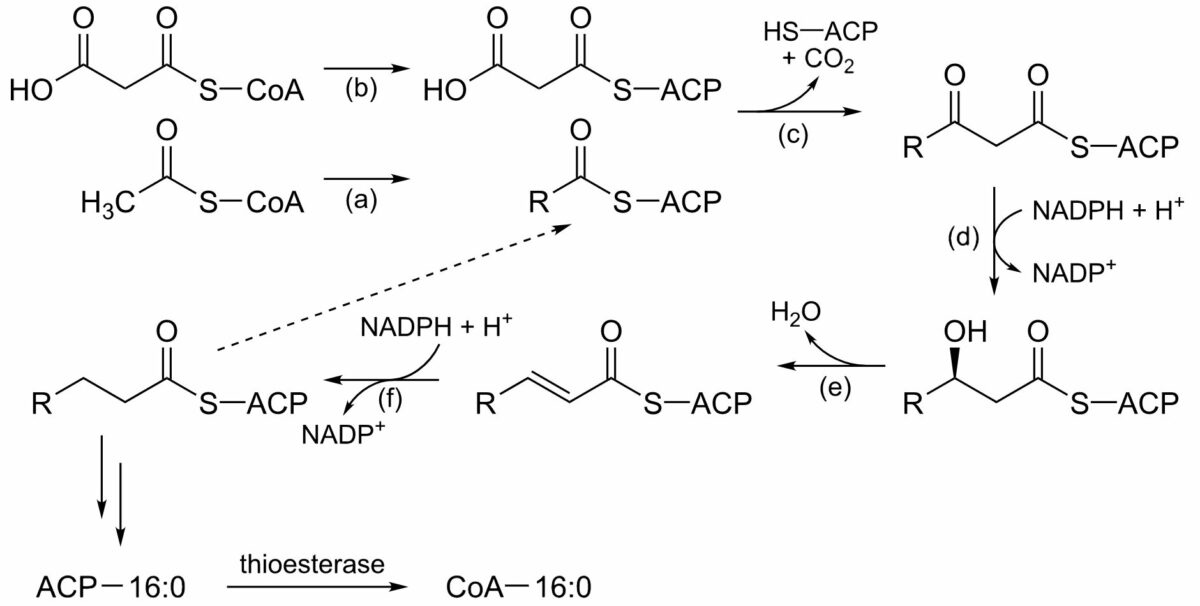
The process of fatty acid synthesis:
This series of reactions repeats, each cycle adding 2 carbons to the growing fatty acid chain, until the maximum of 16 carbons is reached (palmitic acid). Fatty acid synthase is the multienzyme complex responsible.
(a): Acetyltransferase
(b): Malonyltransferase
(c): Beta-ketoacyl ACP synthase
(d): Beta-ketoacyl ACP reductase
(e): 3-hydroxyacyl ACP dehydratase
(f): Enoyl ACP reductase
NADPH: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
NADP+: oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
ACP: acyl-carrier protein
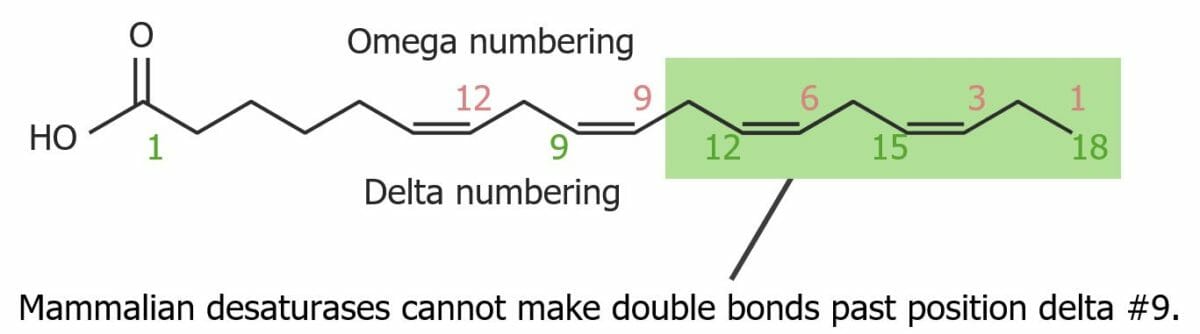
Structure of an unsaturated fatty acid. It is not possible to make double bonds beyond position delta #9.
Image by Lecturio.Beta oxidation is the process of fatty acid breakdown.
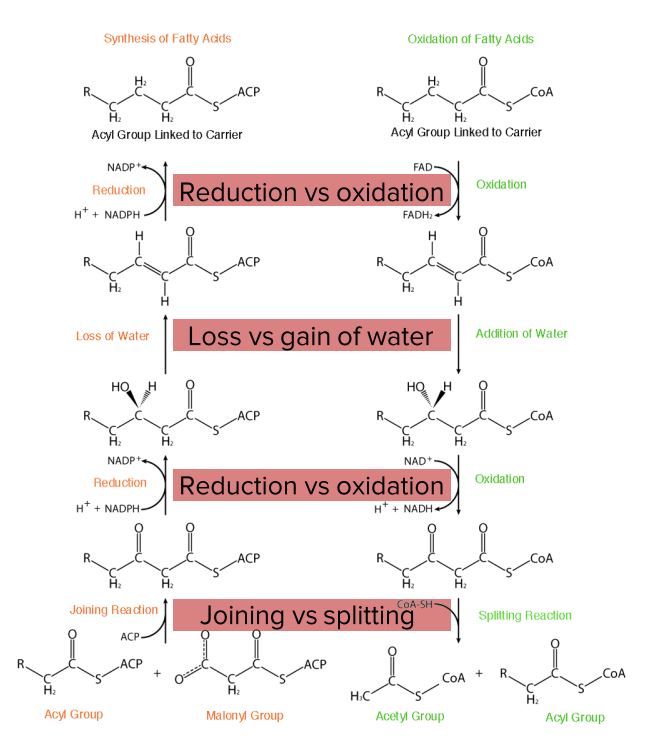
Diagram comparing fatty acid synthesis and oxidation.
Image by Lecturio.Before oxidation happens, fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance need to be activated in the cytoplasm and transported to the mitochondrion.
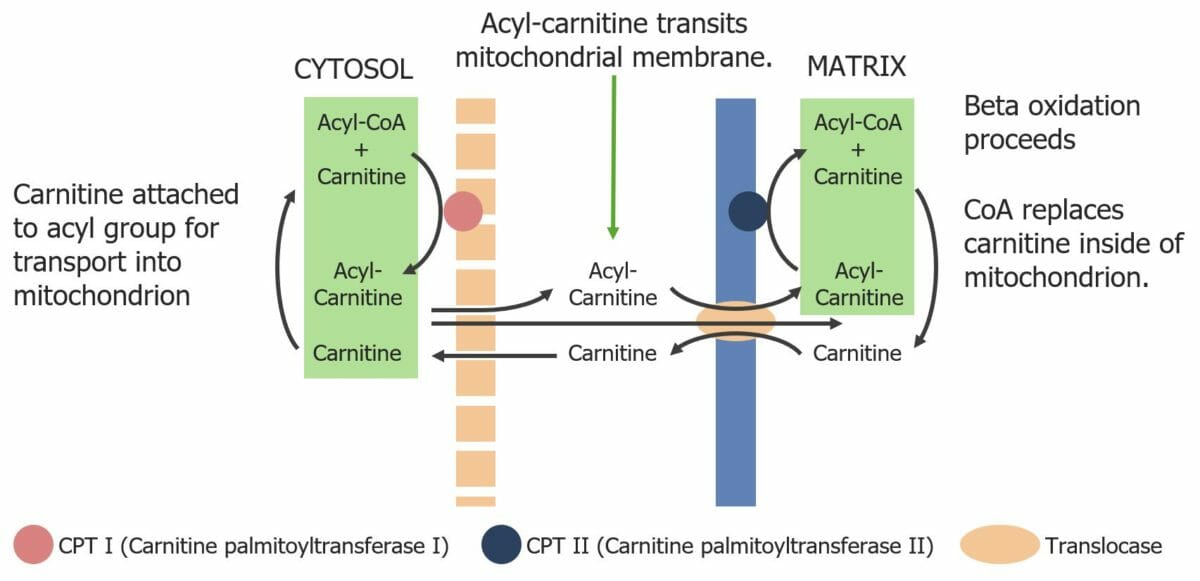
Diagram showing the transport of fatty acyl-CoA molecules across the mitochondrial membrane via the carnitine shuttle.
Image by Lecturio.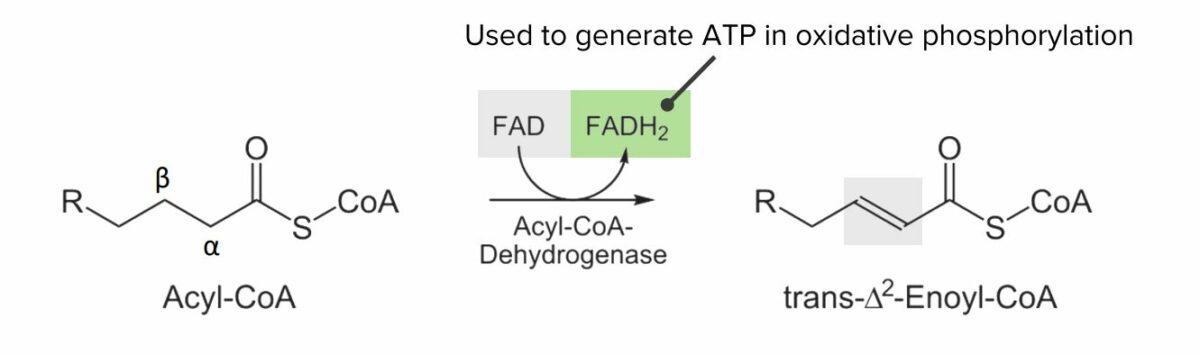
Diagram showing the 1st step of the beta oxidation process: Oxidation of acyl-CoA into trans-Δ2-enoyl-CoA. This step converts flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) to FADH2, which can be utilized to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Image by Lecturio.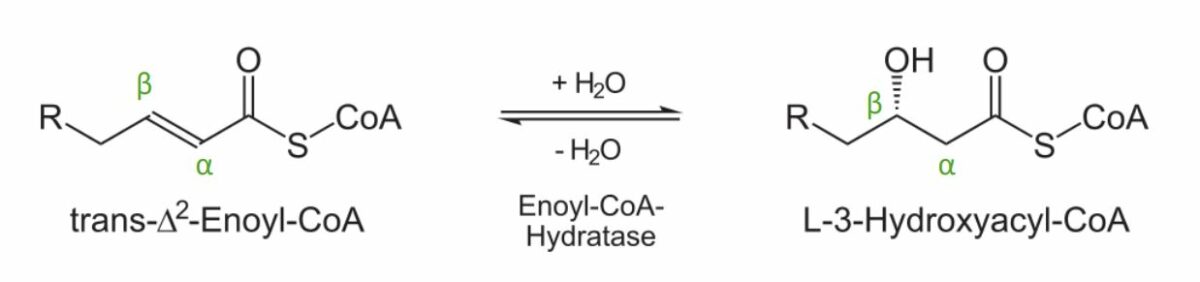
Diagram showing the 2nd step of the beta oxidation process: Addition of a water molecule to create L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA.
Image by Lecturio.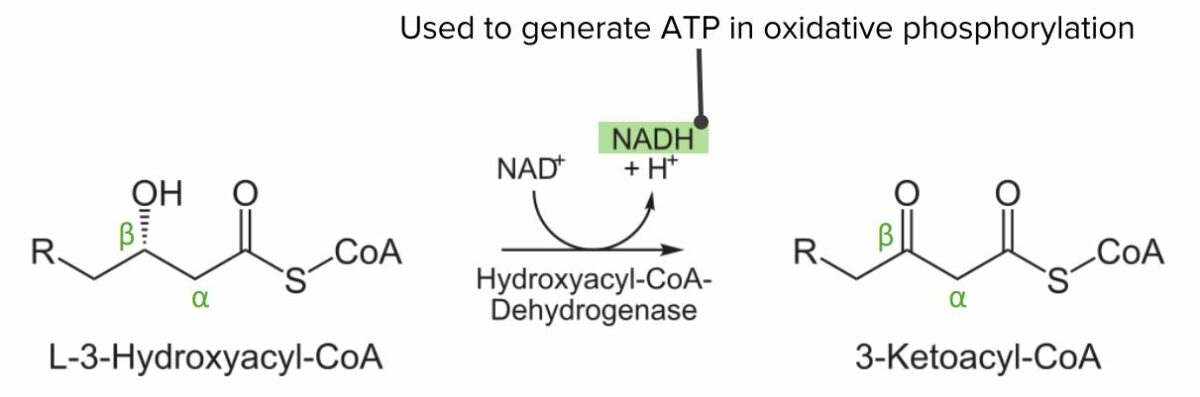
Diagram showing the 3rd step of the beta oxidation process: Oxidation of L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA. This step converts NAD to NADH, which can be used to generate ATP.
Image by Lecturio.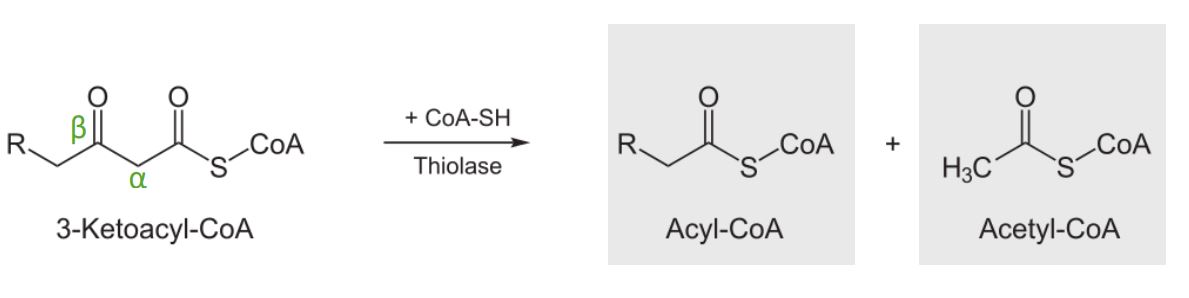
Diagram showing the 4thstep of the beta oxidation process: cleavage of 3-ketoacyl-CoA. These products can then go on to the citric acid cycle or be used to produce ketone bodies.
Image by Lecturio.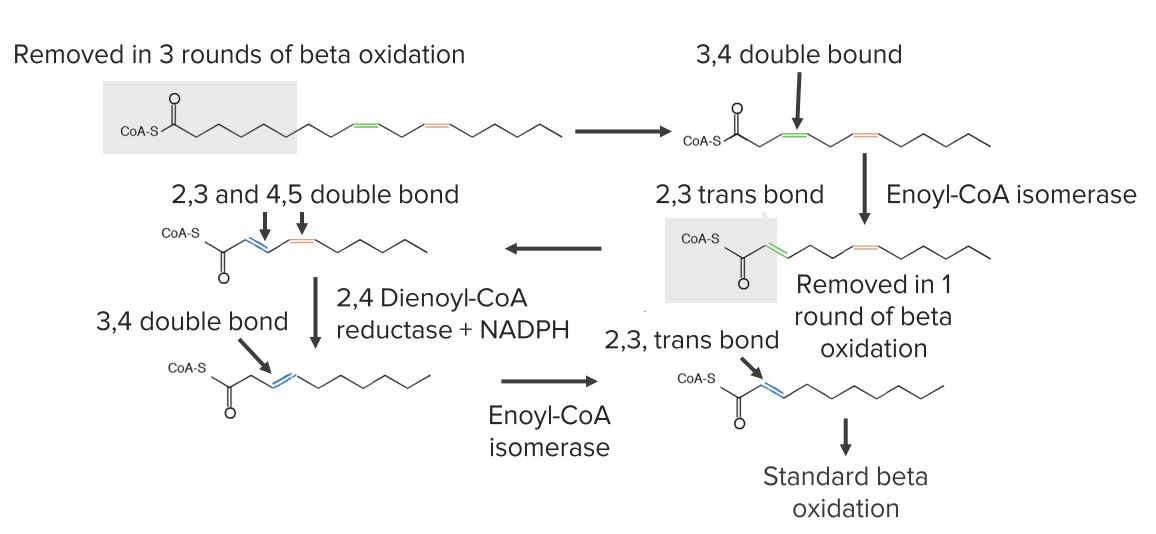
Diagram showing the reactions needed for the beginning of unsaturated fatty acid oxidation.
Image by Lecturio.For fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance with > 20 carbons:
Fatty acids Acids Chemical compounds which yield hydrogen ions or protons when dissolved in water, whose hydrogen can be replaced by metals or basic radicals, or which react with bases to form salts and water (neutralization). An extension of the term includes substances dissolved in media other than water. Acid-Base Balance with an odd number of carbons produce propionyl-CoA (3 carbons).
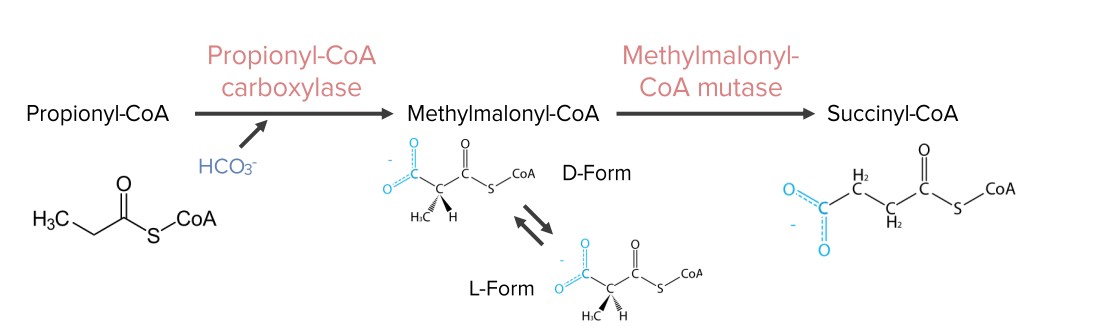
Diagram showing the reactions needed for the synthesis of succinyl-CoA from propionyl-CoA. Succinyl-CoA is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle.
Image by Lecturio.Occurs:
Process:
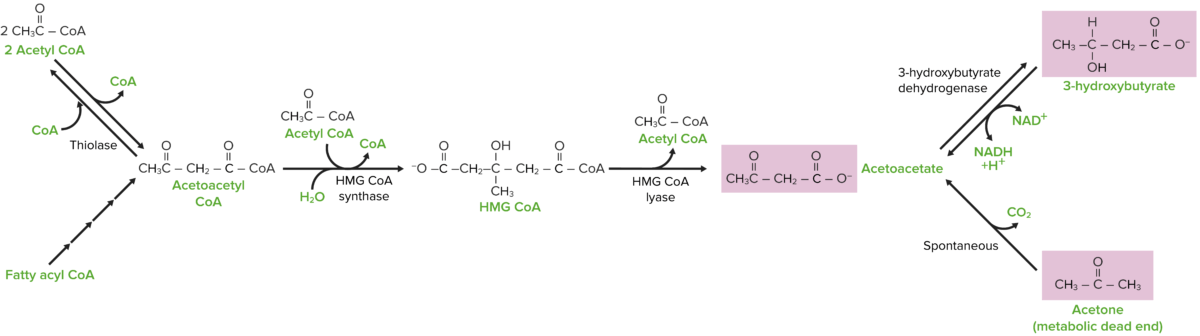
Ketone body synthesis pathway
Image by Lecturio.